Yuhan Hsi
UniCoN: Universal Conditional Networks for Multi-Age Embryonic Cartilage Segmentation with Sparsely Annotated Data
Oct 16, 2024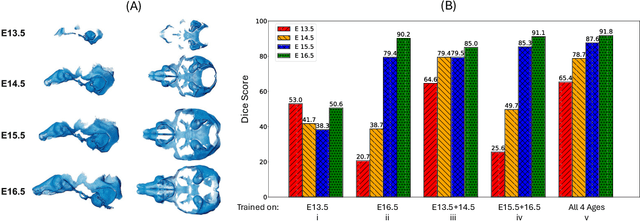
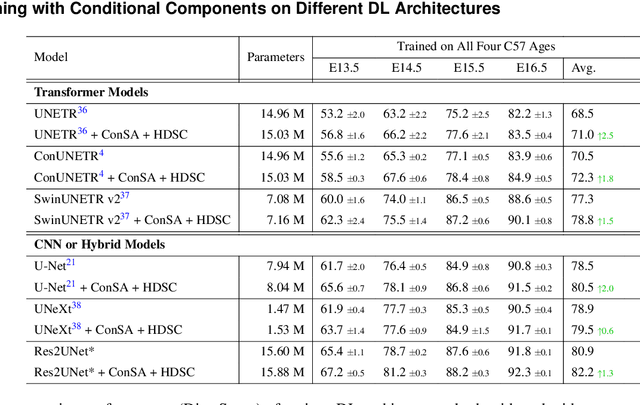
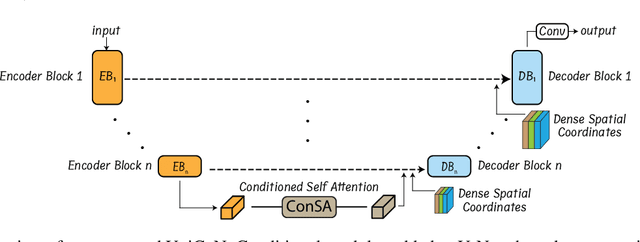
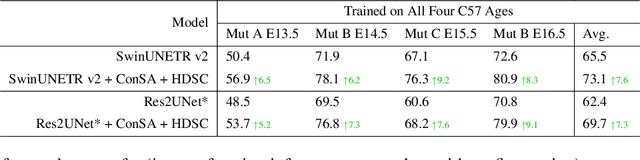
Abstract:Osteochondrodysplasia, affecting 2-3% of newborns globally, is a group of bone and cartilage disorders that often result in head malformations, contributing to childhood morbidity and reduced quality of life. Current research on this disease using mouse models faces challenges since it involves accurately segmenting the developing cartilage in 3D micro-CT images of embryonic mice. Tackling this segmentation task with deep learning (DL) methods is laborious due to the big burden of manual image annotation, expensive due to the high acquisition costs of 3D micro-CT images, and difficult due to embryonic cartilage's complex and rapidly changing shapes. While DL approaches have been proposed to automate cartilage segmentation, most such models have limited accuracy and generalizability, especially across data from different embryonic age groups. To address these limitations, we propose novel DL methods that can be adopted by any DL architectures -- including CNNs, Transformers, or hybrid models -- which effectively leverage age and spatial information to enhance model performance. Specifically, we propose two new mechanisms, one conditioned on discrete age categories and the other on continuous image crop locations, to enable an accurate representation of cartilage shape changes across ages and local shape details throughout the cranial region. Extensive experiments on multi-age cartilage segmentation datasets show significant and consistent performance improvements when integrating our conditional modules into popular DL segmentation architectures. On average, we achieve a 1.7% Dice score increase with minimal computational overhead and a 7.5% improvement on unseen data. These results highlight the potential of our approach for developing robust, universal models capable of handling diverse datasets with limited annotated data, a key challenge in DL-based medical image analysis.
ConUNETR: A Conditional Transformer Network for 3D Micro-CT Embryonic Cartilage Segmentation
Feb 06, 2024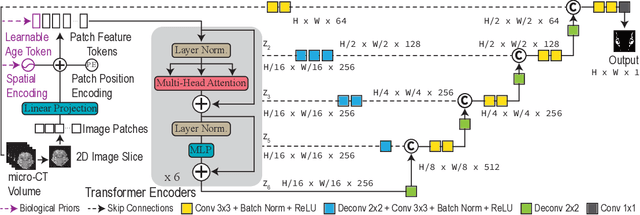
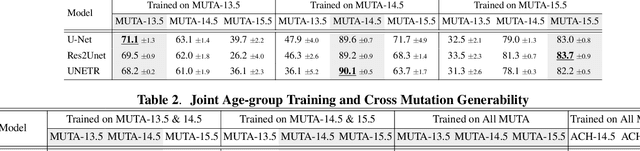
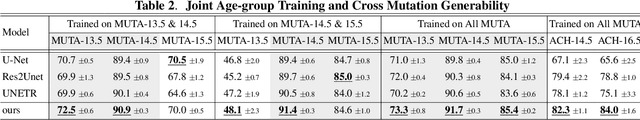
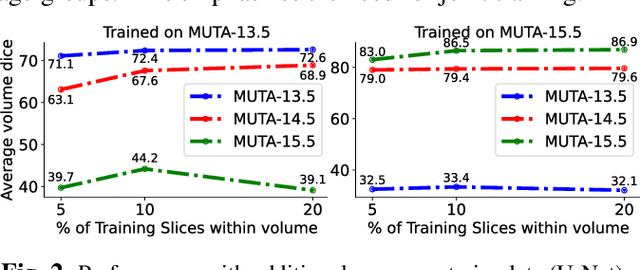
Abstract:Studying the morphological development of cartilaginous and osseous structures is critical to the early detection of life-threatening skeletal dysmorphology. Embryonic cartilage undergoes rapid structural changes within hours, introducing biological variations and morphological shifts that limit the generalization of deep learning-based segmentation models that infer across multiple embryonic age groups. Obtaining individual models for each age group is expensive and less effective, while direct transfer (predicting an age unseen during training) suffers a potential performance drop due to morphological shifts. We propose a novel Transformer-based segmentation model with improved biological priors that better distills morphologically diverse information through conditional mechanisms. This enables a single model to accurately predict cartilage across multiple age groups. Experiments on the mice cartilage dataset show the superiority of our new model compared to other competitive segmentation models. Additional studies on a separate mice cartilage dataset with a distinct mutation show that our model generalizes well and effectively captures age-based cartilage morphology patterns.
Dynamic Data Augmentation via MCTS for Prostate MRI Segmentation
May 25, 2023Abstract:Medical image data are often limited due to the expensive acquisition and annotation process. Hence, training a deep-learning model with only raw data can easily lead to overfitting. One solution to this problem is to augment the raw data with various transformations, improving the model's ability to generalize to new data. However, manually configuring a generic augmentation combination and parameters for different datasets is non-trivial due to inconsistent acquisition approaches and data distributions. Therefore, automatic data augmentation is proposed to learn favorable augmentation strategies for different datasets while incurring large GPU overhead. To this end, we present a novel method, called Dynamic Data Augmentation (DDAug), which is efficient and has negligible computation cost. Our DDAug develops a hierarchical tree structure to represent various augmentations and utilizes an efficient Monte-Carlo tree searching algorithm to update, prune, and sample the tree. As a result, the augmentation pipeline can be optimized for each dataset automatically. Experiments on multiple Prostate MRI datasets show that our method outperforms the current state-of-the-art data augmentation strategies.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge