Zhengyao Fang
Recognition-Synergistic Scene Text Editing
Mar 11, 2025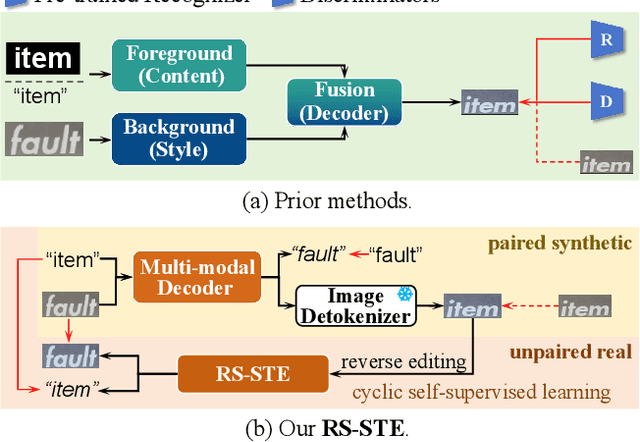
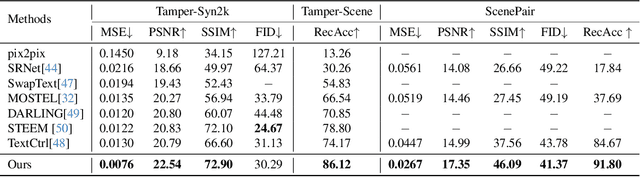
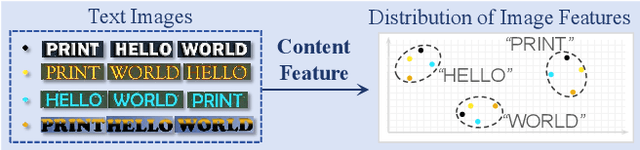
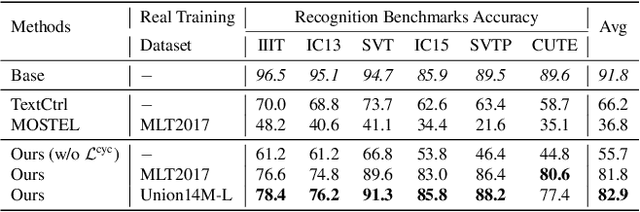
Abstract:Scene text editing aims to modify text content within scene images while maintaining style consistency. Traditional methods achieve this by explicitly disentangling style and content from the source image and then fusing the style with the target content, while ensuring content consistency using a pre-trained recognition model. Despite notable progress, these methods suffer from complex pipelines, leading to suboptimal performance in complex scenarios. In this work, we introduce Recognition-Synergistic Scene Text Editing (RS-STE), a novel approach that fully exploits the intrinsic synergy of text recognition for editing. Our model seamlessly integrates text recognition with text editing within a unified framework, and leverages the recognition model's ability to implicitly disentangle style and content while ensuring content consistency. Specifically, our approach employs a multi-modal parallel decoder based on transformer architecture, which predicts both text content and stylized images in parallel. Additionally, our cyclic self-supervised fine-tuning strategy enables effective training on unpaired real-world data without ground truth, enhancing style and content consistency through a twice-cyclic generation process. Built on a relatively simple architecture, \mymodel achieves state-of-the-art performance on both synthetic and real-world benchmarks, and further demonstrates the effectiveness of leveraging the generated hard cases to boost the performance of downstream recognition tasks. Code is available at https://github.com/ZhengyaoFang/RS-STE.
WeCromCL: Weakly Supervised Cross-Modality Contrastive Learning for Transcription-only Supervised Text Spotting
Jul 28, 2024Abstract:Transcription-only Supervised Text Spotting aims to learn text spotters relying only on transcriptions but no text boundaries for supervision, thus eliminating expensive boundary annotation. The crux of this task lies in locating each transcription in scene text images without location annotations. In this work, we formulate this challenging problem as a Weakly Supervised Cross-modality Contrastive Learning problem, and design a simple yet effective model dubbed WeCromCL that is able to detect each transcription in a scene image in a weakly supervised manner. Unlike typical methods for cross-modality contrastive learning that focus on modeling the holistic semantic correlation between an entire image and a text description, our WeCromCL conducts atomistic contrastive learning to model the character-wise appearance consistency between a text transcription and its correlated region in a scene image to detect an anchor point for the transcription in a weakly supervised manner. The detected anchor points by WeCromCL are further used as pseudo location labels to guide the learning of text spotting. Extensive experiments on four challenging benchmarks demonstrate the superior performance of our model over other methods. Code will be released.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge