Zhitong Zheng
Binary Neural Networks for Large Language Model: A Survey
Feb 26, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have wide applications in the field of natural language processing(NLP), such as GPT-4 and Llama. However, with the exponential growth of model parameter sizes, LLMs bring significant resource overheads. Low-bit quantization, as a key technique, reduces memory usage and computational demands by decreasing the bit-width of model parameters, activations, and gradients. Previous quantization methods for LLMs have largely employed Post-Training Quantization (PTQ) and Quantization-Aware Training (QAT). PTQ does not require any retraining of the original model, while QAT involves optimizing precision during training to achieve the best quantization parameters. The BitNet team proposed a radically different approach, where quantization is performed from the start of model training, utilizing low-precision binary weights during the training process. This approach has led to the emergence of many binary quantization techniques for large language models. This paper provides a comprehensive review of these binary quantization techniques. Specifically, we will introduce binary quantization techniques in deep neural networks and further explore their application to LLMs, reviewing their various contributions, implementations, and applications.
Convolutional Embedding Makes Hierarchical Vision Transformer Stronger
Aug 01, 2022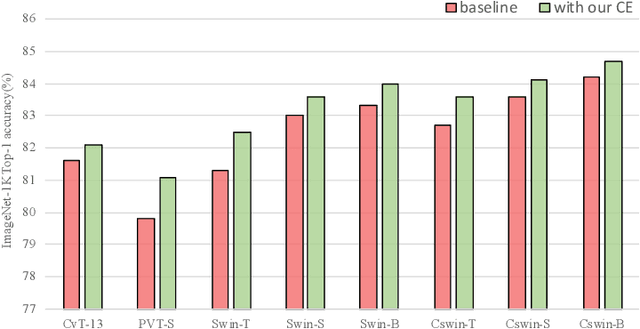
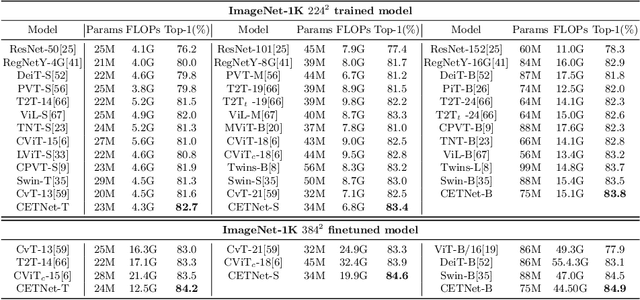
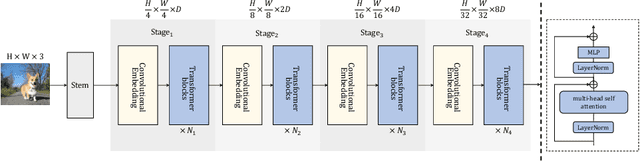
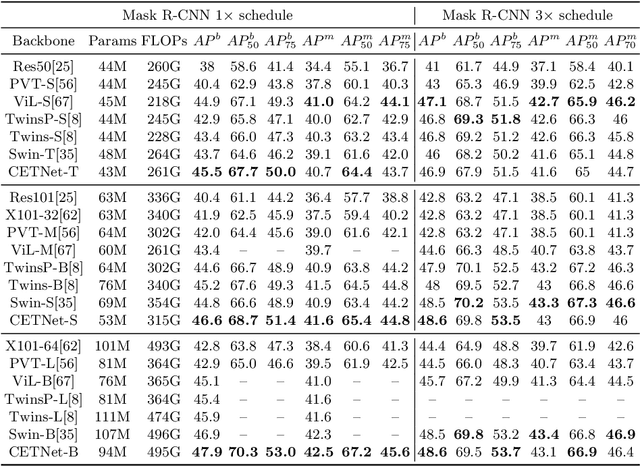
Abstract:Vision Transformers (ViTs) have recently dominated a range of computer vision tasks, yet it suffers from low training data efficiency and inferior local semantic representation capability without appropriate inductive bias. Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) inherently capture regional-aware semantics, inspiring researchers to introduce CNNs back into the architecture of the ViTs to provide desirable inductive bias for ViTs. However, is the locality achieved by the micro-level CNNs embedded in ViTs good enough? In this paper, we investigate the problem by profoundly exploring how the macro architecture of the hybrid CNNs/ViTs enhances the performances of hierarchical ViTs. Particularly, we study the role of token embedding layers, alias convolutional embedding (CE), and systemically reveal how CE injects desirable inductive bias in ViTs. Besides, we apply the optimal CE configuration to 4 recently released state-of-the-art ViTs, effectively boosting the corresponding performances. Finally, a family of efficient hybrid CNNs/ViTs, dubbed CETNets, are released, which may serve as generic vision backbones. Specifically, CETNets achieve 84.9% Top-1 accuracy on ImageNet-1K (training from scratch), 48.6% box mAP on the COCO benchmark, and 51.6% mIoU on the ADE20K, substantially improving the performances of the corresponding state-of-the-art baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge