Yuli Huang
SEA-LION: Southeast Asian Languages in One Network
Apr 08, 2025Abstract:Recently, Large Language Models (LLMs) have dominated much of the artificial intelligence scene with their ability to process and generate natural languages. However, the majority of LLM research and development remains English-centric, leaving low-resource languages such as those in the Southeast Asian (SEA) region under-represented. To address this representation gap, we introduce Llama-SEA-LION-v3-8B-IT and Gemma-SEA-LION-v3-9B-IT, two cutting-edge multilingual LLMs designed for SEA languages. The SEA-LION family of LLMs supports 11 SEA languages, namely English, Chinese, Indonesian, Vietnamese, Malay, Thai, Burmese, Lao, Filipino, Tamil, and Khmer. Our work leverages large-scale multilingual continued pre-training with a comprehensive post-training regime involving multiple stages of instruction fine-tuning, alignment, and model merging. Evaluation results on multilingual benchmarks indicate that our models achieve state-of-the-art performance across LLMs supporting SEA languages. We open-source the models to benefit the wider SEA community.
Iterative self-transfer learning: A general methodology for response time-history prediction based on small dataset
Jun 14, 2023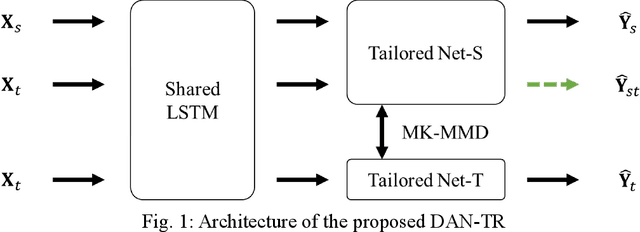
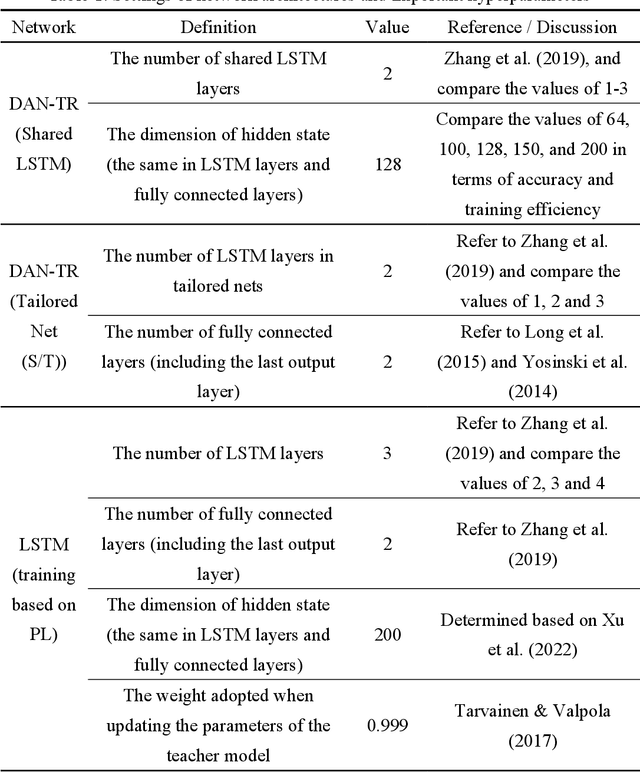
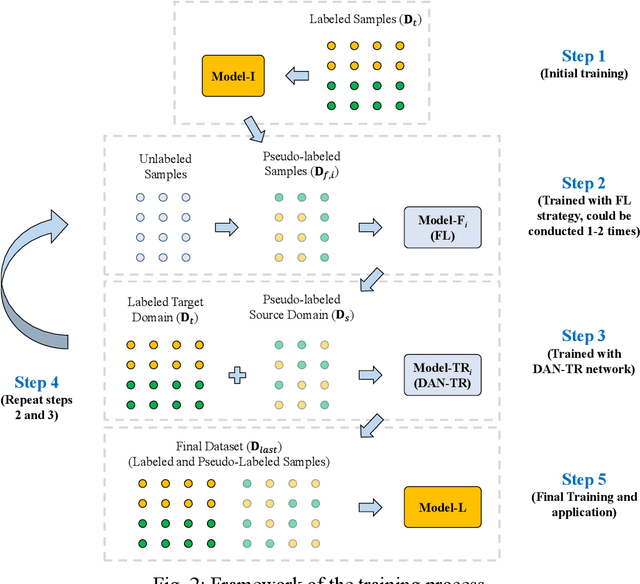
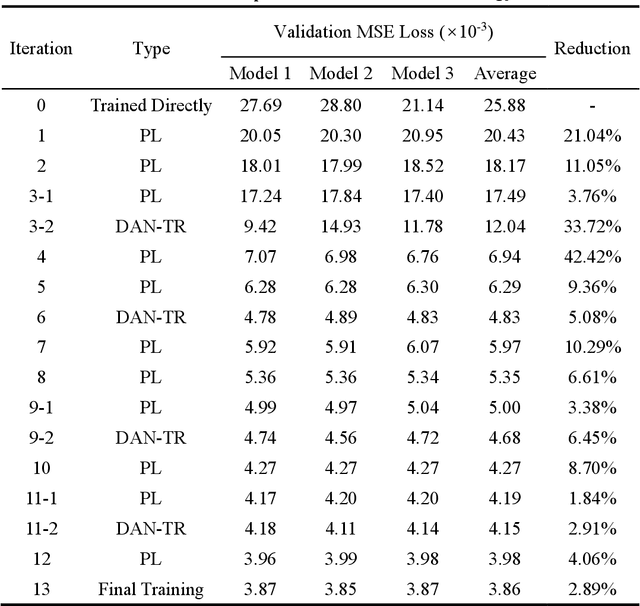
Abstract:There are numerous advantages of deep neural network surrogate modeling for response time-history prediction. However, due to the high cost of refined numerical simulations and actual experiments, the lack of data has become an unavoidable bottleneck in practical applications. An iterative self-transfer learningmethod for training neural networks based on small datasets is proposed in this study. A new mapping-based transfer learning network, named as deep adaptation network with three branches for regression (DAN-TR), is proposed. A general iterative network training strategy is developed by coupling DAN-TR and the pseudo-label strategy, and the establishment of corresponding datasets is also discussed. Finally, a complex component is selected as a case study. The results show that the proposed method can improve the model performance by near an order of magnitude on small datasets without the need of external labeled samples,well behaved pre-trainedmodels, additional artificial labeling, and complex physical/mathematical analysis.
* 14 pages, 8 figures; Published on Journal of Computational Design and Engineering, 9(5), 2089-2102
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge