Yushi Cheng
Soft Weighted Machine Unlearning
May 24, 2025Abstract:Machine unlearning, as a post-hoc processing technique, has gained widespread adoption in addressing challenges like bias mitigation and robustness enhancement, colloquially, machine unlearning for fairness and robustness. However, existing non-privacy unlearning-based solutions persist in using binary data removal framework designed for privacy-driven motivation, leading to significant information loss, a phenomenon known as over-unlearning. While over-unlearning has been largely described in many studies as primarily causing utility degradation, we investigate its fundamental causes and provide deeper insights in this work through counterfactual leave-one-out analysis. In this paper, we introduce a weighted influence function that assigns tailored weights to each sample by solving a convex quadratic programming problem analytically. Building on this, we propose a soft-weighted framework enabling fine-grained model adjustments to address the over-unlearning challenge. We demonstrate that the proposed soft-weighted scheme is versatile and can be seamlessly integrated into most existing unlearning algorithms. Extensive experiments show that in fairness- and robustness-driven tasks, the soft-weighted scheme significantly outperforms hard-weighted schemes in fairness/robustness metrics and alleviates the decline in utility metric, thereby enhancing machine unlearning algorithm as an effective correction solution.
CamPro: Camera-based Anti-Facial Recognition
Dec 30, 2023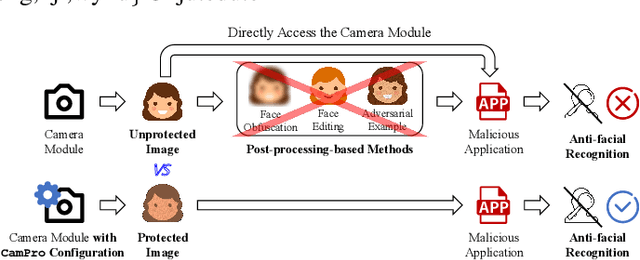

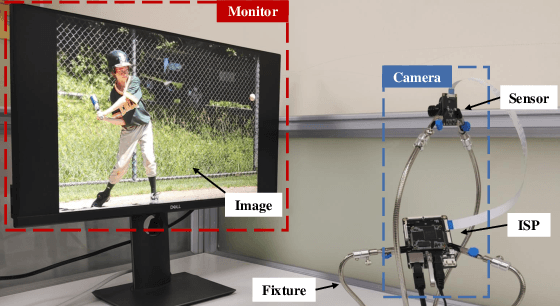

Abstract:The proliferation of images captured from millions of cameras and the advancement of facial recognition (FR) technology have made the abuse of FR a severe privacy threat. Existing works typically rely on obfuscation, synthesis, or adversarial examples to modify faces in images to achieve anti-facial recognition (AFR). However, the unmodified images captured by camera modules that contain sensitive personally identifiable information (PII) could still be leaked. In this paper, we propose a novel approach, CamPro, to capture inborn AFR images. CamPro enables well-packed commodity camera modules to produce images that contain little PII and yet still contain enough information to support other non-sensitive vision applications, such as person detection. Specifically, CamPro tunes the configuration setup inside the camera image signal processor (ISP), i.e., color correction matrix and gamma correction, to achieve AFR, and designs an image enhancer to keep the image quality for possible human viewers. We implemented and validated CamPro on a proof-of-concept camera, and our experiments demonstrate its effectiveness on ten state-of-the-art black-box FR models. The results show that CamPro images can significantly reduce face identification accuracy to 0.3\% while having little impact on the targeted non-sensitive vision application. Furthermore, we find that CamPro is resilient to adaptive attackers who have re-trained their FR models using images generated by CamPro, even with full knowledge of privacy-preserving ISP parameters.
TPatch: A Triggered Physical Adversarial Patch
Dec 30, 2023



Abstract:Autonomous vehicles increasingly utilize the vision-based perception module to acquire information about driving environments and detect obstacles. Correct detection and classification are important to ensure safe driving decisions. Existing works have demonstrated the feasibility of fooling the perception models such as object detectors and image classifiers with printed adversarial patches. However, most of them are indiscriminately offensive to every passing autonomous vehicle. In this paper, we propose TPatch, a physical adversarial patch triggered by acoustic signals. Unlike other adversarial patches, TPatch remains benign under normal circumstances but can be triggered to launch a hiding, creating or altering attack by a designed distortion introduced by signal injection attacks towards cameras. To avoid the suspicion of human drivers and make the attack practical and robust in the real world, we propose a content-based camouflage method and an attack robustness enhancement method to strengthen it. Evaluations with three object detectors, YOLO V3/V5 and Faster R-CNN, and eight image classifiers demonstrate the effectiveness of TPatch in both the simulation and the real world. We also discuss possible defenses at the sensor, algorithm, and system levels.
Enrollment-stage Backdoor Attacks on Speaker Recognition Systems via Adversarial Ultrasound
Jun 28, 2023Abstract:Automatic Speaker Recognition Systems (SRSs) have been widely used in voice applications for personal identification and access control. A typical SRS consists of three stages, i.e., training, enrollment, and recognition. Previous work has revealed that SRSs can be bypassed by backdoor attacks at the training stage or by adversarial example attacks at the recognition stage. In this paper, we propose TUNER, a new type of backdoor attack against the enrollment stage of SRS via adversarial ultrasound modulation, which is inaudible, synchronization-free, content-independent, and black-box. Our key idea is to first inject the backdoor into the SRS with modulated ultrasound when a legitimate user initiates the enrollment, and afterward, the polluted SRS will grant access to both the legitimate user and the adversary with high confidence. Our attack faces a major challenge of unpredictable user articulation at the enrollment stage. To overcome this challenge, we generate the ultrasonic backdoor by augmenting the optimization process with random speech content, vocalizing time, and volume of the user. Furthermore, to achieve real-world robustness, we improve the ultrasonic signal over traditional methods using sparse frequency points, pre-compensation, and single-sideband (SSB) modulation. We extensively evaluate TUNER on two common datasets and seven representative SRS models. Results show that our attack can successfully bypass speaker recognition systems while remaining robust to various speakers, speech content, et
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge