H. Bai
Latte-Mix: Measuring Sentence Semantic Similarity with Latent Categorical Mixtures
Oct 21, 2020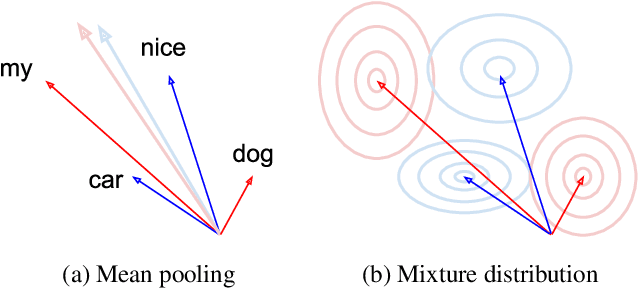
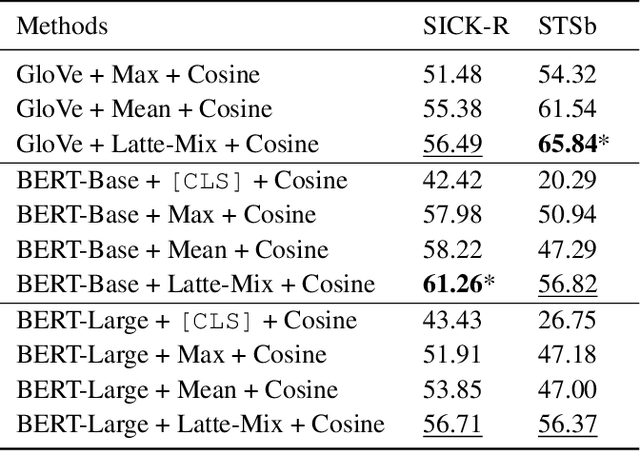
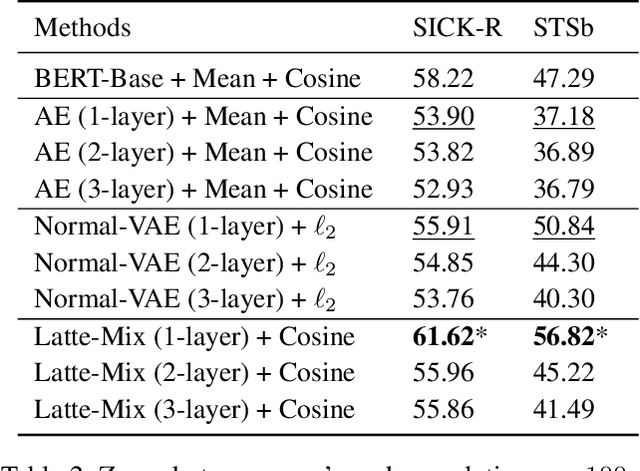
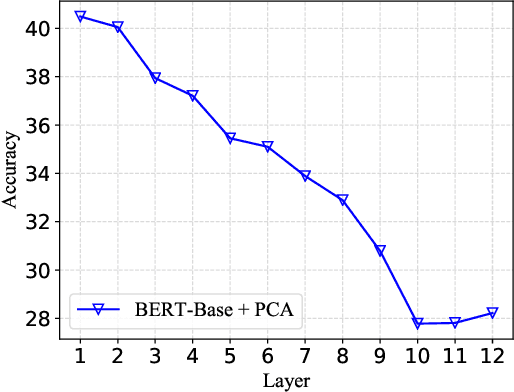
Abstract:Measuring sentence semantic similarity using pre-trained language models such as BERT generally yields unsatisfactory zero-shot performance, and one main reason is ineffective token aggregation methods such as mean pooling. In this paper, we demonstrate under a Bayesian framework that distance between primitive statistics such as the mean of word embeddings are fundamentally flawed for capturing sentence-level semantic similarity. To remedy this issue, we propose to learn a categorical variational autoencoder (VAE) based on off-the-shelf pre-trained language models. We theoretically prove that measuring the distance between the latent categorical mixtures, namely Latte-Mix, can better reflect the true sentence semantic similarity. In addition, our Bayesian framework provides explanations for why models finetuned on labelled sentence pairs have better zero-shot performance. We also empirically demonstrate that these finetuned models could be further improved by Latte-Mix. Our method not only yields the state-of-the-art zero-shot performance on semantic similarity datasets such as STS, but also enjoy the benefits of fast training and having small memory footprints.
Compressed Sensing with Probability-based Prior Information
Oct 27, 2019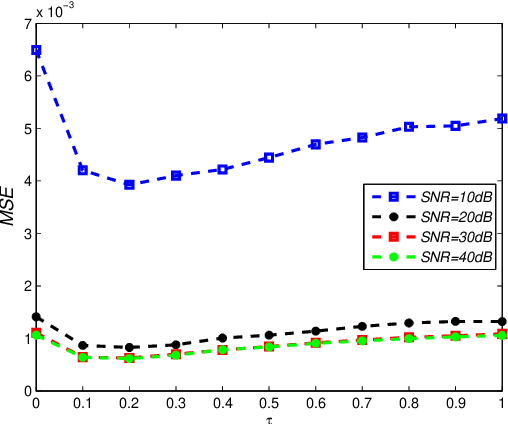
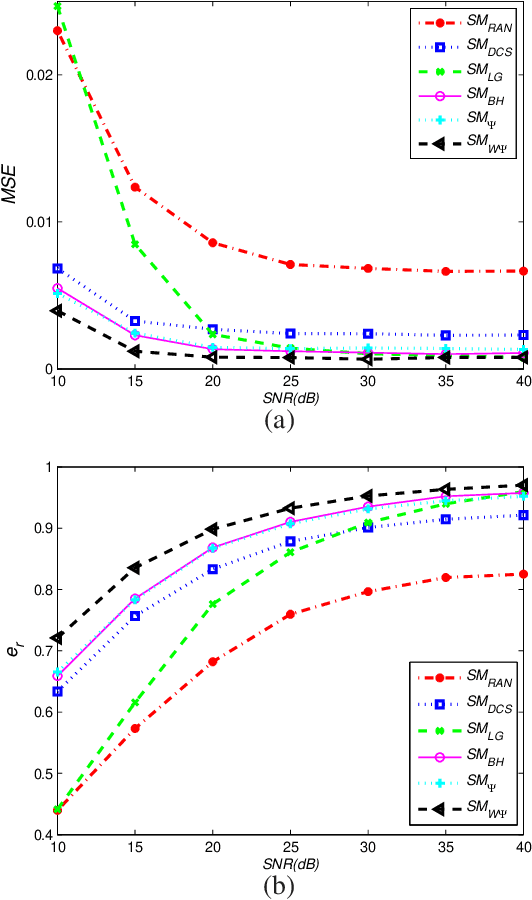
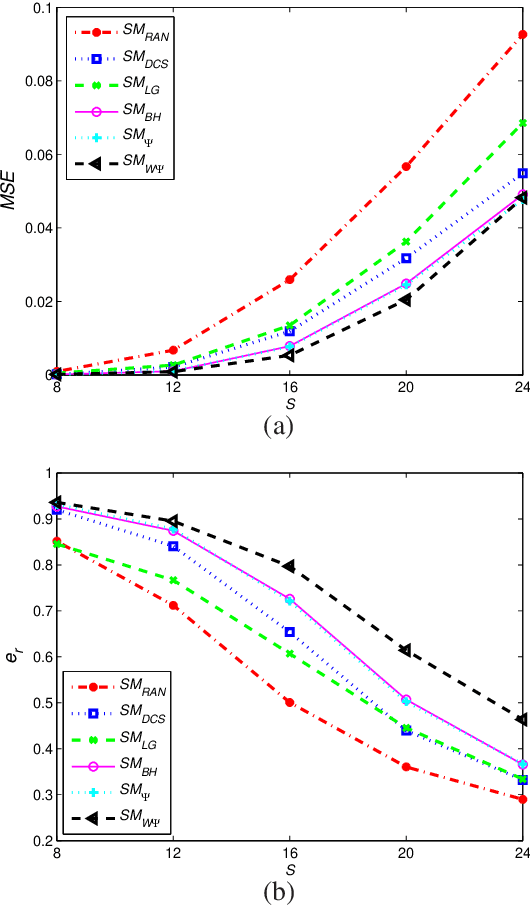
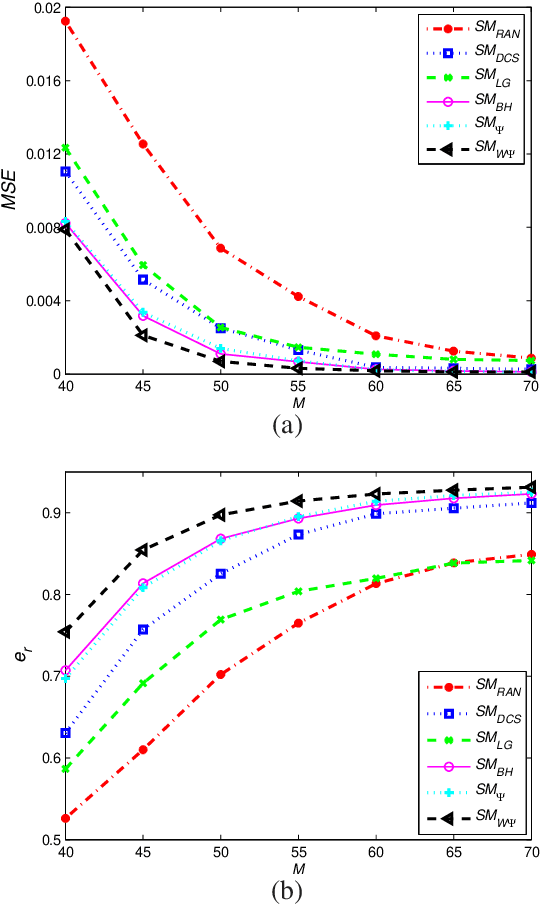
Abstract:This paper deals with the design of a sensing matrix along with a sparse recovery algorithm by utilizing the probability-based prior information for compressed sensing system. With the knowledge of the probability for each atom of the dictionary being used, a diagonal weighted matrix is obtained and then the sensing matrix is designed by minimizing a weighted function such that the Gram of the equivalent dictionary is as close to the Gram of dictionary as possible. An analytical solution for the corresponding sensing matrix is derived which leads to low computational complexity. We also exploit this prior information through the sparse recovery stage and propose a probability-driven orthogonal matching pursuit algorithm that improves the accuracy of the recovery. Simulations for synthetic data and application scenarios of surveillance video are carried out to compare the performance of the proposed methods with some existing algorithms. The results reveal that the proposed CS system outperforms existing CS systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge