Kunitake Kaneko
Large Language Models Lack Understanding of Character Composition of Words
May 18, 2024Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable performances on a wide range of natural language tasks. Yet, LLMs' successes have been largely restricted to tasks concerning words, sentences, or documents, and it remains questionable how much they understand the minimal units of text, namely characters. In this paper, we examine contemporary LLMs regarding their ability to understand character composition of words, and show that most of them fail to reliably carry out even the simple tasks that can be handled by humans with perfection. We analyze their behaviors with comparison to token level performances, and discuss the potential directions for future research.
The Lost Melody: Empirical Observations on Text-to-Video Generation From A Storytelling Perspective
May 13, 2024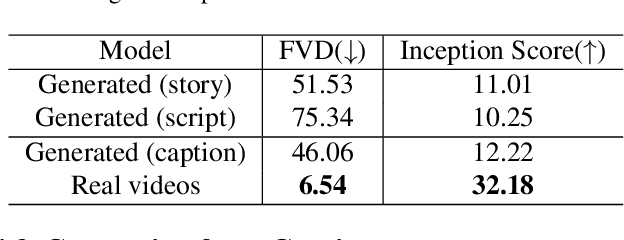

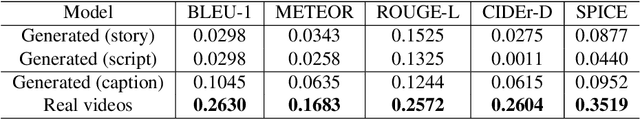

Abstract:Text-to-video generation task has witnessed a notable progress, with the generated outcomes reflecting the text prompts with high fidelity and impressive visual qualities. However, current text-to-video generation models are invariably focused on conveying the visual elements of a single scene, and have so far been indifferent to another important potential of the medium, namely a storytelling. In this paper, we examine text-to-video generation from a storytelling perspective, which has been hardly investigated, and make empirical remarks that spotlight the limitations of current text-to-video generation scheme. We also propose an evaluation framework for storytelling aspects of videos, and discuss the potential future directions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge