Yusuke Mori
The Lost Melody: Empirical Observations on Text-to-Video Generation From A Storytelling Perspective
May 13, 2024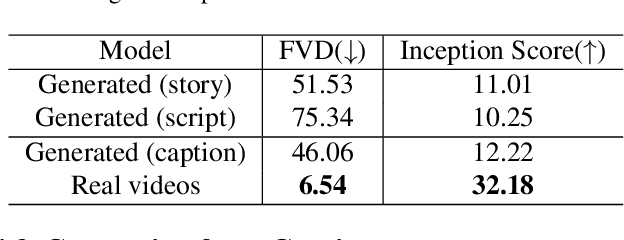

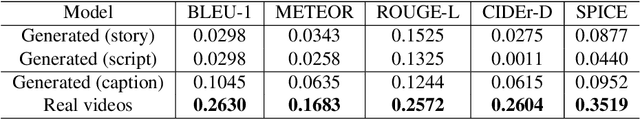

Abstract:Text-to-video generation task has witnessed a notable progress, with the generated outcomes reflecting the text prompts with high fidelity and impressive visual qualities. However, current text-to-video generation models are invariably focused on conveying the visual elements of a single scene, and have so far been indifferent to another important potential of the medium, namely a storytelling. In this paper, we examine text-to-video generation from a storytelling perspective, which has been hardly investigated, and make empirical remarks that spotlight the limitations of current text-to-video generation scheme. We also propose an evaluation framework for storytelling aspects of videos, and discuss the potential future directions.
Computational Storytelling and Emotions: A Survey
May 23, 2022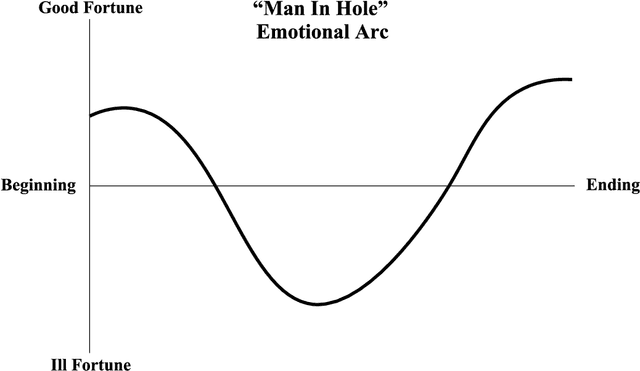
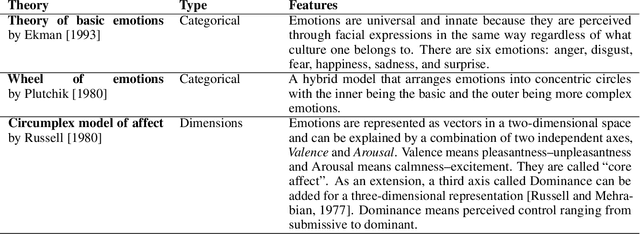
Abstract:Storytelling has always been vital for human nature. From ancient times, humans have used stories for several objectives including entertainment, advertisement, and education. Various analyses have been conducted by researchers and creators to determine the way of producing good stories. The deep relationship between stories and emotions is a prime example. With the advancement in deep learning technology, computers are expected to understand and generate stories. This survey paper is intended to summarize and further contribute to the development of research being conducted on the relationship between stories and emotions. We believe creativity research is not to replace humans with computers, but to find a way of collaboration between humans and computers to enhance the creativity. With the intention of creating a new intersection between computational storytelling research and human creative writing, we introduced creative techniques used by professional storytellers.
COMPASS: a Creative Support System that Alerts Novelists to the Unnoticed Missing Contents
Feb 26, 2022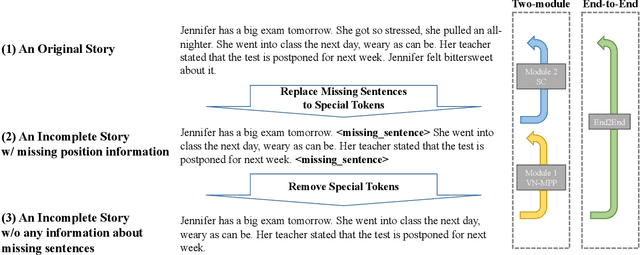
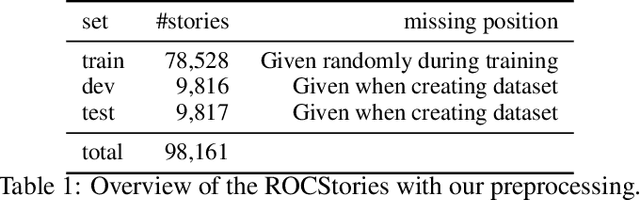
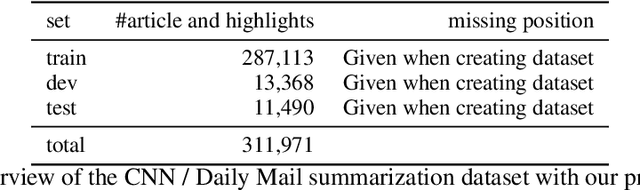
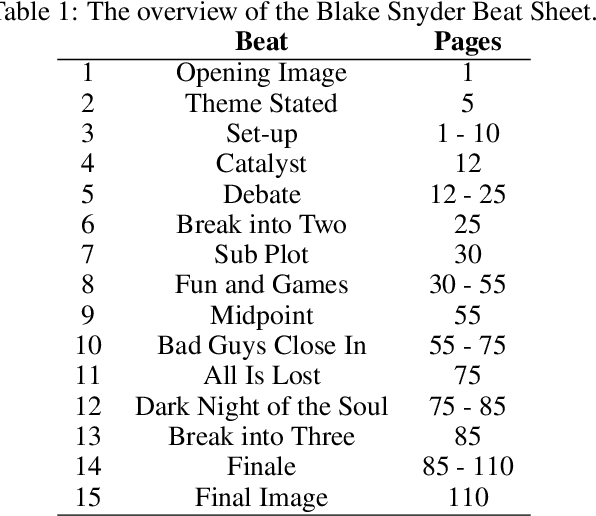
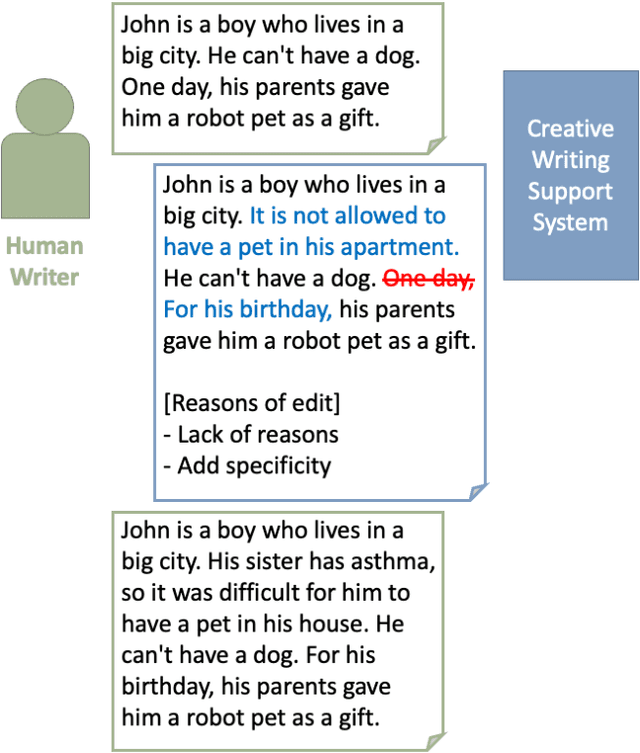
Abstract:When humans write, they may unintentionally omit some information. Complementing the omitted information using a computer is helpful in providing writing support. Recently, in the field of story understanding and generation, story completion (SC) was proposed to generate the missing parts of an incomplete story. Although its applicability is limited because it requires that the user have prior knowledge of the missing part of a story, missing position prediction (MPP) can be used to compensate for this problem. MPP aims to predict the position of the missing part, but the prerequisite knowledge that "one sentence is missing" is still required. In this study, we propose Variable Number MPP (VN-MPP), a new MPP task that removes this restriction; that is, the task to predict multiple missing sentences or to judge whether there are no missing sentences in the first place. We also propose two methods for this new MPP task. Furthermore, based on the novel task and methods, we developed a creative writing support system, COMPASS. The results of a user experiment involving professional creators who write texts in Japanese confirm the efficacy and utility of the developed system.
ViNTER: Image Narrative Generation with Emotion-Arc-Aware Transformer
Feb 15, 2022
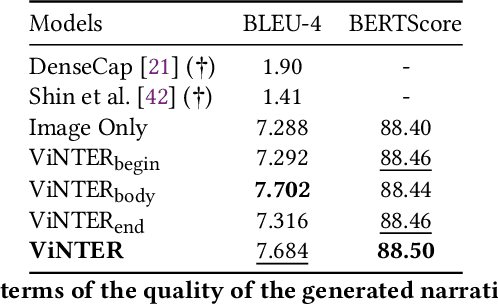
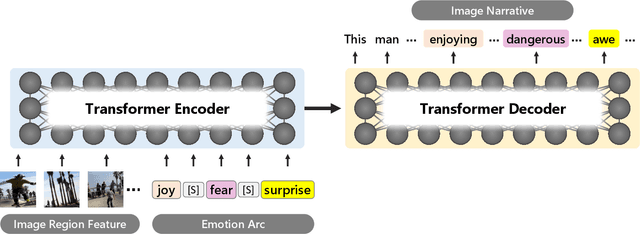
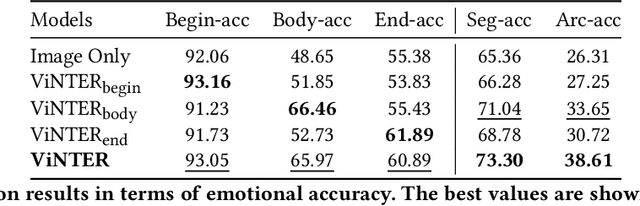
Abstract:Image narrative generation describes the creation of stories regarding the content of image data from a subjective viewpoint. Given the importance of the subjective feelings of writers, characters, and readers in storytelling, image narrative generation methods must consider human emotion, which is their major difference from descriptive caption generation tasks. The development of automated methods to generate story-like text associated with images may be considered to be of considerable social significance, because stories serve essential functions both as entertainment and also for many practical purposes such as education and advertising. In this study, we propose a model called ViNTER (Visual Narrative Transformer with Emotion arc Representation) to generate image narratives that focus on time series representing varying emotions as "emotion arcs," to take advantage of recent advances in multimodal Transformer-based pre-trained models. We present experimental results of both manual and automatic evaluations, which demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed emotion-aware approach to image narrative generation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge