Yuqiao Xian
Joint Selection for Large-Scale Pre-Training Data via Policy Gradient-based Mask Learning
Dec 30, 2025Abstract:A fine-grained data recipe is crucial for pre-training large language models, as it can significantly enhance training efficiency and model performance. One important ingredient in the recipe is to select samples based on scores produced by defined rules, LLM judgment, or statistical information in embeddings, which can be roughly categorized into quality and diversity metrics. Due to the high computational cost when applied to trillion-scale token pre-training datasets such as FineWeb and DCLM, these two or more types of metrics are rarely considered jointly in a single selection process. However, in our empirical study, selecting samples based on quality metrics exhibit severe diminishing returns during long-term pre-training, while selecting on diversity metrics removes too many valuable high-quality samples, both of which limit pre-trained LLMs' capabilities. Therefore, we introduce DATAMASK, a novel and efficient joint learning framework designed for large-scale pre-training data selection that can simultaneously optimize multiple types of metrics in a unified process, with this study focusing specifically on quality and diversity metrics. DATAMASK approaches the selection process as a mask learning problem, involving iterative sampling of data masks, computation of policy gradients based on predefined objectives with sampled masks, and updating of mask sampling logits. Through policy gradient-based optimization and various acceleration enhancements, it significantly reduces selection time by 98.9% compared to greedy algorithm, enabling our study to explore joint learning within trillion-scale tokens. With DATAMASK, we select a subset of about 10% from the 15 trillion-token FineWeb dataset, termed FineWeb-Mask. Evaluated across 12 diverse tasks, we achieves significant improvements of 3.2% on a 1.5B dense model and 1.9% on a 7B MoE model.
Virtual Width Networks
Nov 17, 2025



Abstract:We introduce Virtual Width Networks (VWN), a framework that delivers the benefits of wider representations without incurring the quadratic cost of increasing the hidden size. VWN decouples representational width from backbone width, expanding the embedding space while keeping backbone compute nearly constant. In our large-scale experiment, an 8-times expansion accelerates optimization by over 2 times for next-token and 3 times for next-2-token prediction. The advantage amplifies over training as both the loss gap grows and the convergence-speedup ratio increases, showing that VWN is not only token-efficient but also increasingly effective with scale. Moreover, we identify an approximately log-linear scaling relation between virtual width and loss reduction, offering an initial empirical basis and motivation for exploring virtual-width scaling as a new dimension of large-model efficiency.
Discriminator-Free Generative Adversarial Attack
Jul 20, 2021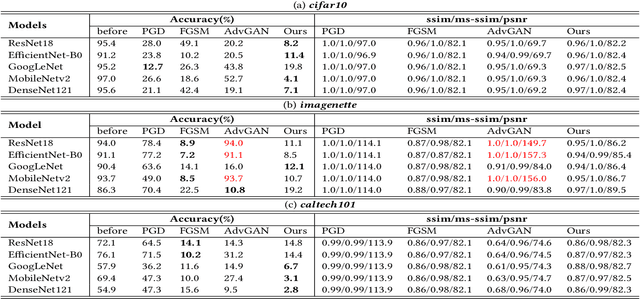
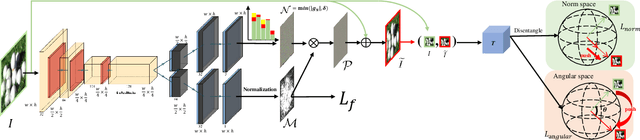
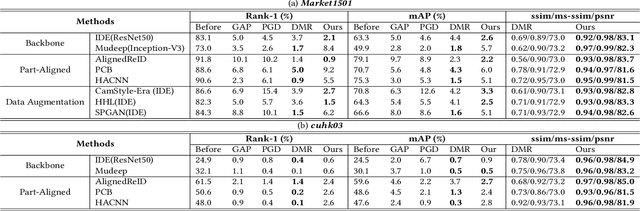
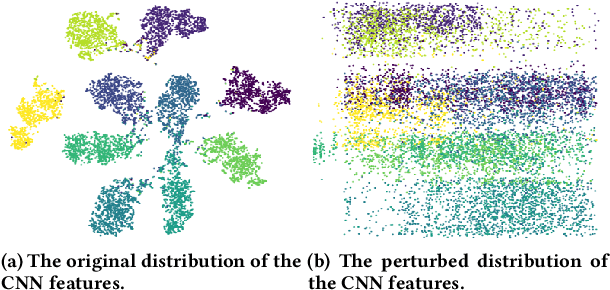
Abstract:The Deep Neural Networks are vulnerable toadversarial exam-ples(Figure 1), making the DNNs-based systems collapsed byadding the inconspicuous perturbations to the images. Most of the existing works for adversarial attack are gradient-based and suf-fer from the latency efficiencies and the load on GPU memory. Thegenerative-based adversarial attacks can get rid of this limitation,and some relative works propose the approaches based on GAN.However, suffering from the difficulty of the convergence of train-ing a GAN, the adversarial examples have either bad attack abilityor bad visual quality. In this work, we find that the discriminatorcould be not necessary for generative-based adversarial attack, andpropose theSymmetric Saliency-based Auto-Encoder (SSAE)to generate the perturbations, which is composed of the saliencymap module and the angle-norm disentanglement of the featuresmodule. The advantage of our proposed method lies in that it is notdepending on discriminator, and uses the generative saliency map to pay more attention to label-relevant regions. The extensive exper-iments among the various tasks, datasets, and models demonstratethat the adversarial examples generated by SSAE not only make thewidely-used models collapse, but also achieves good visual quality.The code is available at https://github.com/BravoLu/SSAE.
Solution for Large-scale Long-tailed Recognition with Noisy Labels
Jun 20, 2021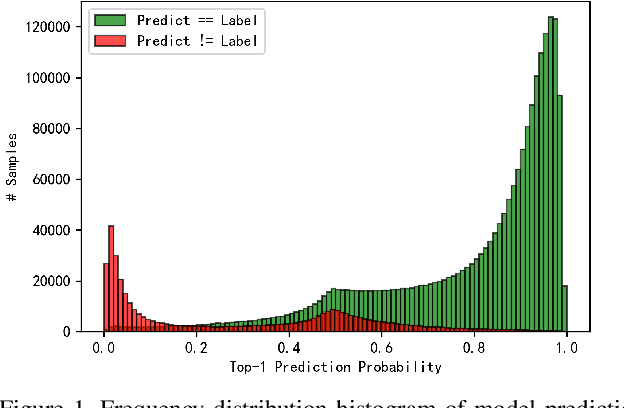
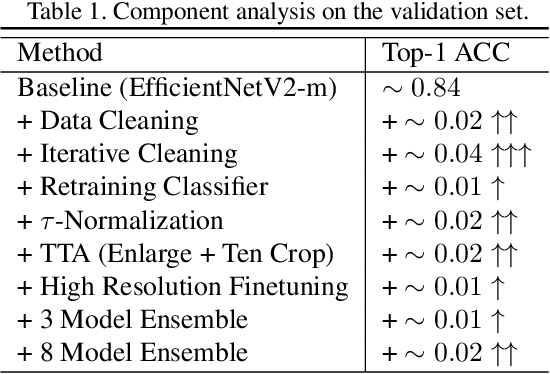
Abstract:This is a technical report for CVPR 2021 AliProducts Challenge. AliProducts Challenge is a competition proposed for studying the large-scale and fine-grained commodity image recognition problem encountered by worldleading ecommerce companies. The large-scale product recognition simultaneously meets the challenge of noisy annotations, imbalanced (long-tailed) data distribution and fine-grained classification. In our solution, we adopt stateof-the-art model architectures of both CNNs and Transformer, including ResNeSt, EfficientNetV2, and DeiT. We found that iterative data cleaning, classifier weight normalization, high-resolution finetuning, and test time augmentation are key components to improve the performance of training with the noisy and imbalanced dataset. Finally, we obtain 6.4365% mean class error rate in the leaderboard with our ensemble model.
* 3 pages
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge