Z. Yang
Channel Estimation for RIS-Aided MIMO Systems: A Partially Decoupled Atomic Norm Minimization Approach
Jul 21, 2023



Abstract:Channel estimation (CE) plays a key role in reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS)-aided multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) communication systems, while it poses a challenging task due to the passive nature of RIS and the cascaded channel structures. In this paper, a partially decoupled atomic norm minimization (PDANM) framework is proposed for CE of RIS-aided MIMO systems, which exploits the three-dimensional angular sparsity of the channel. In particular, PDANM partially decouples the differential angles at the RIS from other angles at the base station and user equipment, reducing the computational complexity compared with existing methods. A reweighted PDANM (RPDANM) algorithm is proposed to further improve CE accuracy, which iteratively refines CE through a specifically designed reweighing strategy. Building upon RPDANM, we propose an iterative approach named RPDANM with adaptive phase control (RPDANM-APC), which adaptively adjusts the RIS phases based on previously estimated channel parameters to facilitate CE, achieving superior CE accuracy while reducing training overhead. Numerical simulations demonstrate the superiority of our proposed approaches in terms of running time, CE accuracy, and training overhead. In particular, the RPDANM-APC approach can achieve higher CE accuracy than existing methods within less than 40 percent training overhead while reducing the running time by tens of times.
Picture Fuzzy Interactional Aggregation Operators via Strict Triangular Norms and Applications to Multi-Criteria Decision Making
Apr 08, 2022



Abstract:The picture fuzzy set, characterized by three membership degrees, is a helpful tool for multi-criteria decision making (MCDM). This paper investigates the structure of the closed operational laws in the picture fuzzy numbers (PFNs) and proposes efficient picture fuzzy MCDM methods. We first introduce an admissible order for PFNs and prove that all PFNs form a complete lattice under this order. Then, we give some specific examples to show the non-closeness of some existing picture fuzzy aggregation operators. To ensure the closeness of the operational laws in PFNs, we construct a new class of picture fuzzy operators based on strict triangular norms, which consider the interaction between the positive degrees (negative degrees) and the neutral degrees. Based on these new operators, we obtain the picture fuzzy interactional weighted average (PFIWA) operator and the picture fuzzy interactional weighted geometric (PFIWG) operator. They are proved to be monotonous, idempotent, bounded, shift-invariant, and homogeneous. We also establish a novel MCDM method under the picture fuzzy environment applying PFIWA and PFIWG operators. Furthermore, we present an illustrative example for a clear understanding of our method. We also give the comparative analysis among the operators induced by six classes of famous triangular norms.
Study of Robust Two-Stage Reduced-Dimension Sparsity-Aware STAP with Coprime Arrays
Dec 23, 2019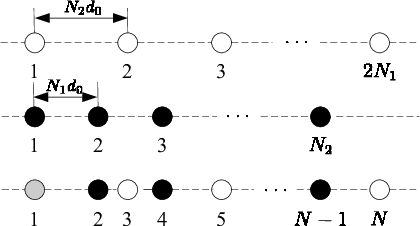
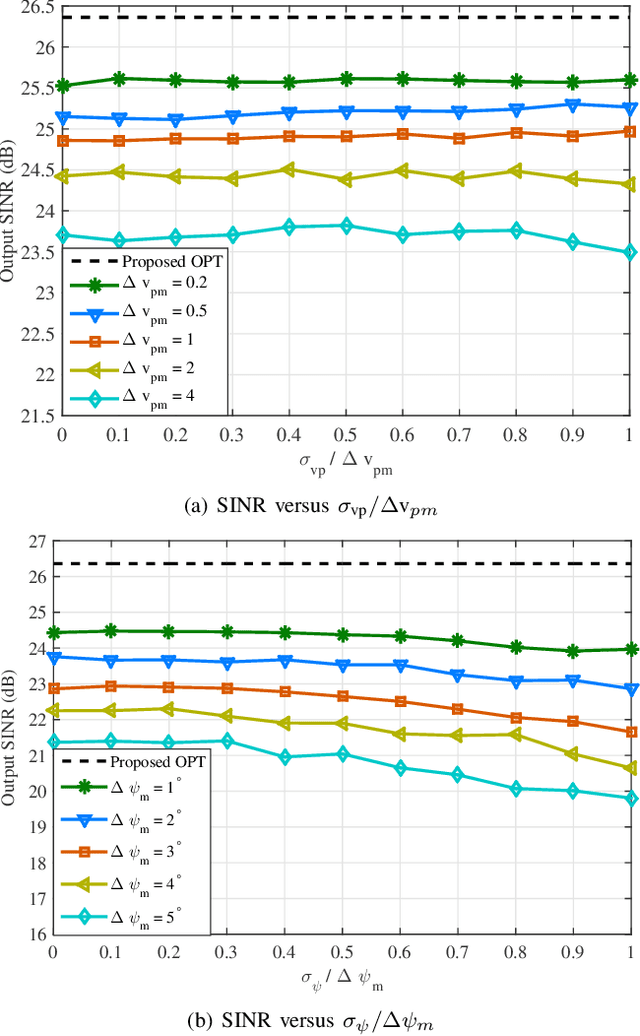
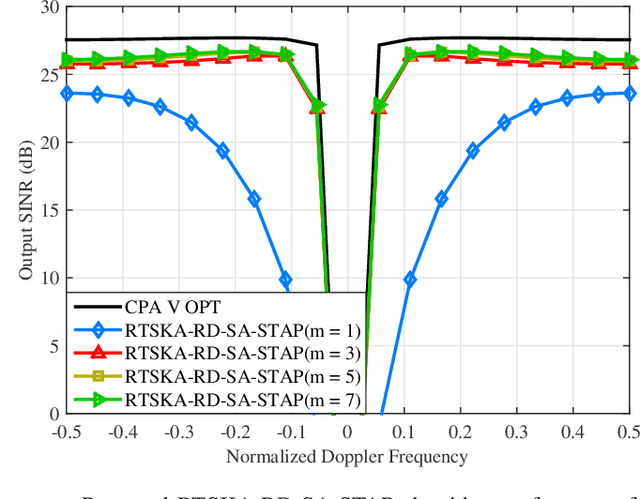
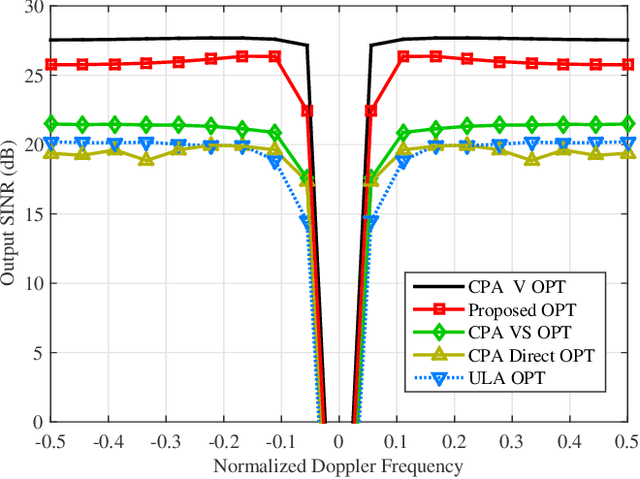
Abstract:Space-time adaptive processing (STAP) algorithms with coprime arrays can provide good clutter suppression potential with low cost in airborne radar systems as compared with their uniform linear arrays counterparts. However, the performance of these algorithms is limited by the training samples support in practical applications. To address this issue, a robust two-stage reduced-dimension (RD) sparsity-aware STAP algorithm is proposed in this work. In the first stage, an RD virtual snapshot is constructed using all spatial channels but only $m$ adjacent Doppler channels around the target Doppler frequency to reduce the slow-time dimension of the signal. In the second stage, an RD sparse measurement modeling is formulated based on the constructed RD virtual snapshot, where the sparsity of clutter and the prior knowledge of the clutter ridge are exploited to formulate an RD overcomplete dictionary. Moreover, an orthogonal matching pursuit (OMP)-like method is proposed to recover the clutter subspace. In order to set the stopping parameter of the OMP-like method, a robust clutter rank estimation approach is developed. Compared with recently developed sparsity-aware STAP algorithms, the size of the proposed sparse representation dictionary is much smaller, resulting in low complexity. Simulation results show that the proposed algorithm is robust to prior knowledge errors and can provide good clutter suppression performance in low sample support.
A Base Camp for Scaling AI
Dec 23, 2016



Abstract:Modern statistical machine learning (SML) methods share a major limitation with the early approaches to AI: there is no scalable way to adapt them to new domains. Human learning solves this in part by leveraging a rich, shared, updateable world model. Such scalability requires modularity: updating part of the world model should not impact unrelated parts. We have argued that such modularity will require both "correctability" (so that errors can be corrected without introducing new errors) and "interpretability" (so that we can understand what components need correcting). To achieve this, one could attempt to adapt state of the art SML systems to be interpretable and correctable; or one could see how far the simplest possible interpretable, correctable learning methods can take us, and try to control the limitations of SML methods by applying them only where needed. Here we focus on the latter approach and we investigate two main ideas: "Teacher Assisted Learning", which leverages crowd sourcing to learn language; and "Factored Dialog Learning", which factors the process of application development into roles where the language competencies needed are isolated, enabling non-experts to quickly create new applications. We test these ideas in an "Automated Personal Assistant" (APA) setting, with two scenarios: that of detecting user intent from a user-APA dialog; and that of creating a class of event reminder applications, where a non-expert "teacher" can then create specific apps. For the intent detection task, we use a dataset of a thousand labeled utterances from user dialogs with Cortana, and we show that our approach matches state of the art SML methods, but in addition provides full transparency: the whole (editable) model can be summarized on one human-readable page. For the reminder app task, we ran small user studies to verify the efficacy of the approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge