Yuta Kanzawa
Multimodal Point-of-Interest Recommendation
Oct 07, 2024



Abstract:Large Language Models are applied to recommendation tasks such as items to buy and news articles to read. Point of Interest is quite a new area to sequential recommendation based on language representations of multimodal datasets. As a first step to prove our concepts, we focused on restaurant recommendation based on each user's past visit history. When choosing a next restaurant to visit, a user would consider genre and location of the venue and, if available, pictures of dishes served there. We created a pseudo restaurant check-in history dataset from the Foursquare dataset and the FoodX-251 dataset by converting pictures into text descriptions with a multimodal model called LLaVA, and used a language-based sequential recommendation framework named Recformer proposed in 2023. A model trained on this semi-multimodal dataset has outperformed another model trained on the same dataset without picture descriptions. This suggests that this semi-multimodal model reflects actual human behaviours and that our path to a multimodal recommendation model is in the right direction.
Global Data Science Project for COVID-19 Summary Report
Jun 10, 2020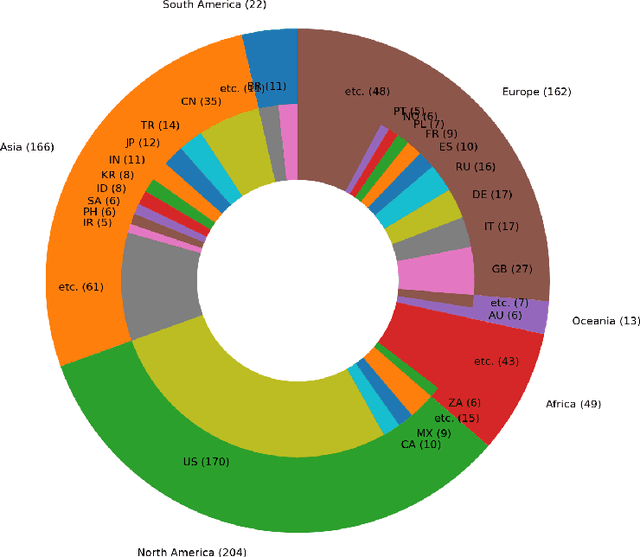
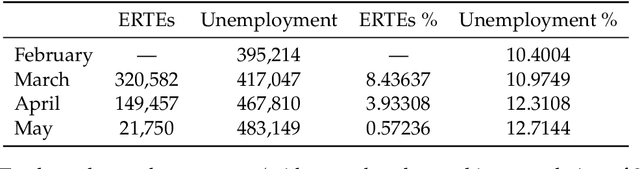
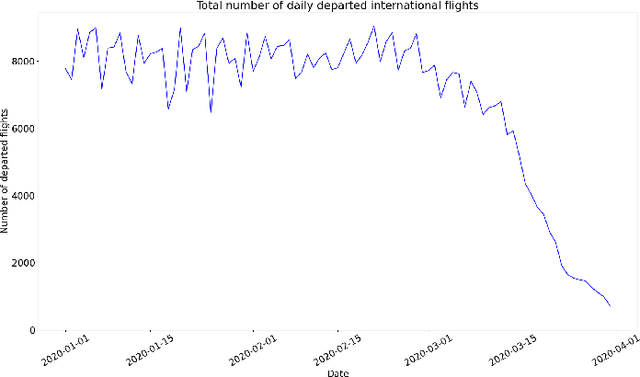
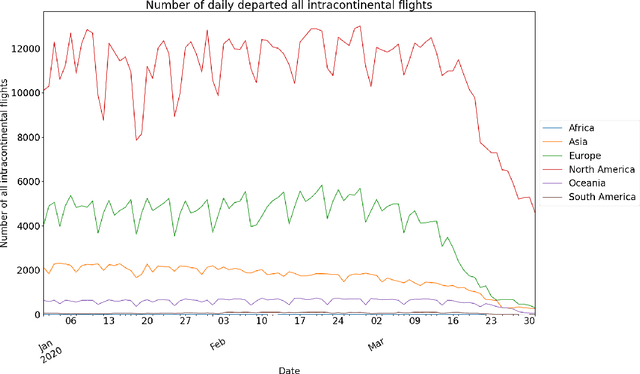
Abstract:This paper aims at providing the summary of the Global Data Science Project (GDSC) for COVID-19. as on May 31 2020. COVID-19 has largely impacted on our societies through both direct and indirect effects transmitted by the policy measures to counter the spread of viruses. We quantitatively analysed the multifaceted impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic on our societies including people's mobility, health, and social behaviour changes. People's mobility has changed significantly due to the implementation of travel restriction and quarantine measurements. Indeed, the physical distance has widened at international (cross-border), national and regional level. At international level, due to the travel restrictions, the number of international flights has plunged overall at around 88 percent during March. In particular, the number of flights connecting Europe dropped drastically in mid of March after the United States announced travel restrictions to Europe and the EU and participating countries agreed to close borders, at 84 percent decline compared to March 10th. Similarly, we examined the impacts of quarantine measures in the major city: Tokyo (Japan), New York City (the United States), and Barcelona (Spain). Within all three cities, we found the significant decline in traffic volume. We also identified the increased concern for mental health through the analysis of posts on social networking services such as Twitter and Instagram. Notably, in the beginning of April 2020, the number of post with #depression on Instagram doubled, which might reflect the rise in mental health awareness among Instagram users. Besides, we identified the changes in a wide range of people's social behaviors, as well as economic impacts through the analysis of Instagram data and primary survey data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge