Yuntao Zhu
Standardized Evaluation of Automatic Methods for Perivascular Spaces Segmentation in MRI -- MICCAI 2024 Challenge Results
Dec 20, 2025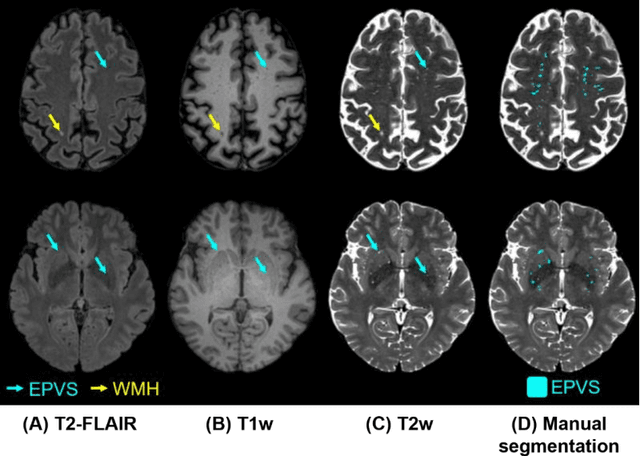
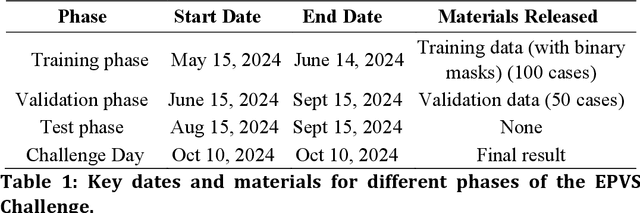
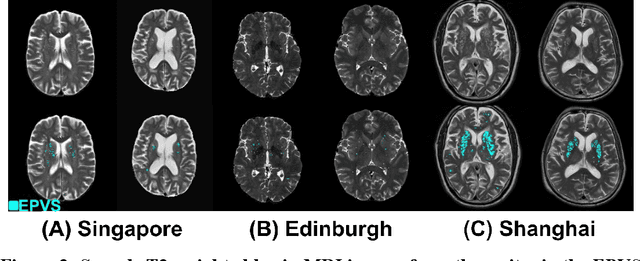
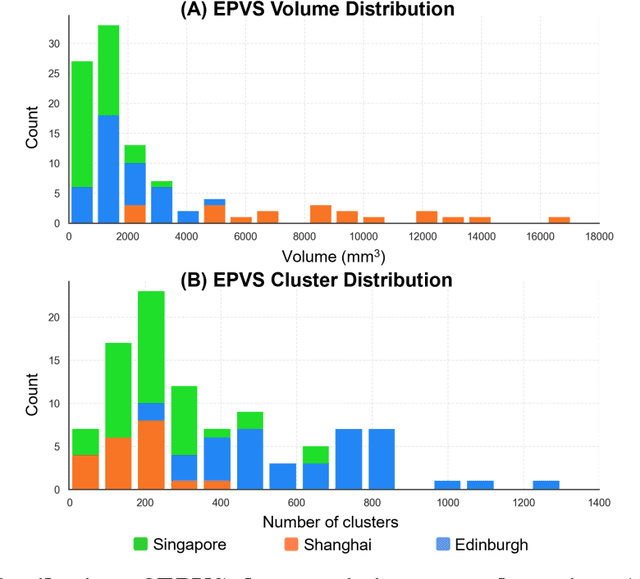
Abstract:Perivascular spaces (PVS), when abnormally enlarged and visible in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) structural sequences, are important imaging markers of cerebral small vessel disease and potential indicators of neurodegenerative conditions. Despite their clinical significance, automatic enlarged PVS (EPVS) segmentation remains challenging due to their small size, variable morphology, similarity with other pathological features, and limited annotated datasets. This paper presents the EPVS Challenge organized at MICCAI 2024, which aims to advance the development of automated algorithms for EPVS segmentation across multi-site data. We provided a diverse dataset comprising 100 training, 50 validation, and 50 testing scans collected from multiple international sites (UK, Singapore, and China) with varying MRI protocols and demographics. All annotations followed the STRIVE protocol to ensure standardized ground truth and covered the full brain parenchyma. Seven teams completed the full challenge, implementing various deep learning approaches primarily based on U-Net architectures with innovations in multi-modal processing, ensemble strategies, and transformer-based components. Performance was evaluated using dice similarity coefficient, absolute volume difference, recall, and precision metrics. The winning method employed MedNeXt architecture with a dual 2D/3D strategy for handling varying slice thicknesses. The top solutions showed relatively good performance on test data from seen datasets, but significant degradation of performance was observed on the previously unseen Shanghai cohort, highlighting cross-site generalization challenges due to domain shift. This challenge establishes an important benchmark for EPVS segmentation methods and underscores the need for the continued development of robust algorithms that can generalize in diverse clinical settings.
The optimal connection model for blood vessels segmentation and the MEA-Net
Jun 02, 2023Abstract:Vascular diseases have long been regarded as a significant health concern. Accurately detecting the location, shape, and afflicted regions of blood vessels from a diverse range of medical images has proven to be a major challenge. Obtaining blood vessels that retain their correct topological structures is currently a crucial research issue. Numerous efforts have sought to reinforce neural networks' learning of vascular geometric features, including measures to ensure the correct topological structure of the segmentation result's vessel centerline. Typically, these methods extract topological features from the network's segmentation result and then apply regular constraints to reinforce the accuracy of critical components and the overall topological structure. However, as blood vessels are three-dimensional structures, it is essential to achieve complete local vessel segmentation, which necessitates enhancing the segmentation of vessel boundaries. Furthermore, current methods are limited to handling 2D blood vessel fragmentation cases. Our proposed boundary attention module directly extracts boundary voxels from the network's segmentation result. Additionally, we have established an optimal connection model based on minimal surfaces to determine the connection order between blood vessels. Our method achieves state-of-the-art performance in 3D multi-class vascular segmentation tasks, as evidenced by the high values of Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC) and Normalized Surface Dice (NSD) metrics. Furthermore, our approach improves the Betti error, LR error, and BR error indicators of vessel richness and structural integrity by more than 10% compared to other methods, and effectively addresses vessel fragmentation and yields blood vessels with a more precise topological structure.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge