Yu-kun Lai
Recent Advances of Deep Robotic Affordance Learning: A Reinforcement Learning Perspective
Mar 10, 2023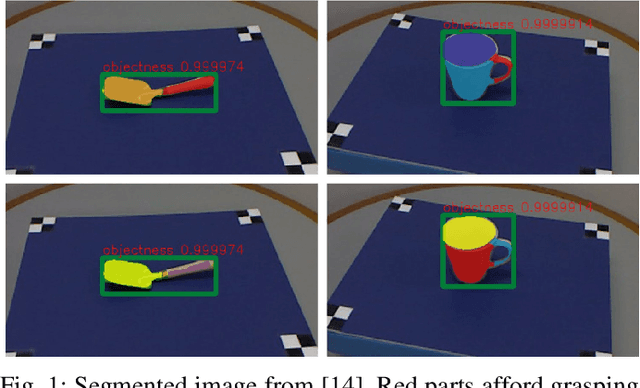
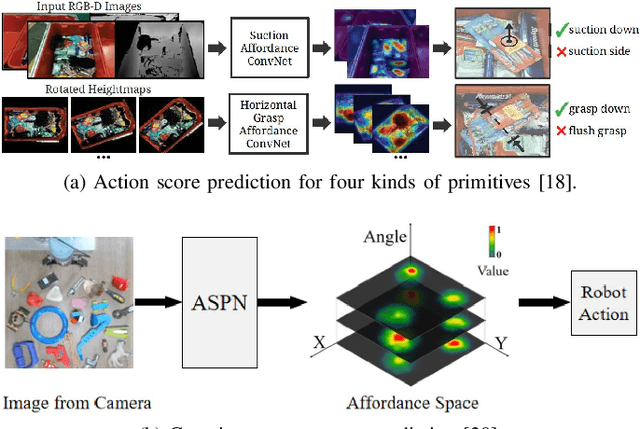
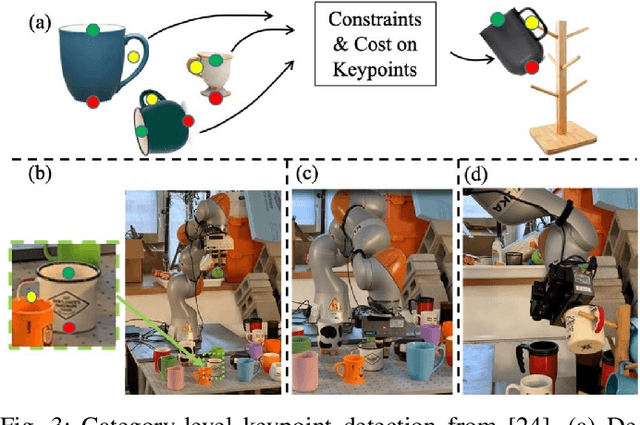
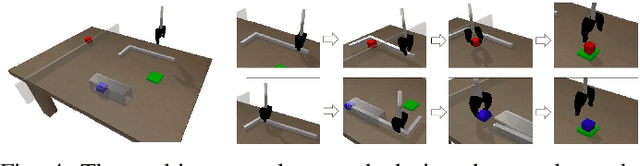
Abstract:As a popular concept proposed in the field of psychology, affordance has been regarded as one of the important abilities that enable humans to understand and interact with the environment. Briefly, it captures the possibilities and effects of the actions of an agent applied to a specific object or, more generally, a part of the environment. This paper provides a short review of the recent developments of deep robotic affordance learning (DRAL), which aims to develop data-driven methods that use the concept of affordance to aid in robotic tasks. We first classify these papers from a reinforcement learning (RL) perspective, and draw connections between RL and affordances. The technical details of each category are discussed and their limitations identified. We further summarise them and identify future challenges from the aspects of observations, actions, affordance representation, data-collection and real-world deployment. A final remark is given at the end to propose a promising future direction of the RL-based affordance definition to include the predictions of arbitrary action consequences.
Abstract Demonstrations and Adaptive Exploration for Efficient and Stable Multi-step Sparse Reward Reinforcement Learning
Jul 19, 2022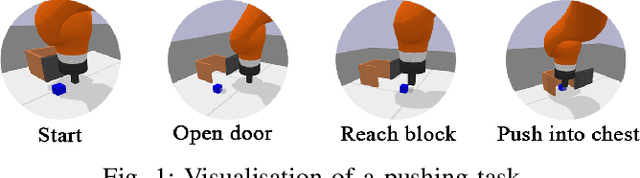
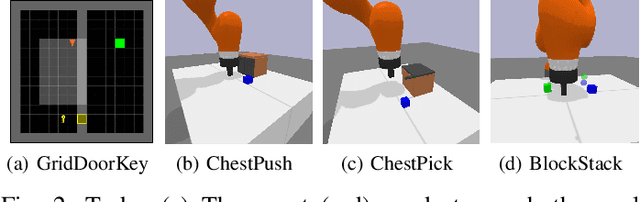
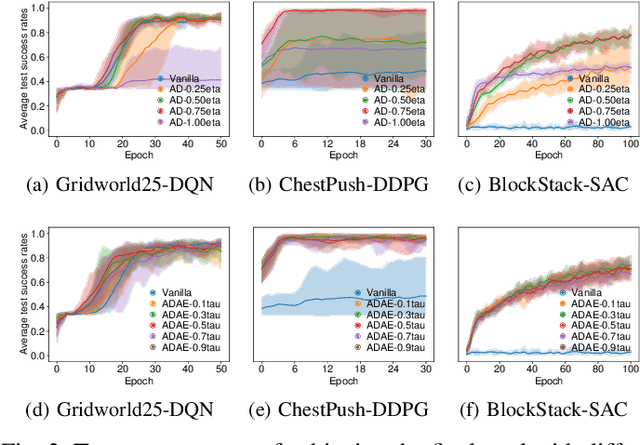
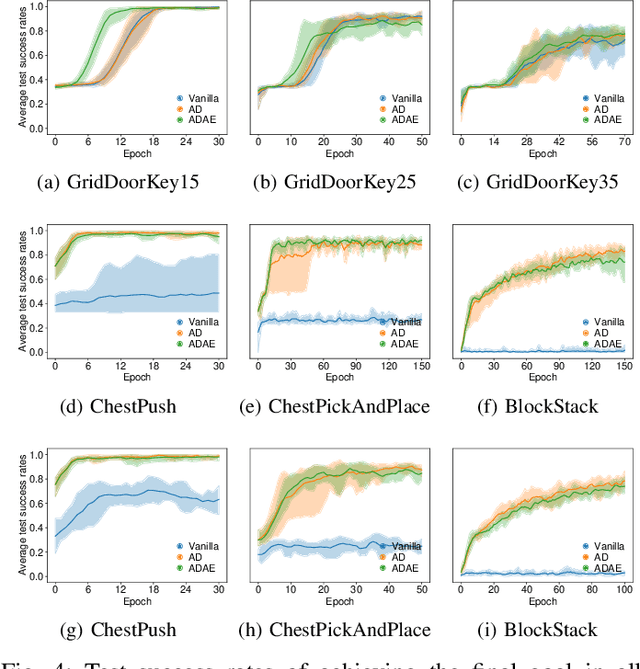
Abstract:Although Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) has been popular in many disciplines including robotics, state-of-the-art DRL algorithms still struggle to learn long-horizon, multi-step and sparse reward tasks, such as stacking several blocks given only a task-completion reward signal. To improve learning efficiency for such tasks, this paper proposes a DRL exploration technique, termed A^2, which integrates two components inspired by human experiences: Abstract demonstrations and Adaptive exploration. A^2 starts by decomposing a complex task into subtasks, and then provides the correct orders of subtasks to learn. During training, the agent explores the environment adaptively, acting more deterministically for well-mastered subtasks and more stochastically for ill-learnt subtasks. Ablation and comparative experiments are conducted on several grid-world tasks and three robotic manipulation tasks. We demonstrate that A^2 can aid popular DRL algorithms (DQN, DDPG, and SAC) to learn more efficiently and stably in these environments.
Robust Pose Transfer with Dynamic Details using Neural Video Rendering
Jul 14, 2021



Abstract:Pose transfer of human videos aims to generate a high fidelity video of a target person imitating actions of a source person. A few studies have made great progress either through image translation with deep latent features or neural rendering with explicit 3D features. However, both of them rely on large amounts of training data to generate realistic results, and the performance degrades on more accessible internet videos due to insufficient training frames. In this paper, we demonstrate that the dynamic details can be preserved even trained from short monocular videos. Overall, we propose a neural video rendering framework coupled with an image-translation-based dynamic details generation network (D2G-Net), which fully utilizes both the stability of explicit 3D features and the capacity of learning components. To be specific, a novel texture representation is presented to encode both the static and pose-varying appearance characteristics, which is then mapped to the image space and rendered as a detail-rich frame in the neural rendering stage. Moreover, we introduce a concise temporal loss in the training stage to suppress the detail flickering that is made more visible due to high-quality dynamic details generated by our method. Through extensive comparisons, we demonstrate that our neural human video renderer is capable of achieving both clearer dynamic details and more robust performance even on accessible short videos with only 2k - 4k frames.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge