Zekun Deng
CHisIEC: An Information Extraction Corpus for Ancient Chinese History
Mar 22, 2024

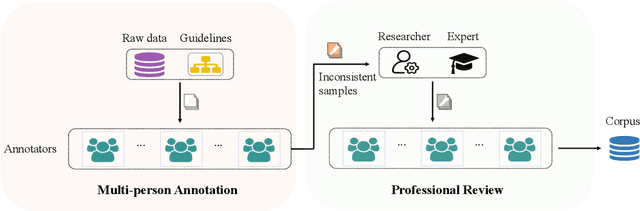

Abstract:Natural Language Processing (NLP) plays a pivotal role in the realm of Digital Humanities (DH) and serves as the cornerstone for advancing the structural analysis of historical and cultural heritage texts. This is particularly true for the domains of named entity recognition (NER) and relation extraction (RE). In our commitment to expediting ancient history and culture, we present the ``Chinese Historical Information Extraction Corpus''(CHisIEC). CHisIEC is a meticulously curated dataset designed to develop and evaluate NER and RE tasks, offering a resource to facilitate research in the field. Spanning a remarkable historical timeline encompassing data from 13 dynasties spanning over 1830 years, CHisIEC epitomizes the extensive temporal range and text heterogeneity inherent in Chinese historical documents. The dataset encompasses four distinct entity types and twelve relation types, resulting in a meticulously labeled dataset comprising 14,194 entities and 8,609 relations. To establish the robustness and versatility of our dataset, we have undertaken comprehensive experimentation involving models of various sizes and paradigms. Additionally, we have evaluated the capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) in the context of tasks related to ancient Chinese history. The dataset and code are available at \url{https://github.com/tangxuemei1995/CHisIEC}.
Can AI Write Classical Chinese Poetry like Humans? An Empirical Study Inspired by Turing Test
Jan 10, 2024Abstract:Some argue that the essence of humanity, such as creativity and sentiment, can never be mimicked by machines. This paper casts doubt on this belief by studying a vital question: Can AI compose poetry as well as humans? To answer the question, we propose ProFTAP, a novel evaluation framework inspired by Turing test to assess AI's poetry writing capability. We apply it on current large language models (LLMs) and find that recent LLMs do indeed possess the ability to write classical Chinese poems nearly indistinguishable from those of humans. We also reveal that various open-source LLMs can outperform GPT-4 on this task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge