Yubin Liu
M2I2HA: Multi-modal Object Detection Based on Intra- and Inter-Modal Hypergraph Attention
Jan 24, 2026Abstract:Recent advances in multi-modal detection have significantly improved detection accuracy in challenging environments (e.g., low light, overexposure). By integrating RGB with modalities such as thermal and depth, multi-modal fusion increases data redundancy and system robustness. However, significant challenges remain in effectively extracting task-relevant information both within and across modalities, as well as in achieving precise cross-modal alignment. While CNNs excel at feature extraction, they are limited by constrained receptive fields, strong inductive biases, and difficulty in capturing long-range dependencies. Transformer-based models offer global context but suffer from quadratic computational complexity and are confined to pairwise correlation modeling. Mamba and other State Space Models (SSMs), on the other hand, are hindered by their sequential scanning mechanism, which flattens 2D spatial structures into 1D sequences, disrupting topological relationships and limiting the modeling of complex higher-order dependencies. To address these issues, we propose a multi-modal perception network based on hypergraph theory called M2I2HA. Our architecture includes an Intra-Hypergraph Enhancement module to capture global many-to-many high-order relationships within each modality, and an Inter-Hypergraph Fusion module to align, enhance, and fuse cross-modal features by bridging configuration and spatial gaps between data sources. We further introduce a M2-FullPAD module to enable adaptive multi-level fusion of multi-modal enhanced features within the network, meanwhile enhancing data distribution and flow across the architecture. Extensive object detection experiments on multiple public datasets against baselines demonstrate that M2I2HA achieves state-of-the-art performance in multi-modal object detection tasks.
M2I2HA: A Multi-modal Object Detection Method Based on Intra- and Inter-Modal Hypergraph Attention
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:Recent advances in multi-modal detection have significantly improved detection accuracy in challenging environments (e.g., low light, overexposure). By integrating RGB with modalities such as thermal and depth, multi-modal fusion increases data redundancy and system robustness. However, significant challenges remain in effectively extracting task-relevant information both within and across modalities, as well as in achieving precise cross-modal alignment. While CNNs excel at feature extraction, they are limited by constrained receptive fields, strong inductive biases, and difficulty in capturing long-range dependencies. Transformer-based models offer global context but suffer from quadratic computational complexity and are confined to pairwise correlation modeling. Mamba and other State Space Models (SSMs), on the other hand, are hindered by their sequential scanning mechanism, which flattens 2D spatial structures into 1D sequences, disrupting topological relationships and limiting the modeling of complex higher-order dependencies. To address these issues, we propose a multi-modal perception network based on hypergraph theory called M2I2HA. Our architecture includes an Intra-Hypergraph Enhancement module to capture global many-to-many high-order relationships within each modality, and an Inter-Hypergraph Fusion module to align, enhance, and fuse cross-modal features by bridging configuration and spatial gaps between data sources. We further introduce a M2-FullPAD module to enable adaptive multi-level fusion of multi-modal enhanced features within the network, meanwhile enhancing data distribution and flow across the architecture. Extensive object detection experiments on multiple public datasets against baselines demonstrate that M2I2HA achieves state-of-the-art performance in multi-modal object detection tasks.
Location-Routing Planning for Last-Mile Deliveries Using Mobile Parcel Lockers: A Hybrid Q-Learning Network Approach
Sep 09, 2022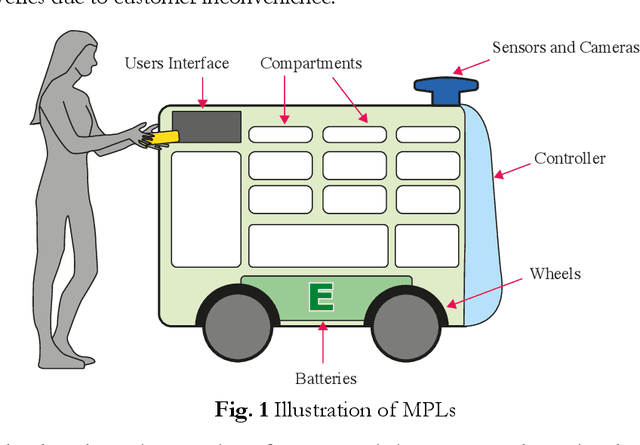

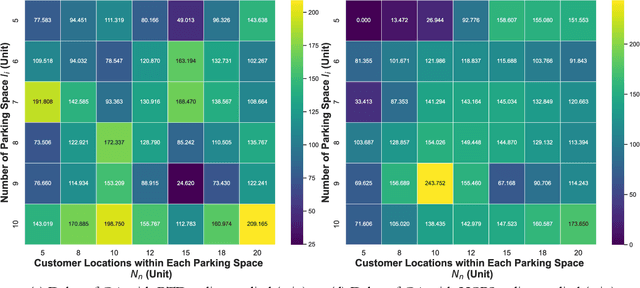
Abstract:Mobile parcel lockers (MPLs) have been recently proposed by logistics operators as a technology that could help reduce traffic congestion and operational costs in urban freight distribution. Given their ability to relocate throughout their area of deployment, they hold the potential to improve customer accessibility and convenience. In this study, we formulate the Mobile Parcel Locker Problem (MPLP), a special case of the Location-Routing Problem (LRP) which determines the optimal stopover location for MPLs throughout the day and plans corresponding delivery routes. A Hybrid Q-Learning-Network-based Method (HQM) is developed to resolve the computational complexity of the resulting large problem instances while escaping local optima. In addition, the HQM is integrated with global and local search mechanisms to resolve the dilemma of exploration and exploitation faced by classic reinforcement learning (RL) methods. We examine the performance of HQM under different problem sizes (up to 200 nodes) and benchmarked it against the Genetic Algorithm (GA). Our results indicate that the average reward obtained by HQM is 1.96 times greater than GA, which demonstrates that HQM has a better optimisation ability. Finally, we identify critical factors that contribute to fleet size requirements, travel distances, and service delays. Our findings outline that the efficiency of MPLs is mainly contingent on the length of time windows and the deployment of MPL stopovers.
Location-routing Optimisation for Urban Logistics Using Mobile Parcel Locker Based on Hybrid Q-Learning Algorithm
Oct 29, 2021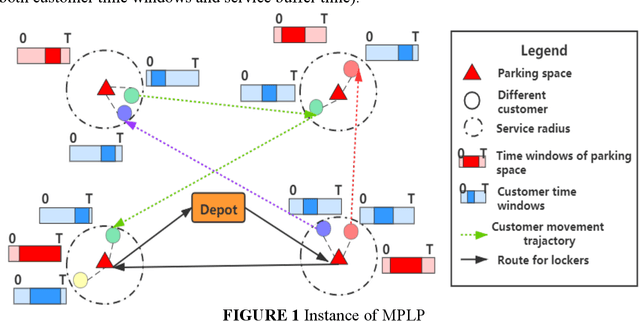
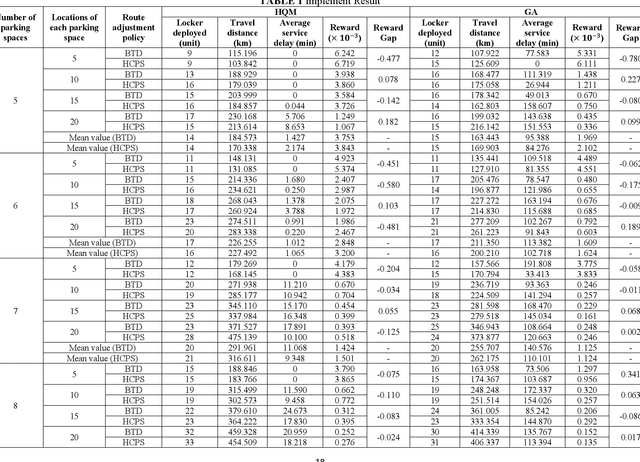
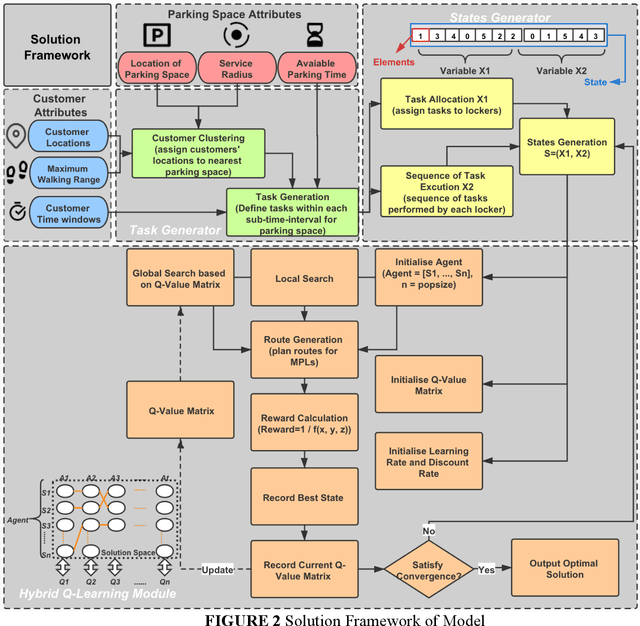
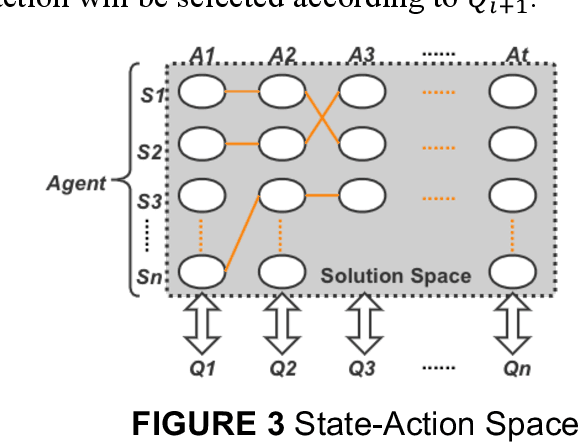
Abstract:Mobile parcel lockers (MPLs) have been recently introduced by urban logistics operators as a means to reduce traffic congestion and operational cost. Their capability to relocate their position during the day has the potential to improve customer accessibility and convenience (if deployed and planned accordingly), allowing customers to collect parcels at their preferred time among one of the multiple locations. This paper proposes an integer programming model to solve the Location Routing Problem for MPLs to determine the optimal configuration and locker routes. In solving this model, a Hybrid Q-Learning algorithm-based Method (HQM) integrated with global and local search mechanisms is developed, the performance of which is examined for different problem sizes and benchmarked with genetic algorithms. Furthermore, we introduced two route adjustment strategies to resolve stochastic events that may cause delays. The results show that HQM achieves 443.41% improvement on average in solution improvement, compared with the 94.91% improvement of heuristic counterparts, suggesting HQM enables a more efficient search for better solutions. Finally, we identify critical factors that contribute to service delays and investigate their effects.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge