Yujiang Pu
SHINE: Saliency-aware HIerarchical NEgative Ranking for Compositional Temporal Grounding
Jul 06, 2024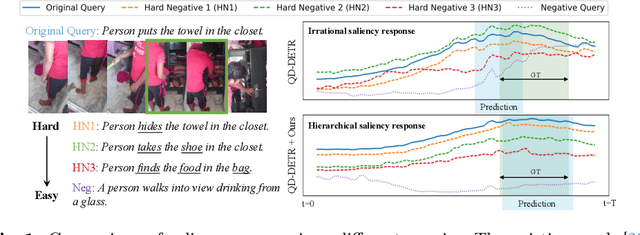
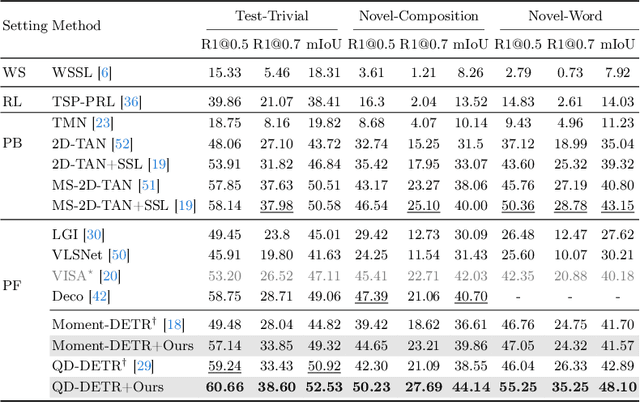
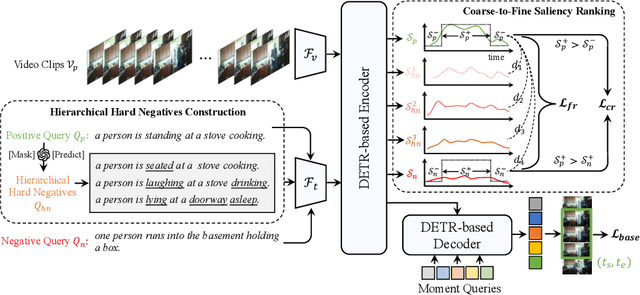
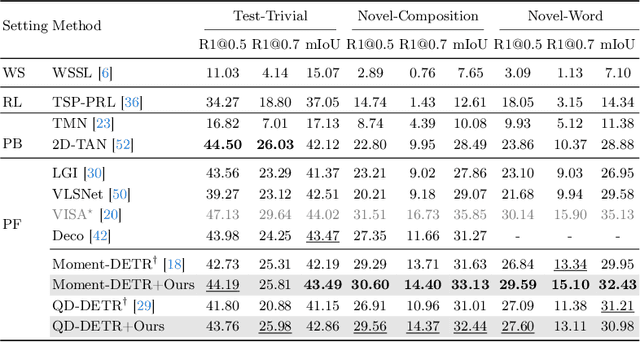
Abstract:Temporal grounding, a.k.a video moment retrieval, aims at locating video segments corresponding to a given query sentence. The compositional nature of natural language enables the localization beyond predefined events, posing a certain challenge to the compositional generalizability of existing methods. Recent studies establish the correspondence between videos and queries through a decompose-reconstruct manner to achieve compositional generalization. However, they only consider dominant primitives and build negative queries through random sampling and recombination, resulting in semantically implausible negatives that hinder the models from learning rational compositions. In addition, recent DETR-based methods still underperform in compositional temporal grounding, showing irrational saliency responses when given negative queries that have subtle differences from positive queries. To address these limitations, we first propose a large language model-driven method for negative query construction, utilizing GPT-3.5-Turbo to generate semantically plausible hard negative queries. Subsequently, we introduce a coarse-to-fine saliency ranking strategy, which encourages the model to learn the multi-granularity semantic relationships between videos and hierarchical negative queries to boost compositional generalization. Extensive experiments on two challenging benchmarks validate the effectiveness and generalizability of our proposed method. Our code is available at https://github.com/zxccade/SHINE.
Learning Prompt-Enhanced Context Features for Weakly-Supervised Video Anomaly Detection
Jun 26, 2023



Abstract:Video anomaly detection under weak supervision is challenging due to the absence of frame-level annotations during the training phase. Previous work has employed graph convolution networks or self-attention mechanisms to model temporal relations, along with multiple instance learning (MIL)-based classification loss to learn discriminative features. However, most of them utilize multi-branches to capture local and global dependencies separately, leading to increased parameters and computational cost. Furthermore, the binarized constraint of the MIL-based loss only ensures coarse-grained interclass separability, ignoring fine-grained discriminability within anomalous classes. In this paper, we propose a weakly supervised anomaly detection framework that emphasizes efficient context modeling and enhanced semantic discriminability. To this end, we first construct a temporal context aggregation (TCA) module that captures complete contextual information by reusing similarity matrix and adaptive fusion. Additionally, we propose a prompt-enhanced learning (PEL) module that incorporates semantic priors into the model by utilizing knowledge-based prompts, aiming at enhancing the discriminative capacity of context features while ensuring separability between anomaly sub-classes. Furthermore, we introduce a score smoothing (SS) module in the testing phase to suppress individual bias and reduce false alarms. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of various components of our method, which achieves competitive performance with fewer parameters and computational effort on three challenging benchmarks: the UCF-crime, XD-violence, and ShanghaiTech datasets. The detection accuracy of some anomaly sub-classes is also improved with a great margin.
Locality-aware Attention Network with Discriminative Dynamics Learning for Weakly Supervised Anomaly Detection
Aug 11, 2022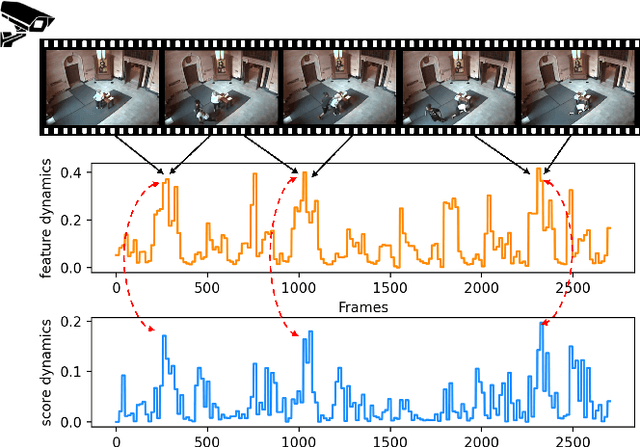
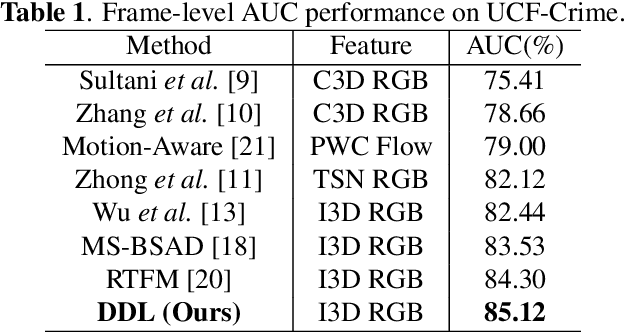


Abstract:Video anomaly detection is recently formulated as a multiple instance learning task under weak supervision, in which each video is treated as a bag of snippets to be determined whether contains anomalies. Previous efforts mainly focus on the discrimination of the snippet itself without modeling the temporal dynamics, which refers to the variation of adjacent snippets. Therefore, we propose a Discriminative Dynamics Learning (DDL) method with two objective functions, i.e., dynamics ranking loss and dynamics alignment loss. The former aims to enlarge the score dynamics gap between positive and negative bags while the latter performs temporal alignment of the feature dynamics and score dynamics within the bag. Moreover, a Locality-aware Attention Network (LA-Net) is constructed to capture global correlations and re-calibrate the location preference across snippets, followed by a multilayer perceptron with causal convolution to obtain anomaly scores. Experimental results show that our method achieves significant improvements on two challenging benchmarks, i.e., UCF-Crime and XD-Violence.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge