MD Muhaimin Rahman
Quantized deep learning models on low-power edge devices for robotic systems
Nov 30, 2019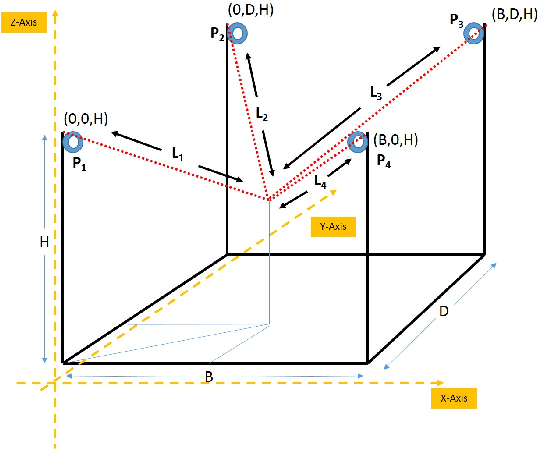
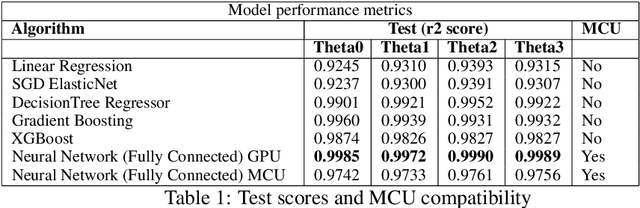
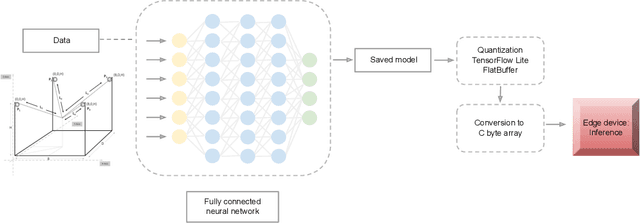
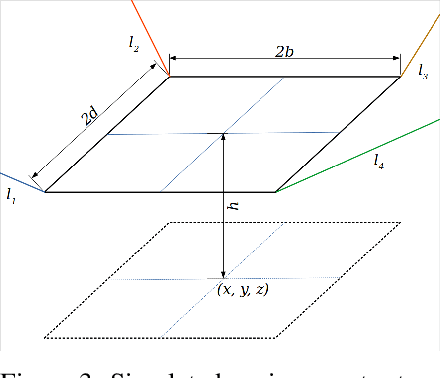
Abstract:In this work, we present a quantized deep neural network deployed on a low-power edge device, inferring learned motor-movements of a suspended robot in a defined space. This serves as the fundamental building block for the original setup, a robotic system for farms or greenhouses aimed at a wide range of agricultural tasks. Deep learning on edge devices and its implications could have a substantial impact on farming systems in the developing world, leading not only to sustainable food production and income, but also increased data privacy and autonomy.
Implementation of Q Learning and Deep Q Network For Controlling a Self Balancing Robot Model
Jul 22, 2018



Abstract:In this paper, the implementation of two Reinforcement learnings namely, Q Learning and Deep Q Network(DQN) on a Self Balancing Robot Gazebo model has been discussed. The goal of the experiments is to make the robot model learn the best actions for staying balanced in an environment. The more time it can stay within a specified limit , the more reward it accumulates and hence more balanced it is. Different experiments with different learning parameters on Q Learning and DQN are conducted and the plots of the experiments are shown.
Comparison of Different Control Theories on a Two Wheeled Self Balancing Robot
Jul 22, 2018



Abstract:. This paper is aimed to discuss and compare three of the most famous Control Theories on a Two wheeled Self Balancing Robot Simulation using Robot Operating System (ROS) and Gazebo. Two Wheeled Self Balancing Robots are one of the most fascinating applications of Inverted Pendulum System. In this paper, PID, LQR and Fuzzy logic controllers are discussed . Also,0 the modeling and algorithms of the robot simulation is discussed. The primary objectives of this paper is to discuss about the building of a robot model in ROS and Gazebo , experimenting different control theories on them, documenting the whole process with the analysis of the robot and comparison of different control theories on the system.
* International Conference on Mechanical Engineering,2017, BUET, Dhaka
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge