Zhonghua Liu
DNA-SE: Towards Deep Neural-Nets Assisted Semiparametric Estimation
Aug 04, 2024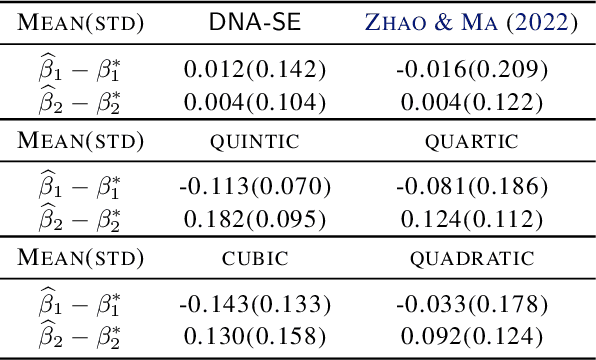
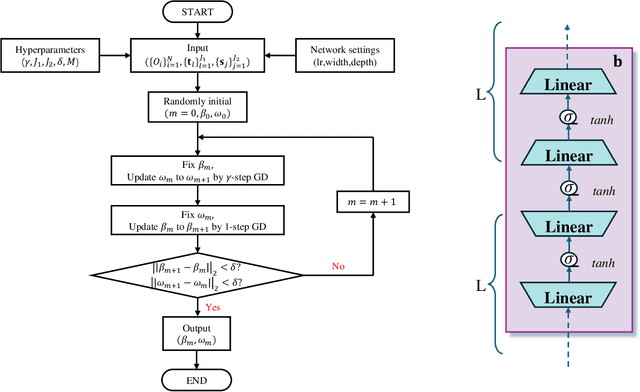
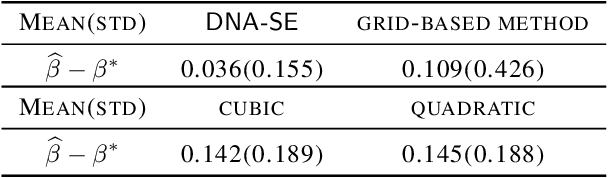
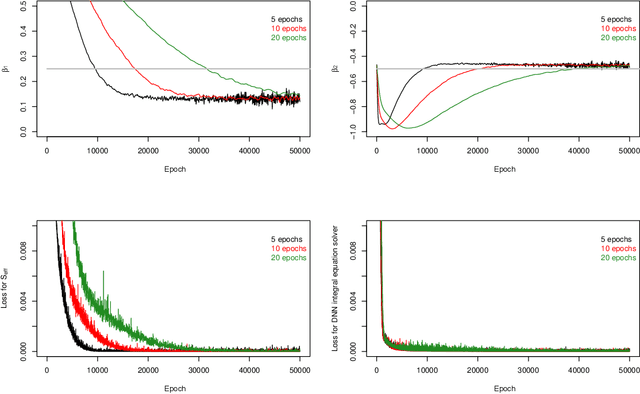
Abstract:Semiparametric statistics play a pivotal role in a wide range of domains, including but not limited to missing data, causal inference, and transfer learning, to name a few. In many settings, semiparametric theory leads to (nearly) statistically optimal procedures that yet involve numerically solving Fredholm integral equations of the second kind. Traditional numerical methods, such as polynomial or spline approximations, are difficult to scale to multi-dimensional problems. Alternatively, statisticians may choose to approximate the original integral equations by ones with closed-form solutions, resulting in computationally more efficient, but statistically suboptimal or even incorrect procedures. To bridge this gap, we propose a novel framework by formulating the semiparametric estimation problem as a bi-level optimization problem; and then we develop a scalable algorithm called Deep Neural-Nets Assisted Semiparametric Estimation (DNA-SE) by leveraging the universal approximation property of Deep Neural-Nets (DNN) to streamline semiparametric procedures. Through extensive numerical experiments and a real data analysis, we demonstrate the numerical and statistical advantages of $\dnase$ over traditional methods. To the best of our knowledge, we are the first to bring DNN into semiparametric statistics as a numerical solver of integral equations in our proposed general framework.
Automatic Speech Disentanglement for Voice Conversion using Rank Module and Speech Augmentation
Jun 21, 2023Abstract:Voice Conversion (VC) converts the voice of a source speech to that of a target while maintaining the source's content. Speech can be mainly decomposed into four components: content, timbre, rhythm and pitch. Unfortunately, most related works only take into account content and timbre, which results in less natural speech. Some recent works are able to disentangle speech into several components, but they require laborious bottleneck tuning or various hand-crafted features, each assumed to contain disentangled speech information. In this paper, we propose a VC model that can automatically disentangle speech into four components using only two augmentation functions, without the requirement of multiple hand-crafted features or laborious bottleneck tuning. The proposed model is straightforward yet efficient, and the empirical results demonstrate that our model can achieve a better performance than the baseline, regarding disentanglement effectiveness and speech naturalness.
DeepMed: Semiparametric Causal Mediation Analysis with Debiased Deep Learning
Oct 10, 2022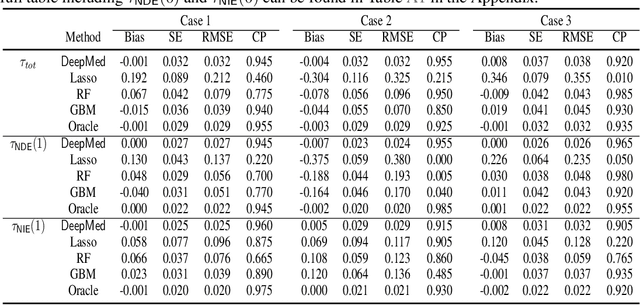
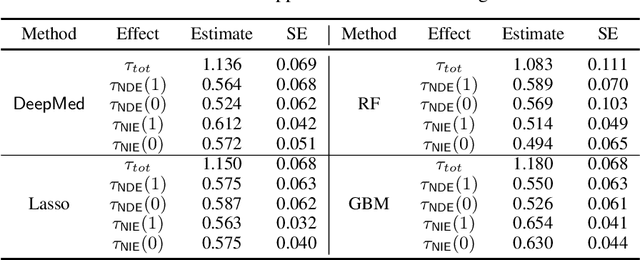
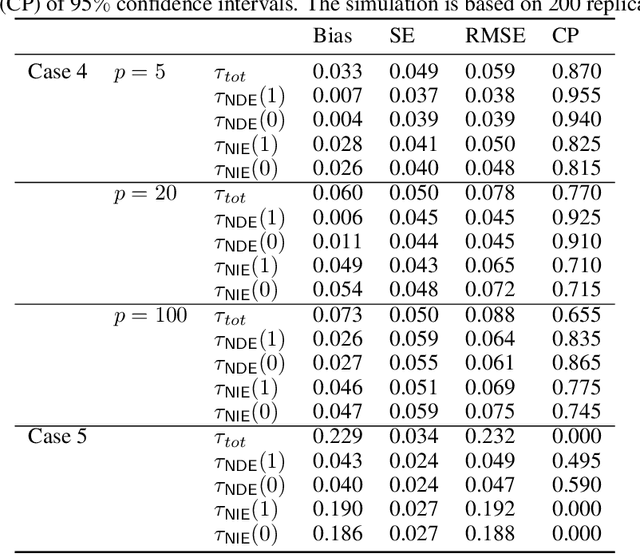
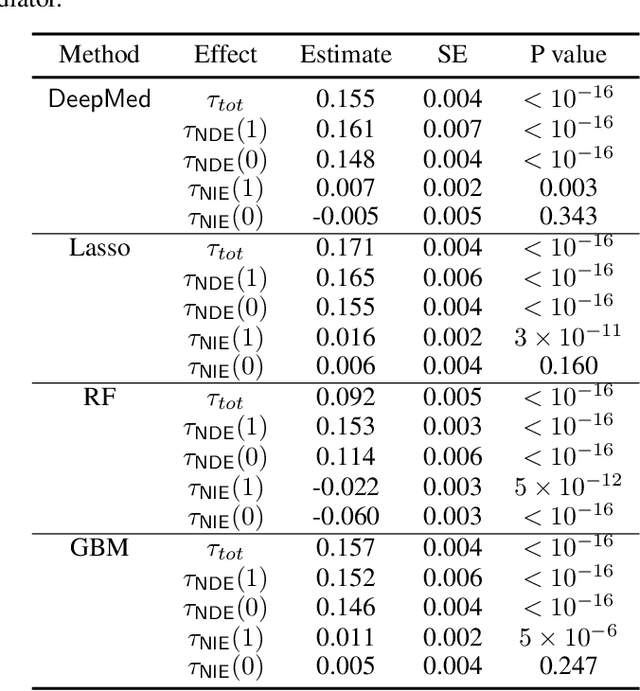
Abstract:Causal mediation analysis can unpack the black box of causality and is therefore a powerful tool for disentangling causal pathways in biomedical and social sciences, and also for evaluating machine learning fairness. To reduce bias for estimating Natural Direct and Indirect Effects in mediation analysis, we propose a new method called DeepMed that uses deep neural networks (DNNs) to cross-fit the infinite-dimensional nuisance functions in the efficient influence functions. We obtain novel theoretical results that our DeepMed method (1) can achieve semiparametric efficiency bound without imposing sparsity constraints on the DNN architecture and (2) can adapt to certain low dimensional structures of the nuisance functions, significantly advancing the existing literature on DNN-based semiparametric causal inference. Extensive synthetic experiments are conducted to support our findings and also expose the gap between theory and practice. As a proof of concept, we apply DeepMed to analyze two real datasets on machine learning fairness and reach conclusions consistent with previous findings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge