Yunxiao Chen
Pairwise Comparisons without Stochastic Transitivity: Model, Theory and Applications
Jan 13, 2025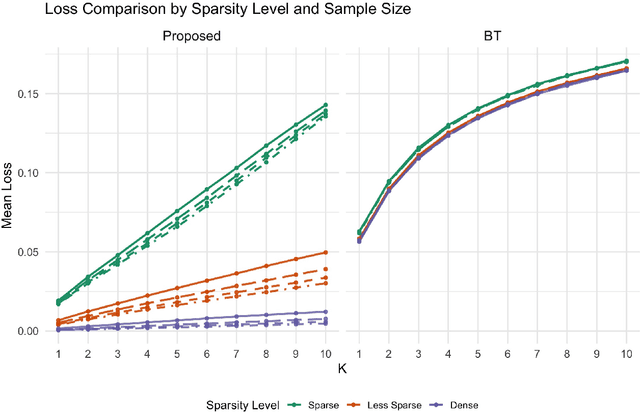
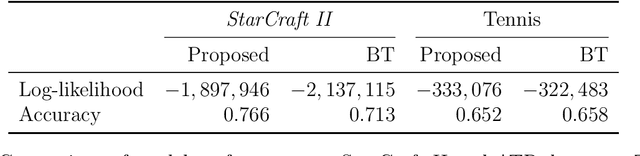
Abstract:Most statistical models for pairwise comparisons, including the Bradley-Terry (BT) and Thurstone models and many extensions, make a relatively strong assumption of stochastic transitivity. This assumption imposes the existence of an unobserved global ranking among all the players/teams/items and monotone constraints on the comparison probabilities implied by the global ranking. However, the stochastic transitivity assumption does not hold in many real-world scenarios of pairwise comparisons, especially games involving multiple skills or strategies. As a result, models relying on this assumption can have suboptimal predictive performance. In this paper, we propose a general family of statistical models for pairwise comparison data without a stochastic transitivity assumption, substantially extending the BT and Thurstone models. In this model, the pairwise probabilities are determined by a (approximately) low-dimensional skew-symmetric matrix. Likelihood-based estimation methods and computational algorithms are developed, which allow for sparse data with only a small proportion of observed pairs. Theoretical analysis shows that the proposed estimator achieves minimax-rate optimality, which adapts effectively to the sparsity level of the data. The spectral theory for skew-symmetric matrices plays a crucial role in the implementation and theoretical analysis. The proposed method's superiority against the BT model, along with its broad applicability across diverse scenarios, is further supported by simulations and real data analysis.
HouYi: An open-source large language model specially designed for renewable energy and carbon neutrality field
Jul 31, 2023Abstract:Renewable energy is important for achieving carbon neutrality goal. With the great success of Large Language Models (LLMs) like ChatGPT in automatic content generation, LLMs are playing an increasingly important role. However, there has not been a specially designed LLM for renewable energy. Meanwhile, there has not been any dataset of renewable energy for training LLMs. Therefore, this paper published the first open-source Renewable Energy Academic Paper (REAP) dataset for non-commercial LLM research of renewable energy. REAP dataset is collected through searching the title and abstract of 1,168,970 academic literatures from Web of Science. Based on REAP dataset, HouYi model, the first LLM for renewable energy, is developed through finetuning general LLMs. HouYi demonstrated powerful academic paper paragraph generation ability in renewable energy field. Experiments show that its ability to generate academic papers on renewable energy is comparable to ChatGPT, slightly outperforms Claude, ERNIE Bot and SparkDesk, and significantly outperforms open-source LLaMA-13B model.
A Generalized Latent Factor Model Approach to Mixed-data Matrix Completion with Entrywise Consistency
Nov 17, 2022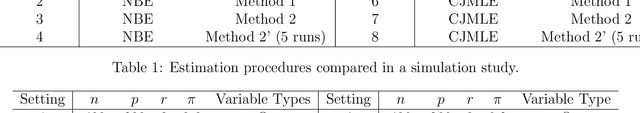
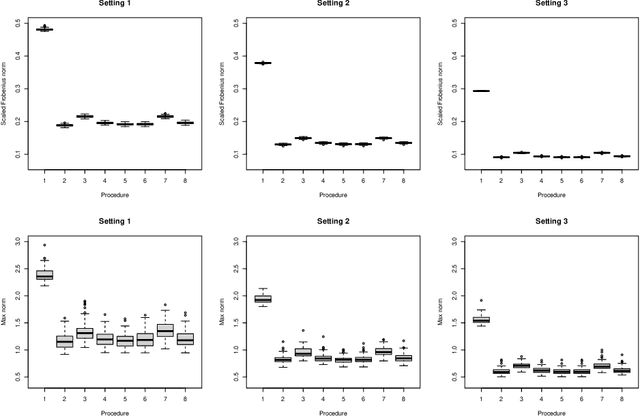
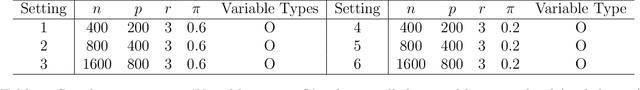
Abstract:Matrix completion is a class of machine learning methods that concerns the prediction of missing entries in a partially observed matrix. This paper studies matrix completion for mixed data, i.e., data involving mixed types of variables (e.g., continuous, binary, ordinal). We formulate it as a low-rank matrix estimation problem under a general family of non-linear factor models and then propose entrywise consistent estimators for estimating the low-rank matrix. Tight probabilistic error bounds are derived for the proposed estimators. The proposed methods are evaluated by simulation studies and real-data applications for collaborative filtering and large-scale educational assessment.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge