Yuanyuan Qi
Next Generation Active Learning: Mixture of LLMs in the Loop
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:With the rapid advancement and strong generalization capabilities of large language models (LLMs), they have been increasingly incorporated into the active learning pipelines as annotators to reduce annotation costs. However, considering the annotation quality, labels generated by LLMs often fall short of real-world applicability. To address this, we propose a novel active learning framework, Mixture of LLMs in the Loop Active Learning, replacing human annotators with labels generated through a Mixture-of-LLMs-based annotation model, aimed at enhancing LLM-based annotation robustness by aggregating the strengths of multiple LLMs. To further mitigate the impact of the noisy labels, we introduce annotation discrepancy and negative learning to identify the unreliable annotations and enhance learning effectiveness. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our framework achieves performance comparable to human annotation and consistently outperforms single-LLM baselines and other LLM-ensemble-based approaches. Moreover, our framework is built on lightweight LLMs, enabling it to operate fully on local machines in real-world applications.
ALScope: A Unified Toolkit for Deep Active Learning
Aug 06, 2025Abstract:Deep Active Learning (DAL) reduces annotation costs by selecting the most informative unlabeled samples during training. As real-world applications become more complex, challenges stemming from distribution shifts (e.g., open-set recognition) and data imbalance have gained increasing attention, prompting the development of numerous DAL algorithms. However, the lack of a unified platform has hindered fair and systematic evaluation under diverse conditions. Therefore, we present a new DAL platform ALScope for classification tasks, integrating 10 datasets from computer vision (CV) and natural language processing (NLP), and 21 representative DAL algorithms, including both classical baselines and recent approaches designed to handle challenges such as distribution shifts and data imbalance. This platform supports flexible configuration of key experimental factors, ranging from algorithm and dataset choices to task-specific factors like out-of-distribution (OOD) sample ratio, and class imbalance ratio, enabling comprehensive and realistic evaluation. We conduct extensive experiments on this platform under various settings. Our findings show that: (1) DAL algorithms' performance varies significantly across domains and task settings; (2) in non-standard scenarios such as imbalanced and open-set settings, DAL algorithms show room for improvement and require further investigation; and (3) some algorithms achieve good performance, but require significantly longer selection time.
Decoupled Multimodal Prototypes for Visual Recognition with Missing Modalities
May 13, 2025



Abstract:Multimodal learning enhances deep learning models by enabling them to perceive and understand information from multiple data modalities, such as visual and textual inputs. However, most existing approaches assume the availability of all modalities, an assumption that often fails in real-world applications. Recent works have introduced learnable missing-case-aware prompts to mitigate performance degradation caused by missing modalities while reducing the need for extensive model fine-tuning. Building upon the effectiveness of missing-case-aware handling for missing modalities, we propose a novel decoupled prototype-based output head, which leverages missing-case-aware class-wise prototypes tailored for each individual modality. This approach dynamically adapts to different missing modality scenarios and can be seamlessly integrated with existing prompt-based methods. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our proposed output head significantly improves performance across a wide range of missing-modality scenarios and varying missing rates.
ReactDance: Progressive-Granular Representation for Long-Term Coherent Reactive Dance Generation
May 08, 2025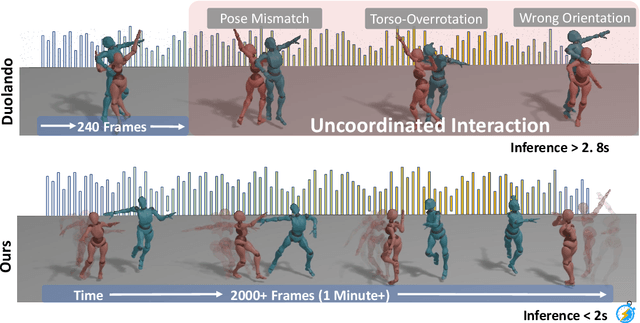
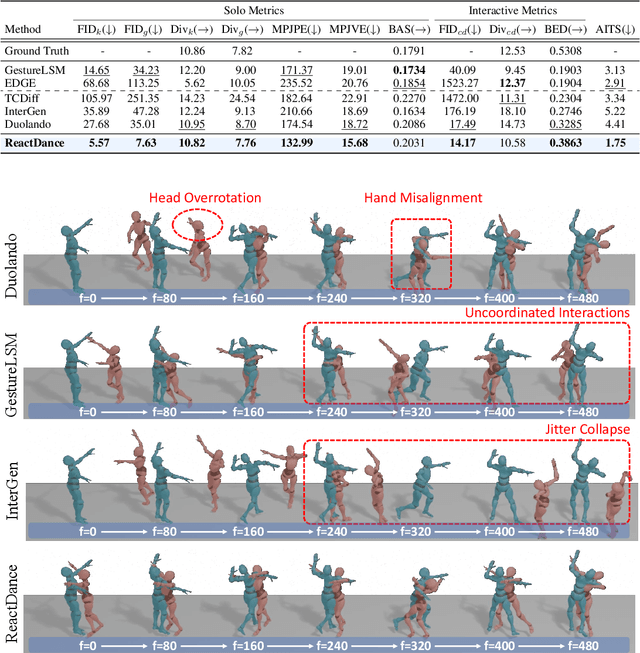
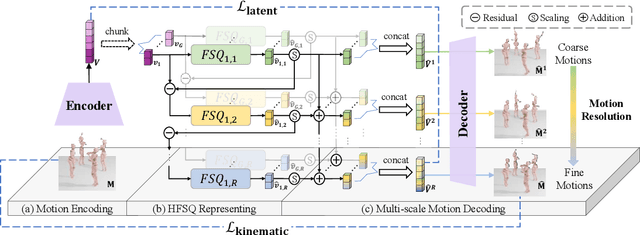
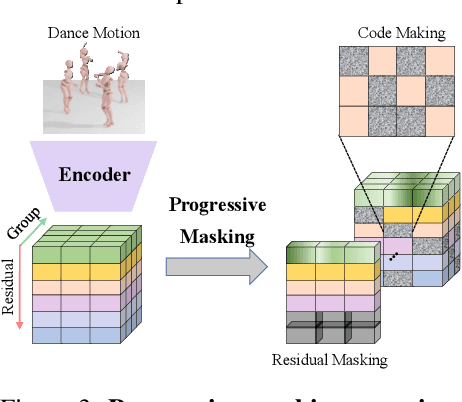
Abstract:Reactive dance generation (RDG) produces follower movements conditioned on guiding dancer and music while ensuring spatial coordination and temporal coherence. However, existing methods overemphasize global constraints and optimization, overlooking local information, such as fine-grained spatial interactions and localized temporal context. Therefore, we present ReactDance, a novel diffusion-based framework for high-fidelity RDG with long-term coherence and multi-scale controllability. Unlike existing methods that struggle with interaction fidelity, synchronization, and temporal consistency in duet synthesis, our approach introduces two key innovations: 1)Group Residual Finite Scalar Quantization (GRFSQ), a multi-scale disentangled motion representation that captures interaction semantics from coarse body rhythms to fine-grained joint dynamics, and 2)Blockwise Local Context (BLC), a sampling strategy eliminating error accumulation in long sequence generation via local block causal masking and periodic positional encoding. Built on the decoupled multi-scale GRFSQ representation, we implement a diffusion model withLayer-Decoupled Classifier-free Guidance (LDCFG), allowing granular control over motion semantics across scales. Extensive experiments on standard benchmarks demonstrate that ReactDance surpasses existing methods, achieving state-of-the-art performance.
Multi-Label Bayesian Active Learning with Inter-Label Relationships
Nov 26, 2024Abstract:The primary challenge of multi-label active learning, differing it from multi-class active learning, lies in assessing the informativeness of an indefinite number of labels while also accounting for the inherited label correlation. Existing studies either require substantial computational resources to leverage correlations or fail to fully explore label dependencies. Additionally, real-world scenarios often require addressing intrinsic biases stemming from imbalanced data distributions. In this paper, we propose a new multi-label active learning strategy to address both challenges. Our method incorporates progressively updated positive and negative correlation matrices to capture co-occurrence and disjoint relationships within the label space of annotated samples, enabling a holistic assessment of uncertainty rather than treating labels as isolated elements. Furthermore, alongside diversity, our model employs ensemble pseudo labeling and beta scoring rules to address data imbalances. Extensive experiments on four realistic datasets demonstrate that our strategy consistently achieves more reliable and superior performance, compared to several established methods.
Neural Topic Modeling with Large Language Models in the Loop
Nov 13, 2024Abstract:Topic modeling is a fundamental task in natural language processing, allowing the discovery of latent thematic structures in text corpora. While Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated promising capabilities in topic discovery, their direct application to topic modeling suffers from issues such as incomplete topic coverage, misalignment of topics, and inefficiency. To address these limitations, we propose LLM-ITL, a novel LLM-in-the-loop framework that integrates LLMs with many existing Neural Topic Models (NTMs). In LLM-ITL, global topics and document representations are learned through the NTM, while an LLM refines the topics via a confidence-weighted Optimal Transport (OT)-based alignment objective. This process enhances the interpretability and coherence of the learned topics, while maintaining the efficiency of NTMs. Extensive experiments demonstrate that LLM-ITL can help NTMs significantly improve their topic interpretability while maintaining the quality of document representation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge