Zhen-Ru Zhang
Towards Adaptive Prefix Tuning for Parameter-Efficient Language Model Fine-tuning
May 24, 2023
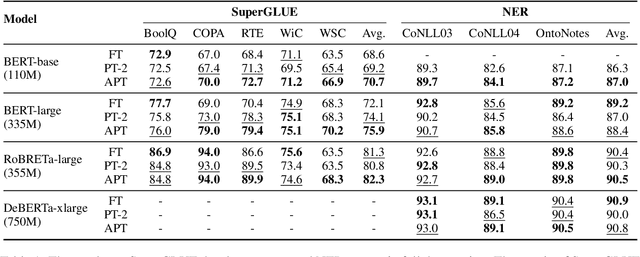
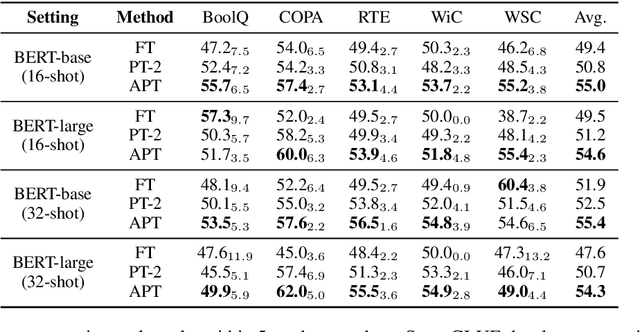
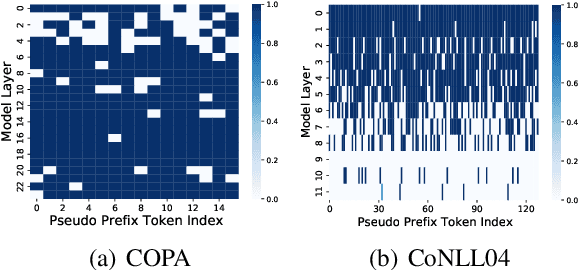
Abstract:Fine-tuning large pre-trained language models on various downstream tasks with whole parameters is prohibitively expensive. Hence, Parameter-efficient fine-tuning has attracted attention that only optimizes a few task-specific parameters with the frozen pre-trained model. In this work, we focus on prefix tuning, which only optimizes continuous prefix vectors (i.e. pseudo tokens) inserted into Transformer layers. Based on the observation that the learned syntax and semantics representation varies a lot at different layers, we argue that the adaptive prefix will be further tailored to each layer than the fixed one, enabling the fine-tuning more effective and efficient. Thus, we propose Adaptive Prefix Tuning (APT) to adjust the prefix in terms of both fine-grained token level and coarse-grained layer level with a gate mechanism. Experiments on the SuperGLUE and NER datasets show the effectiveness of APT. In addition, taking the gate as a probing, we validate the efficiency and effectiveness of the variable prefix.
VECO 2.0: Cross-lingual Language Model Pre-training with Multi-granularity Contrastive Learning
Apr 17, 2023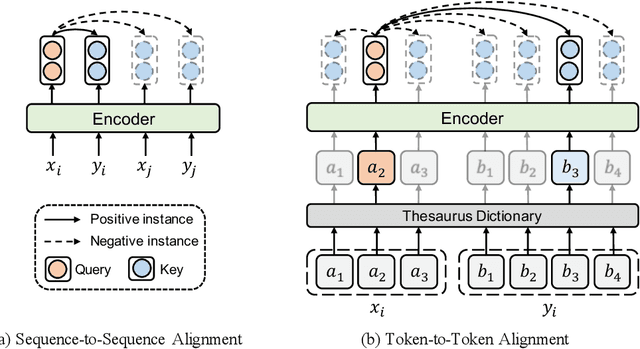
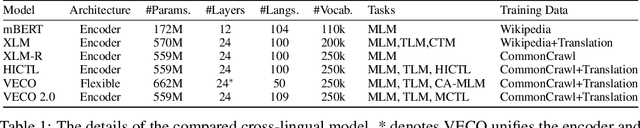
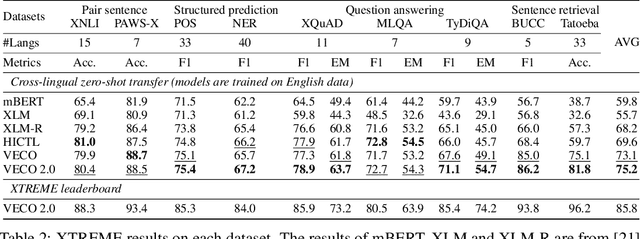
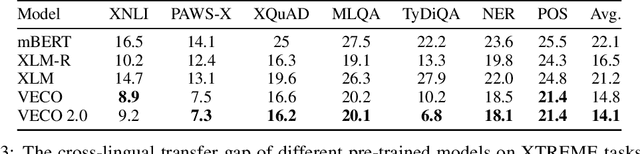
Abstract:Recent studies have demonstrated the potential of cross-lingual transferability by training a unified Transformer encoder for multiple languages. In addition to involving the masked language model objective, existing cross-lingual pre-training works leverage sentence-level contrastive learning or plugs in extra cross-attention module to complement the insufficient capabilities of cross-lingual alignment. Nonetheless, synonym pairs residing in bilingual corpus are not exploited and aligned, which is more crucial than sentence interdependence establishment for token-level tasks. In this work, we propose a cross-lingual pre-trained model VECO~2.0 based on contrastive learning with multi-granularity alignments. Specifically, the sequence-to-sequence alignment is induced to maximize the similarity of the parallel pairs and minimize the non-parallel pairs. Then, token-to-token alignment is integrated to bridge the gap between synonymous tokens excavated via the thesaurus dictionary from the other unpaired tokens in a bilingual instance. Experiments show the effectiveness of the proposed strategy for cross-lingual model pre-training on the XTREME benchmark.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge