Yves Quemener
Real-time Neuron Segmentation for Voltage Imaging
Mar 25, 2024Abstract:In voltage imaging, where the membrane potentials of individual neurons are recorded at from hundreds to thousand frames per second using fluorescence microscopy, data processing presents a challenge. Even a fraction of a minute of recording with a limited image size yields gigabytes of video data consisting of tens of thousands of frames, which can be time-consuming to process. Moreover, millisecond-level short exposures lead to noisy video frames, obscuring neuron footprints especially in deep-brain samples where noisy signals are buried in background fluorescence. To address this challenge, we propose a fast neuron segmentation method able to detect multiple, potentially overlapping, spiking neurons from noisy video frames, and implement a data processing pipeline incorporating the proposed segmentation method along with GPU-accelerated motion correction. By testing on existing datasets as well as on new datasets we introduce, we show that our pipeline extracts neuron footprints that agree well with human annotation even from cluttered datasets, and demonstrate real-time processing of voltage imaging data on a single desktop computer for the first time.
Quantized deep learning models on low-power edge devices for robotic systems
Nov 30, 2019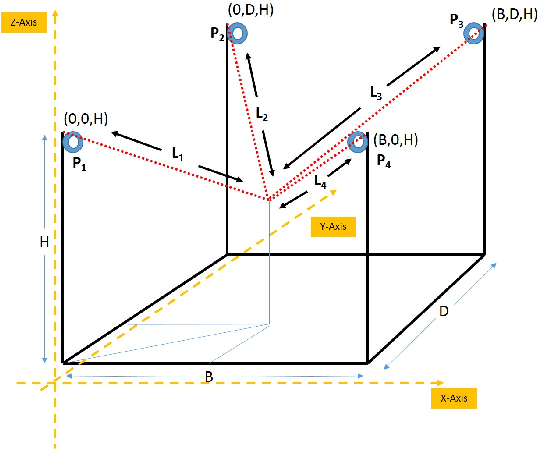
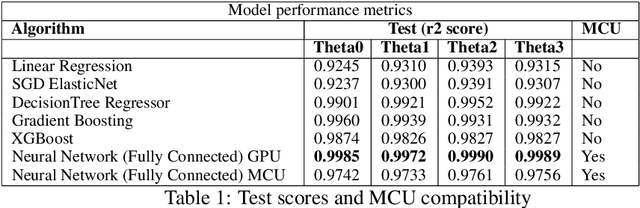
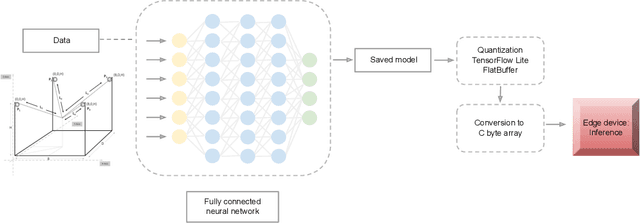
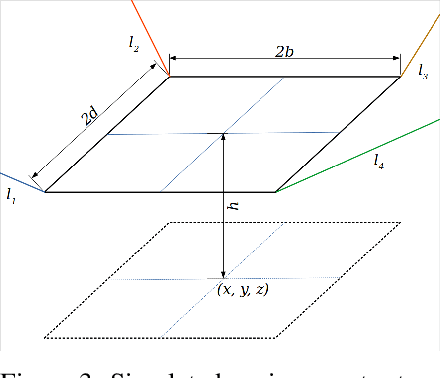
Abstract:In this work, we present a quantized deep neural network deployed on a low-power edge device, inferring learned motor-movements of a suspended robot in a defined space. This serves as the fundamental building block for the original setup, a robotic system for farms or greenhouses aimed at a wide range of agricultural tasks. Deep learning on edge devices and its implications could have a substantial impact on farming systems in the developing world, leading not only to sustainable food production and income, but also increased data privacy and autonomy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge