Zhengkang Fan
DTC: A Deformable Transposed Convolution Module for Medical Image Segmentation
Jan 25, 2026Abstract:In medical image segmentation, particularly in UNet-like architectures, upsampling is primarily used to transform smaller feature maps into larger ones, enabling feature fusion between encoder and decoder features and supporting multi-scale prediction. Conventional upsampling methods, such as transposed convolution and linear interpolation, operate on fixed positions: transposed convolution applies kernel elements to predetermined pixel or voxel locations, while linear interpolation assigns values based on fixed coordinates in the original feature map. These fixed-position approaches may fail to capture structural information beyond predefined sampling positions and can lead to artifacts or loss of detail. Inspired by deformable convolutions, we propose a novel upsampling method, Deformable Transposed Convolution (DTC), which learns dynamic coordinates (i.e., sampling positions) to generate high-resolution feature maps for both 2D and 3D medical image segmentation tasks. Experiments on 3D (e.g., BTCV15) and 2D datasets (e.g., ISIC18, BUSI) demonstrate that DTC can be effectively integrated into existing medical image segmentation models, consistently improving the decoder's feature reconstruction and detail recovery capability.
Developing A Fair Individualized Polysocial Risk Score (iPsRS) for Identifying Increased Social Risk of Hospitalizations in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes (T2D)
Sep 05, 2023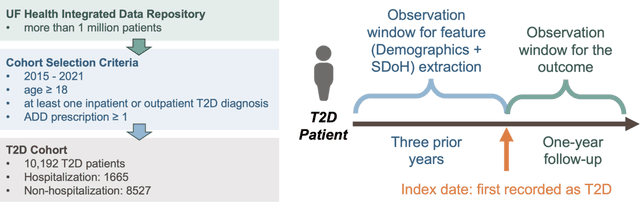
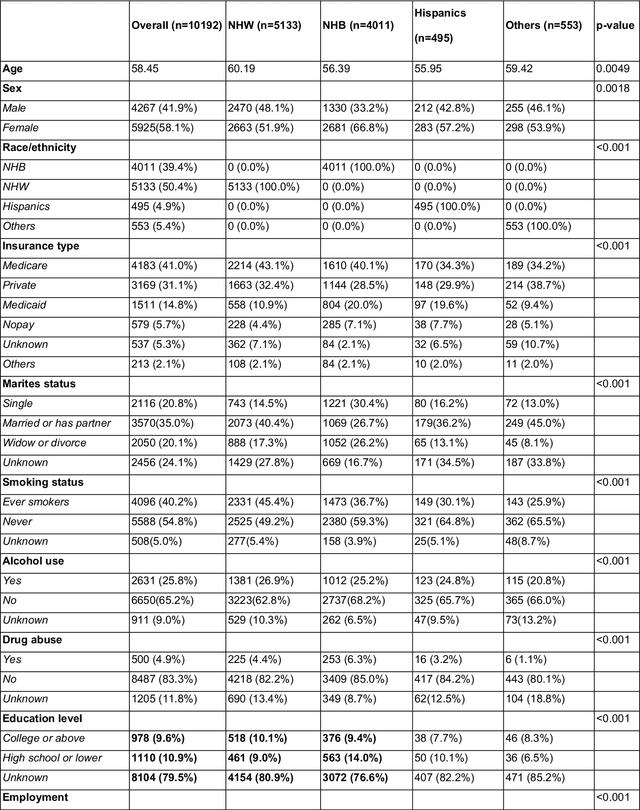
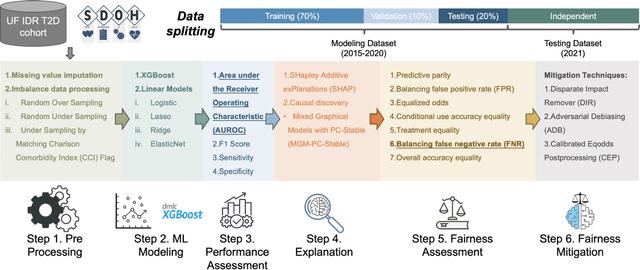
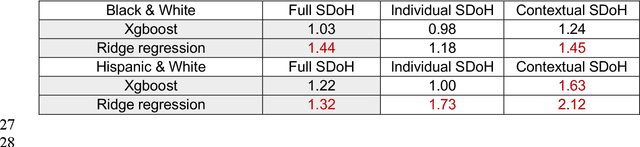
Abstract:Background: Racial and ethnic minority groups and individuals facing social disadvantages, which often stem from their social determinants of health (SDoH), bear a disproportionate burden of type 2 diabetes (T2D) and its complications. It is therefore crucial to implement effective social risk management strategies at the point of care. Objective: To develop an EHR-based machine learning (ML) analytical pipeline to identify the unmet social needs associated with hospitalization risk in patients with T2D. Methods: We identified 10,192 T2D patients from the EHR data (from 2012 to 2022) from the University of Florida Health Integrated Data Repository, including contextual SDoH (e.g., neighborhood deprivation) and individual-level SDoH (e.g., housing stability). We developed an electronic health records (EHR)-based machine learning (ML) analytic pipeline, namely individualized polysocial risk score (iPsRS), to identify high social risk associated with hospitalizations in T2D patients, along with explainable AI (XAI) techniques and fairness assessment and optimization. Results: Our iPsRS achieved a C statistic of 0.72 in predicting 1-year hospitalization after fairness optimization across racial-ethnic groups. The iPsRS showed excellent utility for capturing individuals at high hospitalization risk; the actual 1-year hospitalization rate in the top 5% of iPsRS was ~13 times as high as the bottom decile. Conclusion: Our ML pipeline iPsRS can fairly and accurately screen for patients who have increased social risk leading to hospitalization in T2D patients.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge