Z. Zhu
Latency Minimization for IRS-enhanced Wideband MEC Networks with Practical Reflection Model
Jul 15, 2024



Abstract:Intelligent reflecting surface (IRS) has been considered as an efficient way to boost the computation capability of mobile edge computing (MEC) system, especially when the communication links is blocked or the communication signal is weak. However, most existing works are restricted to narrow-band channel and ideal IRS reflection model, which is not practical and may lead to significant performance degradation in realistic systems. To further exploit the benefits of IRS in MEC system, we consider an IRS-enhanced wideband MEC system with practical IRS reflection model. With the aim of minimizing the weighted latency of all devices, the offloading data volume, edge computing resource, BS's receiving vector, and IRS passive beamforming are jointly optimized. Since the formulated problem is non-convex, we employ the block coordinate descent (BCD) technique to decouple it into two subproblems for alternatively optimizing computing and communication settings. The effectiveness and convergence of the proposed algorithm are validate via numerical analyses. In addition, simulation results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm can achieve lower latency compared to that based on the ideal IRS reflection model, which confirms the necessary of considering practical model when designing an IRS-enhanced wideband MEC system.
Picture Fuzzy Interactional Aggregation Operators via Strict Triangular Norms and Applications to Multi-Criteria Decision Making
Apr 08, 2022



Abstract:The picture fuzzy set, characterized by three membership degrees, is a helpful tool for multi-criteria decision making (MCDM). This paper investigates the structure of the closed operational laws in the picture fuzzy numbers (PFNs) and proposes efficient picture fuzzy MCDM methods. We first introduce an admissible order for PFNs and prove that all PFNs form a complete lattice under this order. Then, we give some specific examples to show the non-closeness of some existing picture fuzzy aggregation operators. To ensure the closeness of the operational laws in PFNs, we construct a new class of picture fuzzy operators based on strict triangular norms, which consider the interaction between the positive degrees (negative degrees) and the neutral degrees. Based on these new operators, we obtain the picture fuzzy interactional weighted average (PFIWA) operator and the picture fuzzy interactional weighted geometric (PFIWG) operator. They are proved to be monotonous, idempotent, bounded, shift-invariant, and homogeneous. We also establish a novel MCDM method under the picture fuzzy environment applying PFIWA and PFIWG operators. Furthermore, we present an illustrative example for a clear understanding of our method. We also give the comparative analysis among the operators induced by six classes of famous triangular norms.
Compressed Sensing with Probability-based Prior Information
Oct 27, 2019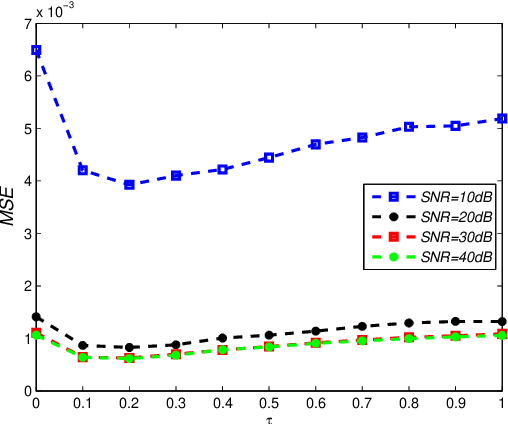
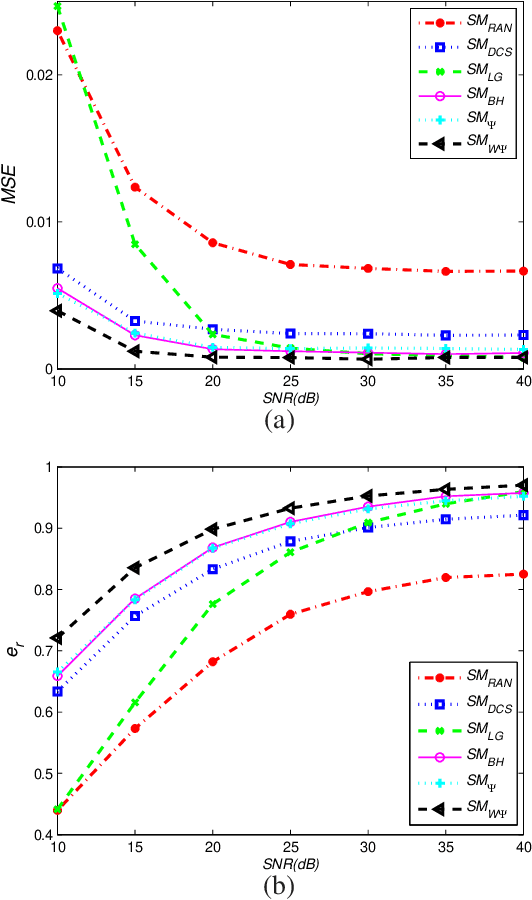
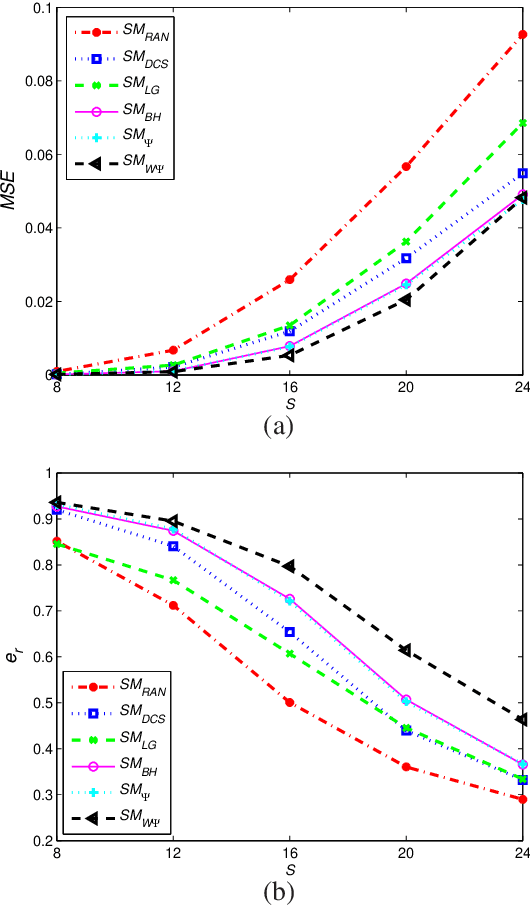
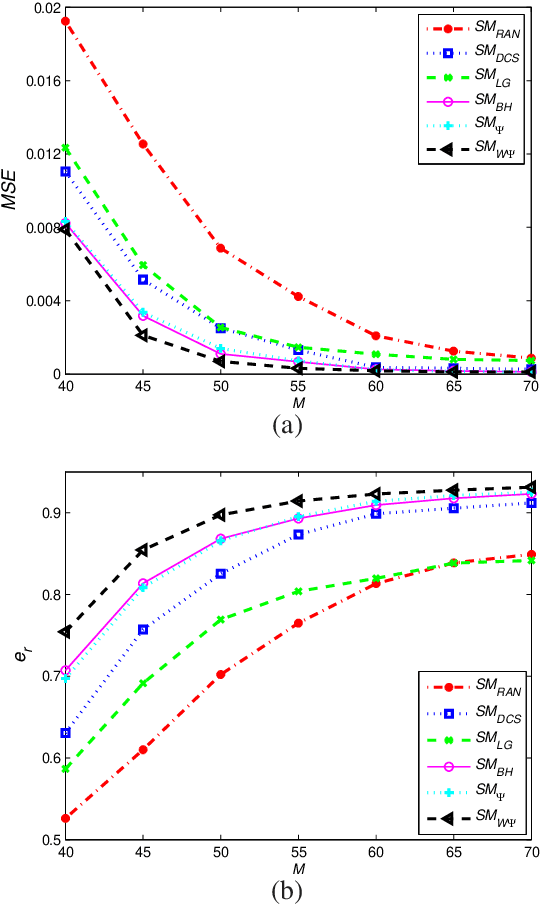
Abstract:This paper deals with the design of a sensing matrix along with a sparse recovery algorithm by utilizing the probability-based prior information for compressed sensing system. With the knowledge of the probability for each atom of the dictionary being used, a diagonal weighted matrix is obtained and then the sensing matrix is designed by minimizing a weighted function such that the Gram of the equivalent dictionary is as close to the Gram of dictionary as possible. An analytical solution for the corresponding sensing matrix is derived which leads to low computational complexity. We also exploit this prior information through the sparse recovery stage and propose a probability-driven orthogonal matching pursuit algorithm that improves the accuracy of the recovery. Simulations for synthetic data and application scenarios of surveillance video are carried out to compare the performance of the proposed methods with some existing algorithms. The results reveal that the proposed CS system outperforms existing CS systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge