Zhongmin Cai
QGEval: A Benchmark for Question Generation Evaluation
Jun 09, 2024
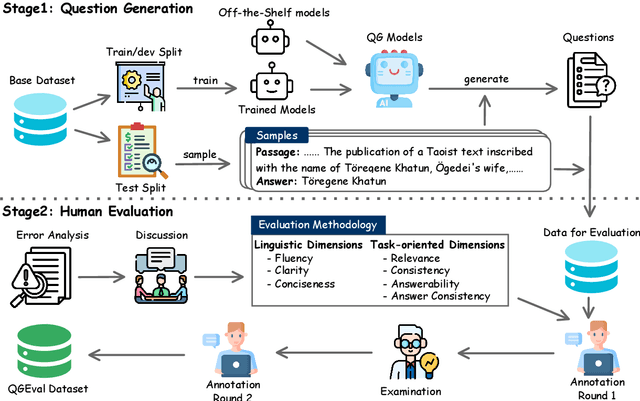
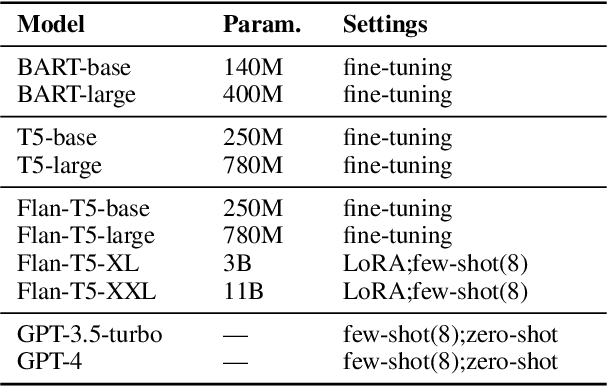
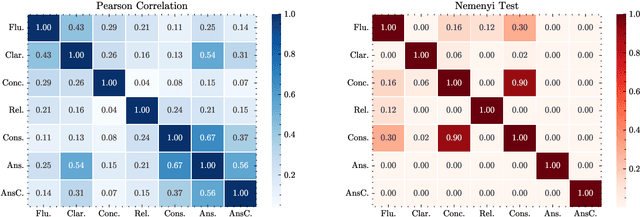
Abstract:Automatically generated questions often suffer from problems such as unclear expression or factual inaccuracies, requiring a reliable and comprehensive evaluation of their quality. Human evaluation is frequently used in the field of question generation (QG) and is one of the most accurate evaluation methods. It also serves as the standard for automatic metrics. However, there is a lack of unified evaluation criteria, which hampers the development of both QG technologies and automatic evaluation methods. To address this, we propose QGEval, a multi-dimensional Evaluation benchmark for Question Generation, which evaluates both generated questions and existing automatic metrics across 7 dimensions: fluency, clarity, conciseness, relevance, consistency, answerability, and answer consistency. We demonstrate the appropriateness of these dimensions by examining their correlations and distinctions. Analysis with QGEval reveals that 1) most QG models perform unsatisfactorily in terms of answerability and answer consistency, and 2) existing metrics fail to align well with human assessments when evaluating generated questions across the 7 dimensions. We expect this work to foster the development of both QG technologies and automatic metrics for QG.
Re-scale AdaBoost for Attack Detection in Collaborative Filtering Recommender Systems
Jun 15, 2015



Abstract:Collaborative filtering recommender systems (CFRSs) are the key components of successful e-commerce systems. Actually, CFRSs are highly vulnerable to attacks since its openness. However, since attack size is far smaller than that of genuine users, conventional supervised learning based detection methods could be too "dull" to handle such imbalanced classification. In this paper, we improve detection performance from following two aspects. First, we extract well-designed features from user profiles based on the statistical properties of the diverse attack models, making hard classification task becomes easier to perform. Then, refer to the general idea of re-scale Boosting (RBoosting) and AdaBoost, we apply a variant of AdaBoost, called the re-scale AdaBoost (RAdaBoost) as our detection method based on extracted features. RAdaBoost is comparable to the optimal Boosting-type algorithm and can effectively improve the performance in some hard scenarios. Finally, a series of experiments on the MovieLens-100K data set are conducted to demonstrate the outperformance of RAdaBoost comparing with some classical techniques such as SVM, kNN and AdaBoost.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge