Zhanat Kappassov
Robotic Perception with a Large Tactile-Vision-Language Model for Physical Property Inference
Jun 24, 2025Abstract:Inferring physical properties can significantly enhance robotic manipulation by enabling robots to handle objects safely and efficiently through adaptive grasping strategies. Previous approaches have typically relied on either tactile or visual data, limiting their ability to fully capture properties. We introduce a novel cross-modal perception framework that integrates visual observations with tactile representations within a multimodal vision-language model. Our physical reasoning framework, which employs a hierarchical feature alignment mechanism and a refined prompting strategy, enables our model to make property-specific predictions that strongly correlate with ground-truth measurements. Evaluated on 35 diverse objects, our approach outperforms existing baselines and demonstrates strong zero-shot generalization. Keywords: tactile perception, visual-tactile fusion, physical property inference, multimodal integration, robot perception
WaveTouch: Active Tactile Sensing Using Vibro-Feedback for Classification of Variable Stiffness and Infill Density Objects
May 21, 2025Abstract:The perception and recognition of the surroundings is one of the essential tasks for a robot. With preliminary knowledge about a target object, it can perform various manipulation tasks such as rolling motion, palpation, and force control. Minimizing possible damage to the sensing system and testing objects during manipulation are significant concerns that persist in existing research solutions. To address this need, we designed a new type of tactile sensor based on the active vibro-feedback for object stiffness classification. With this approach, the classification can be performed during the gripping process, enabling the robot to quickly estimate the appropriate level of gripping force required to avoid damaging or dropping the object. This contrasts with passive vibration sensing, which requires to be triggered by object movement and is often inefficient for establishing a secure grip. The main idea is to observe the received changes in artificially injected vibrations that propagate through objects with different physical properties and molecular structures. The experiments with soft subjects demonstrated higher absorption of the received vibrations, while the opposite is true for the rigid subjects that not only demonstrated low absorption but also enhancement of the vibration signal.
Survey on Vision-Language-Action Models
Feb 07, 2025Abstract:This paper presents an AI-generated review of Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models, summarizing key methodologies, findings, and future directions. The content is produced using large language models (LLMs) and is intended only for demonstration purposes. This work does not represent original research, but highlights how AI can help automate literature reviews. As AI-generated content becomes more prevalent, ensuring accuracy, reliability, and proper synthesis remains a challenge. Future research will focus on developing a structured framework for AI-assisted literature reviews, exploring techniques to enhance citation accuracy, source credibility, and contextual understanding. By examining the potential and limitations of LLM in academic writing, this study aims to contribute to the broader discussion of integrating AI into research workflows. This work serves as a preliminary step toward establishing systematic approaches for leveraging AI in literature review generation, making academic knowledge synthesis more efficient and scalable.
NUSense: Robust Soft Optical Tactile Sensor
Oct 30, 2024Abstract:While most tactile sensors rely on measuring pressure, insights from continuum mechanics suggest that measuring shear strain provides critical information for tactile sensing. In this work, we introduce an optical tactile sensing principle based on shear strain detection. A silicone rubber layer, dyed with color inks, is used to quantify the shear magnitude of the sensing layer. This principle was validated using the NUSense camera-based tactile sensor. The wide-angle camera captures the elongation of the soft pad under mechanical load, a phenomenon attributed to the Poisson effect. The physical and optical properties of the inked pad are essential and should ideally remain stable over time. We tested the robustness of the sensor by subjecting the outermost layer to multiple load cycles using a robot arm. Additionally, we discussed potential applications of this sensor in force sensing and contact localization.
Color-Coded Fiber-Optic Tactile Sensor for an Elastomeric Robot Skin
Aug 10, 2019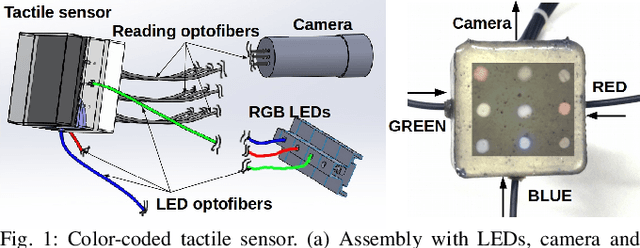
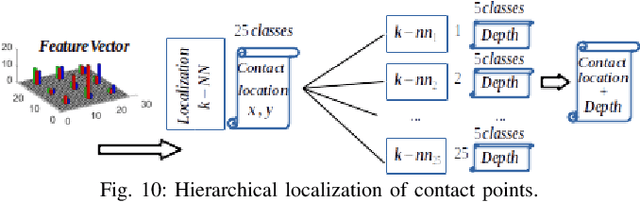
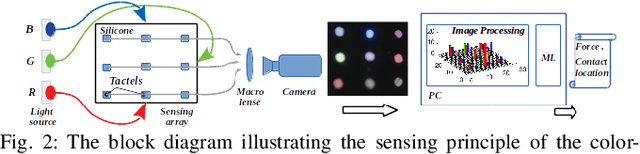
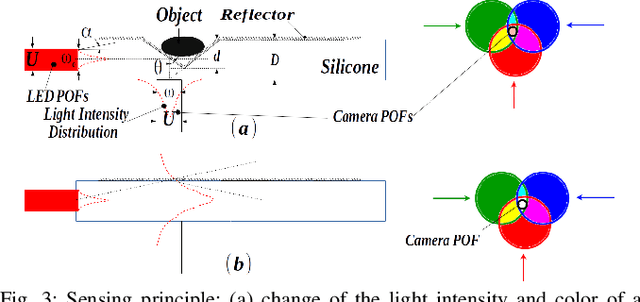
Abstract:The sense of touch is essential for reliable mapping between the environment and a robot which interacts physically with objects. Presumably, an artificial tactile skin would facilitate safe interaction of the robots with the environment. In this work, we present our color-coded tactile sensor, incorporating plastic optical fibers (POF), transparent silicone rubber and an off-the-shelf color camera. Processing electronics are placed away from the sensing surface to make the sensor robust to harsh environments. Contact localization is possible thanks to the lower number of light sources compared to the number of camera POFs. Classical machine learning techniques and a hierarchical classification scheme were used for contact localization. Specifically, we generated the mapping from stimulation to sensation of a robotic perception system using our sensor. We achieved a force sensing range up to 18 N with the force resolution of around 3.6~N and the spatial resolution of 8~mm. The color-coded tactile sensor is suitable for tactile exploration and might enable further innovations in robust tactile sensing.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge