Zeinab Maleki
Detecting individual-level infections using sparse group-testing through graph-coupled hidden Markov models
Jun 05, 2023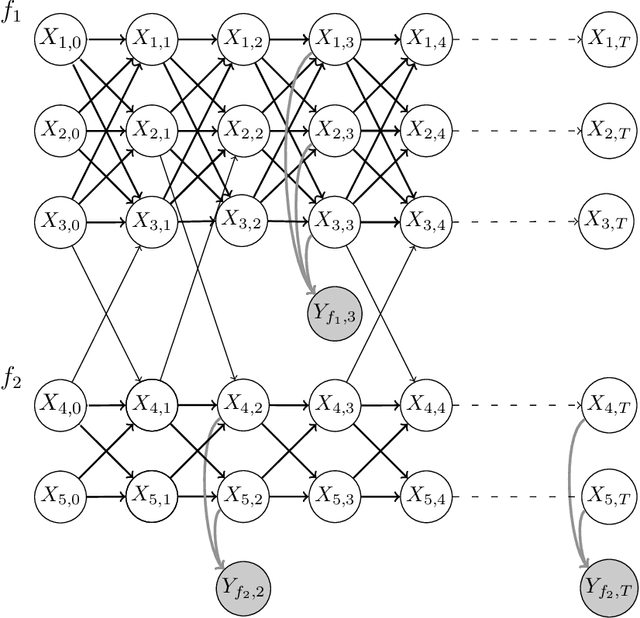
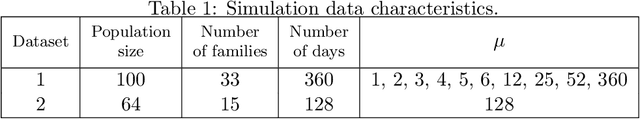
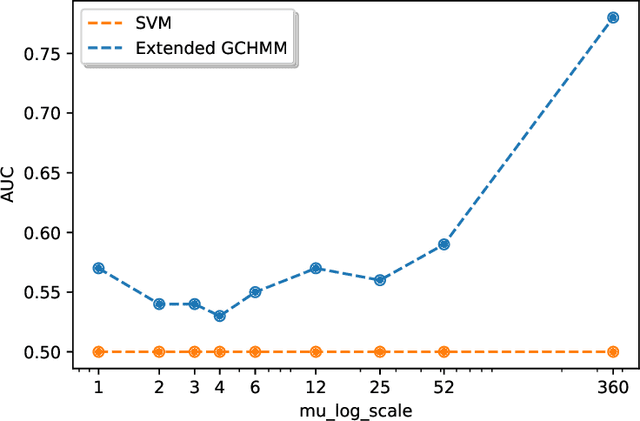
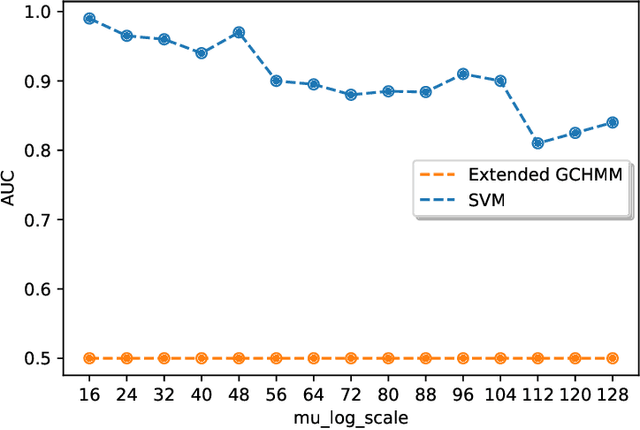
Abstract:Identifying the infection status of each individual during infectious diseases informs public health management. However, performing frequent individual-level tests may not be feasible. Instead, sparse and sometimes group-level tests are performed. Determining the infection status of individuals using sparse group-level tests remains an open problem. We have tackled this problem by extending graph-coupled hidden Markov models with individuals infection statuses as the hidden states and the group test results as the observations. We fitted the model to simulation datasets using the Gibbs sampling method. The model performed about 0.55 AUC for low testing frequencies and increased to 0.80 AUC in the case where the groups were tested every day. The model was separately tested on a daily basis case to predict the statuses over time and after 15 days of the beginning of the spread, which resulted in 0.98 AUC at day 16 and remained above 0.80 AUC until day 128. Therefore, although dealing with sparse tests remains unsolved, the results open the possibility of using initial group screenings during pandemics to accurately estimate individuals infection statuses.
Evaluating Sparse Interpretable Word Embeddings for Biomedical Domain
May 11, 2020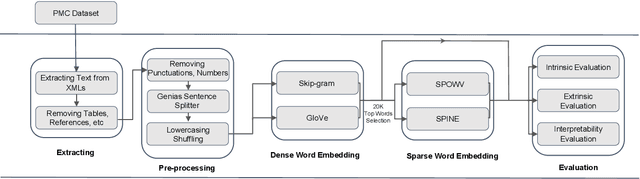
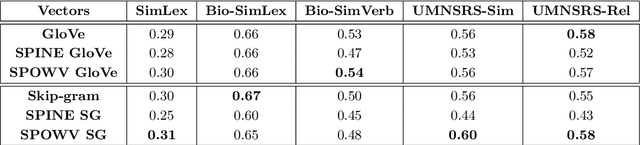
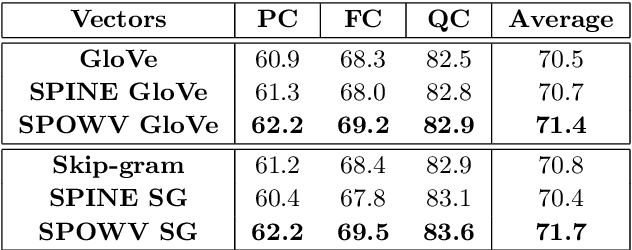
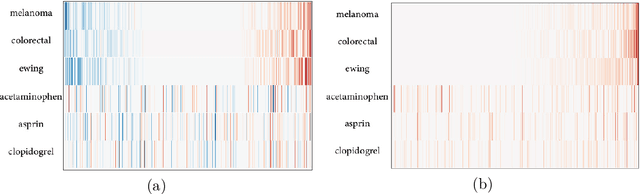
Abstract:Word embeddings have found their way into a wide range of natural language processing tasks including those in the biomedical domain. While these vector representations successfully capture semantic and syntactic word relations, hidden patterns and trends in the data, they fail to offer interpretability. Interpretability is a key means to justification which is an integral part when it comes to biomedical applications. We present an inclusive study on interpretability of word embeddings in the medical domain, focusing on the role of sparse methods. Qualitative and quantitative measurements and metrics for interpretability of word vector representations are provided. For the quantitative evaluation, we introduce an extensive categorized dataset that can be used to quantify interpretability based on category theory. Intrinsic and extrinsic evaluation of the studied methods are also presented. As for the latter, we propose datasets which can be utilized for effective extrinsic evaluation of word vectors in the biomedical domain. Based on our experiments, it is seen that sparse word vectors show far more interpretability while preserving the performance of their original vectors in downstream tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge