Zhiming Tan
Enhanced Semantic Segmentation Pipeline for WeatherProof Dataset Challenge
Jun 07, 2024Abstract:This report describes the winning solution to the WeatherProof Dataset Challenge (CVPR 2024 UG2+ Track 3). Details regarding the challenge are available at https://cvpr2024ug2challenge.github.io/track3.html. We propose an enhanced semantic segmentation pipeline for this challenge. Firstly, we improve semantic segmentation models, using backbone pretrained with Depth Anything to improve UperNet model and SETRMLA model, and adding language guidance based on both weather and category information to InternImage model. Secondly, we introduce a new dataset WeatherProofExtra with wider viewing angle and employ data augmentation methods, including adverse weather and super-resolution. Finally, effective training strategies and ensemble method are applied to improve final performance further. Our solution is ranked 1st on the final leaderboard. Code will be available at https://github.com/KaneiGi/WeatherProofChallenge.
3D WholeBody Pose Estimation based on Semantic Graph Attention Network and Distance Information
Jun 03, 2024Abstract:In recent years, a plethora of diverse methods have been proposed for 3D pose estimation. Among these, self-attention mechanisms and graph convolutions have both been proven to be effective and practical methods. Recognizing the strengths of those two techniques, we have developed a novel Semantic Graph Attention Network which can benefit from the ability of self-attention to capture global context, while also utilizing the graph convolutions to handle the local connectivity and structural constraints of the skeleton. We also design a Body Part Decoder that assists in extracting and refining the information related to specific segments of the body. Furthermore, our approach incorporates Distance Information, enhancing our model's capability to comprehend and accurately predict spatial relationships. Finally, we introduce a Geometry Loss who makes a critical constraint on the structural skeleton of the body, ensuring that the model's predictions adhere to the natural limits of human posture. The experimental results validate the effectiveness of our approach, demonstrating that every element within the system is essential for improving pose estimation outcomes. With comparison to state-of-the-art, the proposed work not only meets but exceeds the existing benchmarks.
The Third Monocular Depth Estimation Challenge
Apr 27, 2024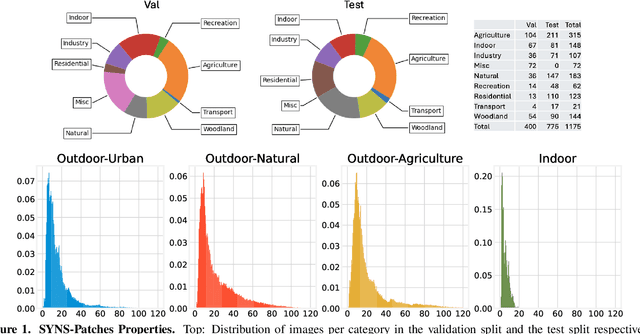

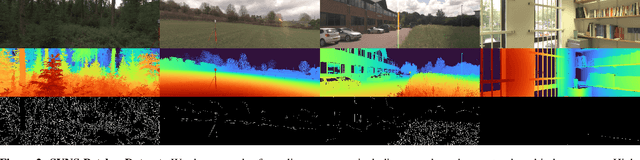
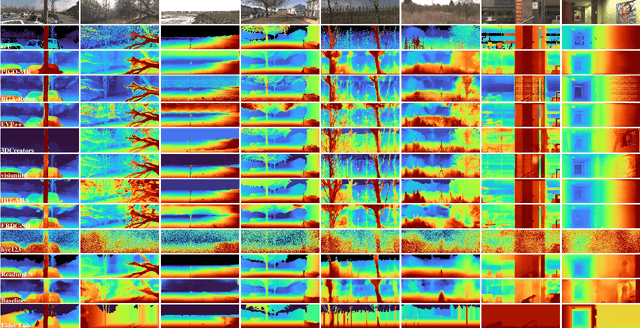
Abstract:This paper discusses the results of the third edition of the Monocular Depth Estimation Challenge (MDEC). The challenge focuses on zero-shot generalization to the challenging SYNS-Patches dataset, featuring complex scenes in natural and indoor settings. As with the previous edition, methods can use any form of supervision, i.e. supervised or self-supervised. The challenge received a total of 19 submissions outperforming the baseline on the test set: 10 among them submitted a report describing their approach, highlighting a diffused use of foundational models such as Depth Anything at the core of their method. The challenge winners drastically improved 3D F-Score performance, from 17.51% to 23.72%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge