Zhengtao Hu
Soft Regrasping Tool Inspired by Jamming Gripper
Sep 17, 2025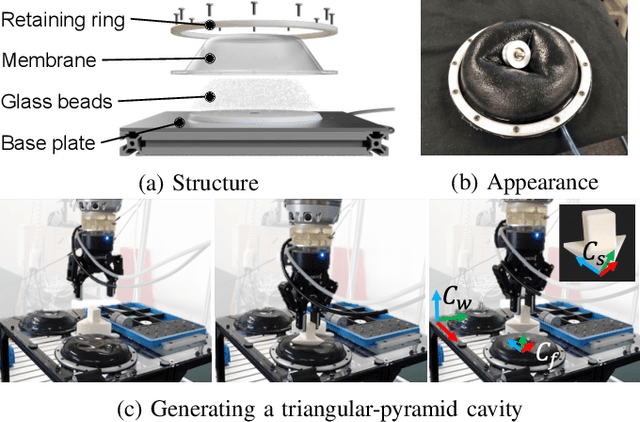
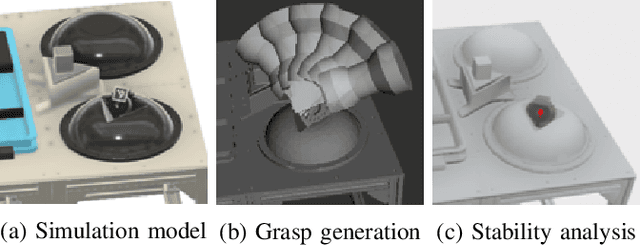
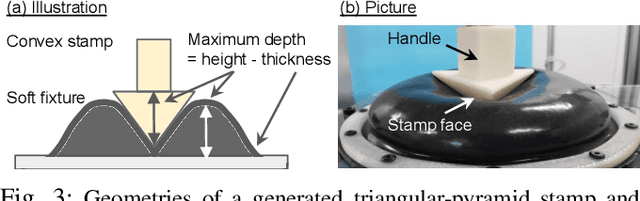
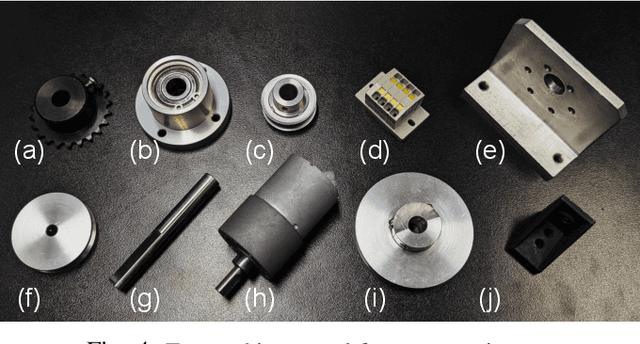
Abstract:Regrasping on fixtures is a promising approach to reduce pose uncertainty in robotic assembly, but conventional rigid fixtures lack adaptability and require dedicated designs for each part. To overcome this limitation, we propose a soft jig inspired by the jamming transition phenomenon, which can be continuously deformed to accommodate diverse object geometries. By pressing a triangular-pyramid-shaped tool into the membrane and evacuating the enclosed air, a stable cavity is formed as a placement space. We further optimize the stamping depth to balance placement stability and gripper accessibility. In soft-jig-based regrasping, the key challenge lies in optimizing the cavity size to achieve precise dropping; once the part is reliably placed, subsequent grasping can be performed with reduced uncertainty. Accordingly, we conducted drop experiments on ten mechanical parts of varying shapes, which achieved placement success rates exceeding 80% for most objects and above 90% for cylindrical ones, while failures were mainly caused by geometric constraints and membrane properties. These results demonstrate that the proposed jig enables general-purpose, accurate, and repeatable regrasping, while also clarifying its current limitations and future potential as a practical alternative to rigid fixtures in assembly automation.
A Multi-Level Similarity Approach for Single-View Object Grasping: Matching, Planning, and Fine-Tuning
Jul 16, 2025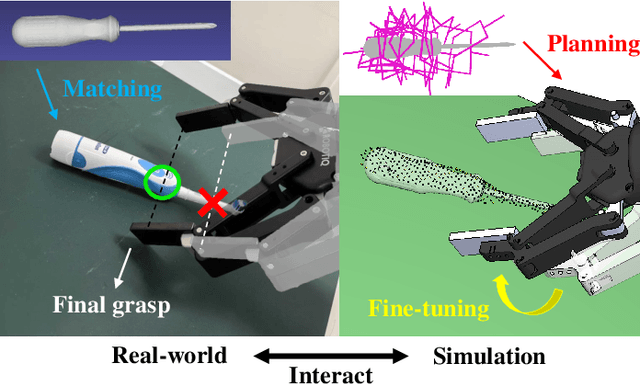
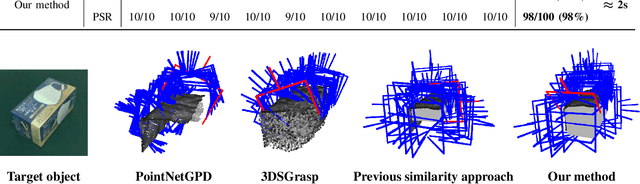
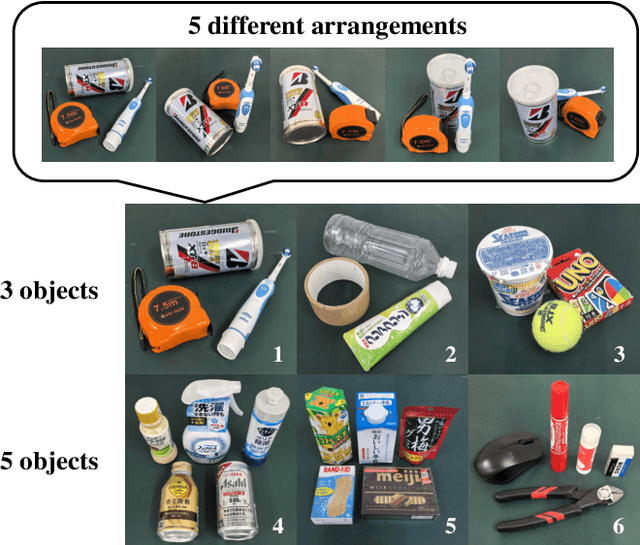
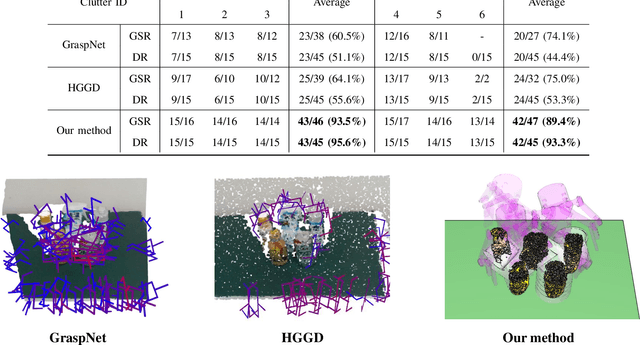
Abstract:Grasping unknown objects from a single view has remained a challenging topic in robotics due to the uncertainty of partial observation. Recent advances in large-scale models have led to benchmark solutions such as GraspNet-1Billion. However, such learning-based approaches still face a critical limitation in performance robustness for their sensitivity to sensing noise and environmental changes. To address this bottleneck in achieving highly generalized grasping, we abandon the traditional learning framework and introduce a new perspective: similarity matching, where similar known objects are utilized to guide the grasping of unknown target objects. We newly propose a method that robustly achieves unknown-object grasping from a single viewpoint through three key steps: 1) Leverage the visual features of the observed object to perform similarity matching with an existing database containing various object models, identifying potential candidates with high similarity; 2) Use the candidate models with pre-existing grasping knowledge to plan imitative grasps for the unknown target object; 3) Optimize the grasp quality through a local fine-tuning process. To address the uncertainty caused by partial and noisy observation, we propose a multi-level similarity matching framework that integrates semantic, geometric, and dimensional features for comprehensive evaluation. Especially, we introduce a novel point cloud geometric descriptor, the C-FPFH descriptor, which facilitates accurate similarity assessment between partial point clouds of observed objects and complete point clouds of database models. In addition, we incorporate the use of large language models, introduce the semi-oriented bounding box, and develop a novel point cloud registration approach based on plane detection to enhance matching accuracy under single-view conditions. Videos are available at https://youtu.be/qQDIELMhQmk.
Bimanual Regrasp Planning and Control for Eliminating Object Pose Uncertainty
Mar 28, 2025Abstract:Precisely grasping an object is a challenging task due to pose uncertainties. Conventional methods have used cameras and fixtures to reduce object uncertainty. They are effective but require intensive preparation, such as designing jigs based on the object geometry and calibrating cameras with high-precision tools fabricated using lasers. In this study, we propose a method to reduce the uncertainty of the position and orientation of a grasped object without using a fixture or a camera. Our method is based on the concept that the flat finger pads of a parallel gripper can reduce uncertainty along its opening/closing direction through flat surface contact. Three orthogonal grasps by parallel grippers with flat finger pads collectively constrain an object's position and orientation to a unique state. Guided by the concepts, we develop a regrasp planning and admittance control approach that sequentially finds and leverages three orthogonal grasps of two robotic arms to eliminate uncertainties in the object pose. We evaluated the proposed method on different initial object uncertainties and verified that the method has satisfactory repeatability accuracy. It outperforms an AR marker detection method implemented using cameras and laser jet printers under standard laboratory conditions.
A Mechanical Screwing Tool for 2-Finger Parallel Grippers -- Design, Optimization, and Manipulation Policies
Jun 18, 2020
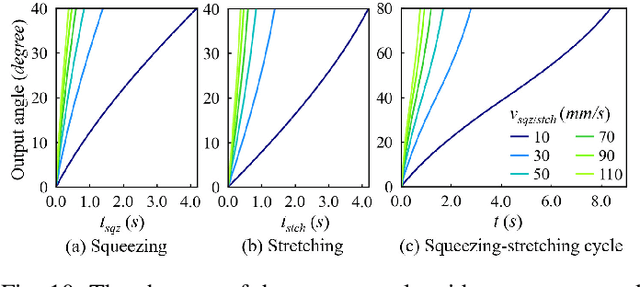
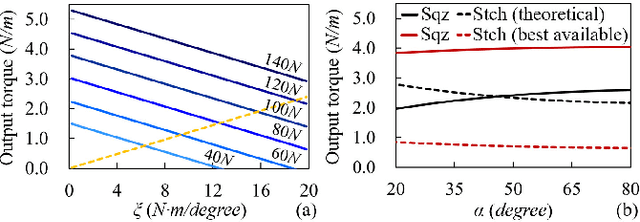

Abstract:This paper develops a mechanical tool as well as its manipulation policies for 2-finger parallel robotic grippers. It primarily focuses on a mechanism that converts the gripping motion of 2-finger parallel grippers into a continuous rotation to realize tasks like fastening screws. The essential structure of the tool comprises a Scissor-Like Element (SLE) mechanism and a double-ratchet mechanism. They together convert repeated linear motion into continuous rotating motion. At the joints of the SLE mechanism, elastic elements are attached to provide resisting force for holding the tool as well as for producing torque output when a gripper releases the tool. The tool is entirely mechanical, allowing robots to use the tool without any peripherals and power supply. The paper presents the details of the tool design, optimizes its dimensions and effective stroke lengths, and studies the contacts and forces to achieve stable grasping and screwing. Besides the design, the paper develops manipulation policies for the tool. The policies include visual recognition, picking-up and manipulation, and exchanging tooltips. The developed tool produces clockwise rotation at the front end and counter-clockwise rotation at the back end. Various tooltips can be installed at both two ends. Robots may employ the developed manipulation policies to exchange the tooltips and rotating directions following the needs of specific fastening or loosening tasks. Robots can also reorient the tool using pick-and-place or handover, and move the tool to work poses using the policies. The designed tool, together with the developed manipulation policies, are analyzed and verified in several real-world applications. The tool is small, cordless, convenient, and has good robustness and adaptability.
Development of a Shape-memorable Adaptive Pin Array Fixture
May 20, 2020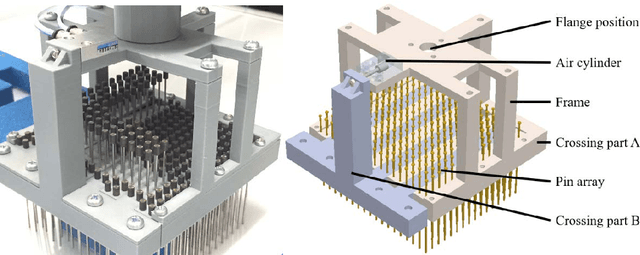

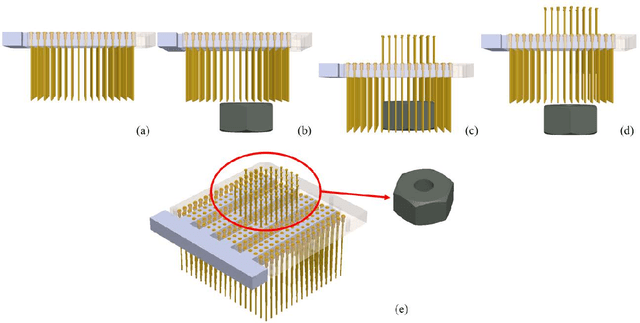

Abstract:This paper proposes an adaptive pin-array fixture. The key idea of this research is to use the shape-memorable mechanism of pin array to fix multiple different shaped parts with common pin configuration. The clamping area consists of a matrix of passively slid-able pins that conform themselves to the contour of the target object. Vertical motion of the pins enables the fixture to encase the profile of the object. The shape memorable mechanism is realized by the combination of the rubber bush and fixing mechanism of a pin. Several physical peg-in-hole tasks is conducted to verify the feasibility of the fixture.
Designing a Mechanical Tool for Robots with 2-Finger Parallel Grippers
Feb 25, 2019



Abstract:This work designs a mechanical tool for robots with 2-finger parallel grippers, which extends the function of the robotic gripper without additional requirements on tool exchangers or other actuators. The fundamental kinematic structure of the mechanical tool is two symmetric parallelograms which transmit the motion of the robotic gripper to the mechanical tool. Four torsion springs are attached to the four inner joints of the two parallelograms to open the tool as the robotic gripper releases. The forces and transmission are analyzed in detail to make sure the tool reacts well with respect to the gripping forces and the spring stiffness. Also, based on the kinematic structure, variety tooltips were designed for the mechanical tool to perform various tasks. The kinematic structure can be a platform to apply various skillful gripper designs. The designed tool could be treated as a normal object and be picked up and used by automatically planned grasps. A robot may locate the tool through the AR markers attached to the tool body, grasp the tool by selecting an automatically planned grasp, and move the tool from any arbitrary pose to a specific pose to grip objects. The robot may also determine the optimal grasps and usage according to the requirements of given tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge