Yunlong Zheng
Temporal Residual Guided Diffusion Framework for Event-Driven Video Reconstruction
Jul 15, 2024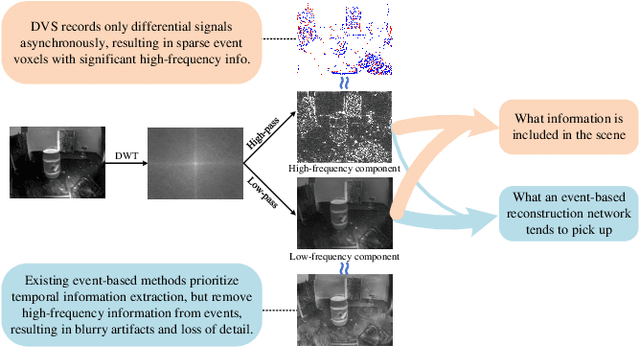
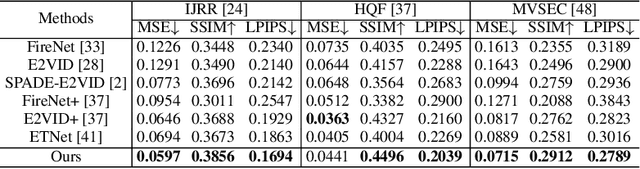
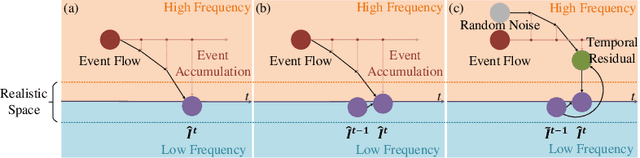
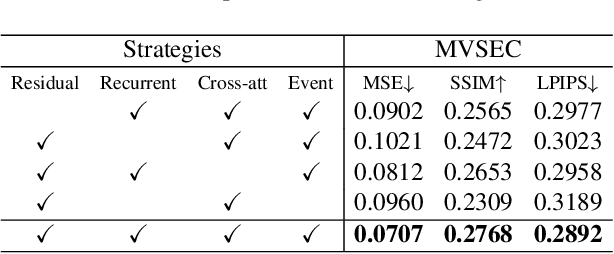
Abstract:Event-based video reconstruction has garnered increasing attention due to its advantages, such as high dynamic range and rapid motion capture capabilities. However, current methods often prioritize the extraction of temporal information from continuous event flow, leading to an overemphasis on low-frequency texture features in the scene, resulting in over-smoothing and blurry artifacts. Addressing this challenge necessitates the integration of conditional information, encompassing temporal features, low-frequency texture, and high-frequency events, to guide the Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Model (DDPM) in producing accurate and natural outputs. To tackle this issue, we introduce a novel approach, the Temporal Residual Guided Diffusion Framework, which effectively leverages both temporal and frequency-based event priors. Our framework incorporates three key conditioning modules: a pre-trained low-frequency intensity estimation module, a temporal recurrent encoder module, and an attention-based high-frequency prior enhancement module. In order to capture temporal scene variations from the events at the current moment, we employ a temporal-domain residual image as the target for the diffusion model. Through the combination of these three conditioning paths and the temporal residual framework, our framework excels in reconstructing high-quality videos from event flow, mitigating issues such as artifacts and over-smoothing commonly observed in previous approaches. Extensive experiments conducted on multiple benchmark datasets validate the superior performance of our framework compared to prior event-based reconstruction methods.
Recurrent Spike-based Image Restoration under General Illumination
Aug 06, 2023Abstract:Spike camera is a new type of bio-inspired vision sensor that records light intensity in the form of a spike array with high temporal resolution (20,000 Hz). This new paradigm of vision sensor offers significant advantages for many vision tasks such as high speed image reconstruction. However, existing spike-based approaches typically assume that the scenes are with sufficient light intensity, which is usually unavailable in many real-world scenarios such as rainy days or dusk scenes. To unlock more spike-based application scenarios, we propose a Recurrent Spike-based Image Restoration (RSIR) network, which is the first work towards restoring clear images from spike arrays under general illumination. Specifically, to accurately describe the noise distribution under different illuminations, we build a physical-based spike noise model according to the sampling process of the spike camera. Based on the noise model, we design our RSIR network which consists of an adaptive spike transformation module, a recurrent temporal feature fusion module, and a frequency-based spike denoising module. Our RSIR can process the spike array in a recursive manner to ensure that the spike temporal information is well utilized. In the training process, we generate the simulated spike data based on our noise model to train our network. Extensive experiments on real-world datasets with different illuminations demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed network. The code and dataset are released at https://github.com/BIT-Vision/RSIR.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge