Ze Hu
An Imitation Learning Based Algorithm Enabling Priori Knowledge Transfer in Modern Electricity Markets for Bayesian Nash Equilibrium Estimation
May 12, 2023Abstract:The Nash Equilibrium (NE) estimation in bidding games of electricity markets is the key concern of both generation companies (GENCOs) for bidding strategy optimization and the Independent System Operator (ISO) for market surveillance. However, existing methods for NE estimation in emerging modern electricity markets (FEM) are inaccurate and inefficient because the priori knowledge of bidding strategies before any environment changes, such as load demand variations, network congestion, and modifications of market design, is not fully utilized. In this paper, a Bayes-adaptive Markov Decision Process in FEM (BAMDP-FEM) is therefore developed to model the GENCOs' bidding strategy optimization considering the priori knowledge. A novel Multi-Agent Generative Adversarial Imitation Learning algorithm (MAGAIL-FEM) is then proposed to enable GENCOs to learn simultaneously from priori knowledge and interactions with changing environments. The obtained NE is a Bayesian Nash Equilibrium (BNE) with priori knowledge transferred from the previous environment. In the case study, the superiority of this proposed algorithm in terms of convergence speed compared with conventional methods is verified. It is concluded that the optimal bidding strategies in the obtained BNE can always lead to more profits than NE due to the effective learning from the priori knowledge. Also, BNE is more accurate and consistent with situations in real-world markets.
Applications of Reinforcement Learning in Deregulated Power Market: A Comprehensive Review
May 07, 2022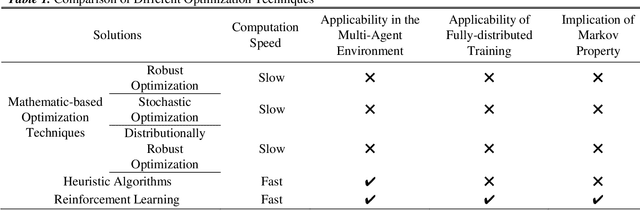
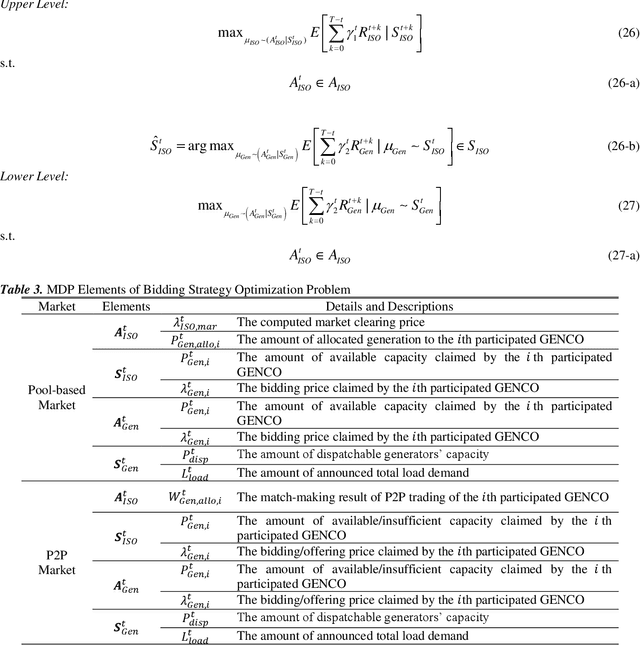


Abstract:The increasing penetration of renewable generations, along with the deregulation and marketization of power industry, promotes the transformation of power market operation paradigms. The optimal bidding strategy and dispatching methodology under these new paradigms are prioritized concerns for both market participants and power system operators, with obstacles of uncertain characteristics, computational efficiency, as well as requirements of hyperopic decision-making. To tackle these problems, the Reinforcement Learning (RL), as an emerging machine learning technique with advantages compared with conventional optimization tools, is playing an increasingly significant role in both academia and industry. This paper presents a comprehensive review of RL applications in deregulated power market operation including bidding and dispatching strategy optimization, based on more than 150 carefully selected literatures. For each application, apart from a paradigmatic summary of generalized methodology, in-depth discussions of applicability and obstacles while deploying RL techniques are also provided. Finally, some RL techniques that have great potentiality to be deployed in bidding and dispatching problems are recommended and discussed.
A deep learning approach for predicting the quality of online health expert question-answering services
Dec 21, 2016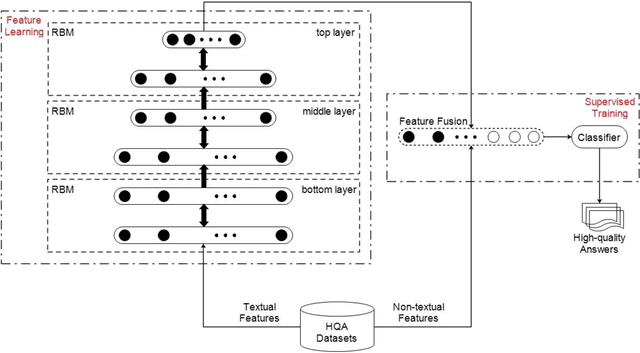
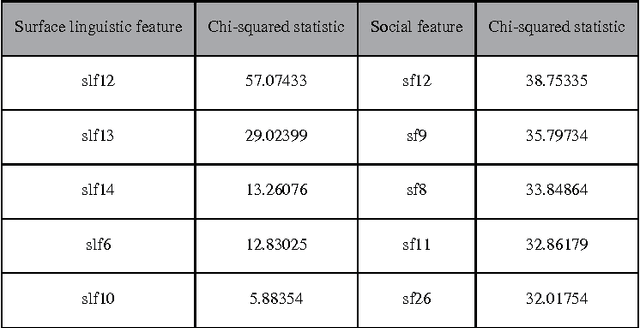
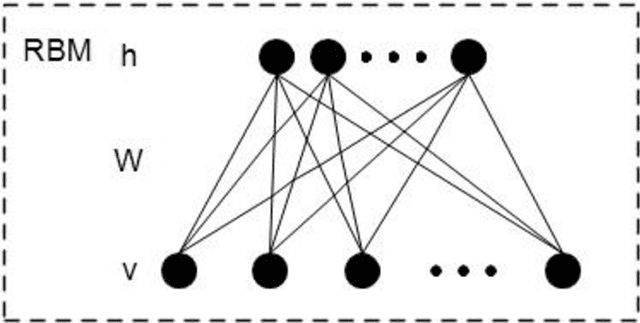
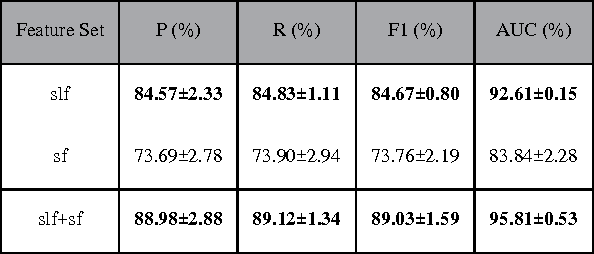
Abstract:Currently, a growing number of health consumers are asking health-related questions online, at any time and from anywhere, which effectively lowers the cost of health care. The most common approach is using online health expert question-answering (HQA) services, as health consumers are more willing to trust answers from professional physicians. However, these answers can be of varying quality depending on circumstance. In addition, as the available HQA services grow, how to predict the answer quality of HQA services via machine learning becomes increasingly important and challenging. In an HQA service, answers are normally short texts, which are severely affected by the data sparsity problem. Furthermore, HQA services lack community features such as best answer and user votes. Therefore, the wisdom of the crowd is not available to rate answer quality. To address these problems, in this paper, the prediction of HQA answer quality is defined as a classification task. First, based on the characteristics of HQA services and feedback from medical experts, a standard for HQA service answer quality evaluation is defined. Next, based on the characteristics of HQA services, several novel non-textual features are proposed, including surface linguistic features and social features. Finally, a deep belief network (DBN)-based HQA answer quality prediction framework is proposed to predict the quality of answers by learning the high-level hidden semantic representation from the physicians' answers. Our results prove that the proposed framework overcomes the problem of overly sparse textual features in short text answers and effectively identifies high-quality answers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge