Yuanzhi Yao
Supervision-by-Hallucination-and-Transfer: A Weakly-Supervised Approach for Robust and Precise Facial Landmark Detection
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:High-precision facial landmark detection (FLD) relies on high-resolution deep feature representations. However, low-resolution face images or the compression (via pooling or strided convolution) of originally high-resolution images hinder the learning of such features, thereby reducing FLD accuracy. Moreover, insufficient training data and imprecise annotations further degrade performance. To address these challenges, we propose a weakly-supervised framework called Supervision-by-Hallucination-and-Transfer (SHT) for more robust and precise FLD. SHT contains two novel mutually enhanced modules: Dual Hallucination Learning Network (DHLN) and Facial Pose Transfer Network (FPTN). By incorporating FLD and face hallucination tasks, DHLN is able to learn high-resolution representations with low-resolution inputs for recovering both facial structures and local details and generating more effective landmark heatmaps. Then, by transforming faces from one pose to another, FPTN can further improve landmark heatmaps and faces hallucinated by DHLN for detecting more accurate landmarks. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to explore weakly-supervised FLD by integrating face hallucination and facial pose transfer tasks. Experimental results of both face hallucination and FLD demonstrate that our method surpasses state-of-the-art techniques.
PPIDSG: A Privacy-Preserving Image Distribution Sharing Scheme with GAN in Federated Learning
Dec 16, 2023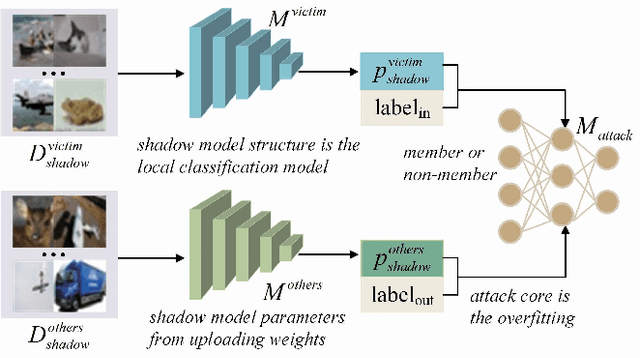
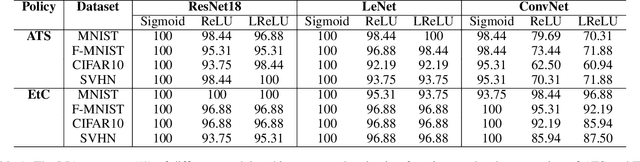
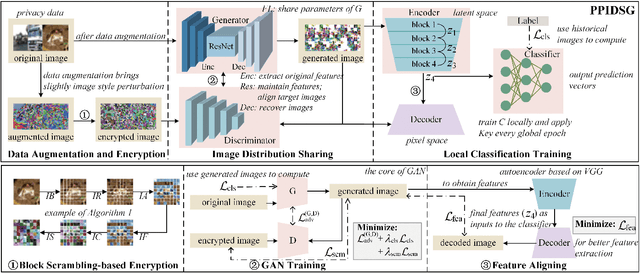
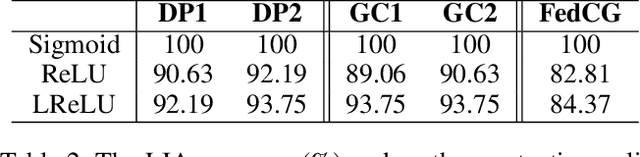
Abstract:Federated learning (FL) has attracted growing attention since it allows for privacy-preserving collaborative training on decentralized clients without explicitly uploading sensitive data to the central server. However, recent works have revealed that it still has the risk of exposing private data to adversaries. In this paper, we conduct reconstruction attacks and enhance inference attacks on various datasets to better understand that sharing trained classification model parameters to a central server is the main problem of privacy leakage in FL. To tackle this problem, a privacy-preserving image distribution sharing scheme with GAN (PPIDSG) is proposed, which consists of a block scrambling-based encryption algorithm, an image distribution sharing method, and local classification training. Specifically, our method can capture the distribution of a target image domain which is transformed by the block encryption algorithm, and upload generator parameters to avoid classifier sharing with negligible influence on model performance. Furthermore, we apply a feature extractor to motivate model utility and train it separately from the classifier. The extensive experimental results and security analyses demonstrate the superiority of our proposed scheme compared to other state-of-the-art defense methods. The code is available at https://github.com/ytingma/PPIDSG.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge