Yu-Chien Tang
OI-Bench: An Option Injection Benchmark for Evaluating LLM Susceptibility to Directive Interference
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:Benchmarking large language models (LLMs) is critical for understanding their capabilities, limitations, and robustness. In addition to interface artifacts, prior studies have shown that LLM decisions can be influenced by directive signals such as social cues, framing, and instructions. In this work, we introduce option injection, a benchmarking approach that augments the multiple-choice question answering (MCQA) interface with an additional option containing a misleading directive, leveraging standardized choice structure and scalable evaluation. We construct OI-Bench, a benchmark of 3,000 questions spanning knowledge, reasoning, and commonsense tasks, with 16 directive types covering social compliance, bonus framing, threat framing, and instructional interference. This setting combines manipulation of the choice interface with directive-based interference, enabling systematic assessment of model susceptibility. We evaluate 12 LLMs to analyze attack success rates, behavioral responses, and further investigate mitigation strategies ranging from inference-time prompting to post-training alignment. Experimental results reveal substantial vulnerabilities and heterogeneous robustness across models. OI-Bench is expected to support more systematic evaluation of LLM robustness to directive interference within choice-based interfaces.
CARPAS: Towards Content-Aware Refinement of Provided Aspects for Summarization in Large Language Models
Oct 08, 2025Abstract:Aspect-based summarization has attracted significant attention for its ability to generate more fine-grained and user-aligned summaries. While most existing approaches assume a set of predefined aspects as input, real-world scenarios often present challenges where these given aspects may be incomplete, irrelevant, or entirely missing from the document. Users frequently expect systems to adaptively refine or filter the provided aspects based on the actual content. In this paper, we initiate this novel task setting, termed Content-Aware Refinement of Provided Aspects for Summarization (CARPAS), with the aim of dynamically adjusting the provided aspects based on the document context before summarizing. We construct three new datasets to facilitate our pilot experiments, and by using LLMs with four representative prompting strategies in this task, we find that LLMs tend to predict an overly comprehensive set of aspects, which often results in excessively long and misaligned summaries. Building on this observation, we propose a preliminary subtask to predict the number of relevant aspects, and demonstrate that the predicted number can serve as effective guidance for the LLMs, reducing the inference difficulty, and enabling them to focus on the most pertinent aspects. Our extensive experiments show that the proposed approach significantly improves performance across all datasets. Moreover, our deeper analyses uncover LLMs' compliance when the requested number of aspects differs from their own estimations, establishing a crucial insight for the deployment of LLMs in similar real-world applications.
MathEDU: Towards Adaptive Feedback for Student Mathematical Problem-Solving
May 23, 2025Abstract:Online learning enhances educational accessibility, offering students the flexibility to learn anytime, anywhere. However, a key limitation is the lack of immediate, personalized feedback, particularly in helping students correct errors in math problem-solving. Several studies have investigated the applications of large language models (LLMs) in educational contexts. In this paper, we explore the capabilities of LLMs to assess students' math problem-solving processes and provide adaptive feedback. The MathEDU dataset is introduced, comprising authentic student solutions annotated with teacher feedback. We evaluate the model's ability to support personalized learning in two scenarios: one where the model has access to students' prior answer histories, and another simulating a cold-start context. Experimental results show that the fine-tuned model performs well in identifying correctness. However, the model still faces challenges in generating detailed feedback for pedagogical purposes.
Stay Hungry, Stay Foolish: On the Extended Reading Articles Generation with LLMs
Apr 21, 2025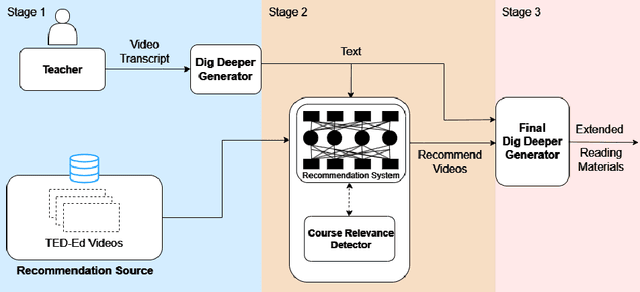

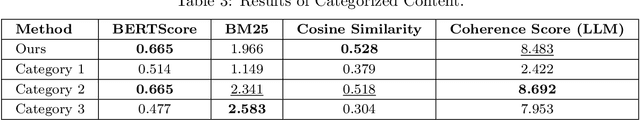
Abstract:The process of creating educational materials is both time-consuming and demanding for educators. This research explores the potential of Large Language Models (LLMs) to streamline this task by automating the generation of extended reading materials and relevant course suggestions. Using the TED-Ed Dig Deeper sections as an initial exploration, we investigate how supplementary articles can be enriched with contextual knowledge and connected to additional learning resources. Our method begins by generating extended articles from video transcripts, leveraging LLMs to include historical insights, cultural examples, and illustrative anecdotes. A recommendation system employing semantic similarity ranking identifies related courses, followed by an LLM-based refinement process to enhance relevance. The final articles are tailored to seamlessly integrate these recommendations, ensuring they remain cohesive and informative. Experimental evaluations demonstrate that our model produces high-quality content and accurate course suggestions, assessed through metrics such as Hit Rate, semantic similarity, and coherence. Our experimental analysis highlight the nuanced differences between the generated and existing materials, underscoring the model's capacity to offer more engaging and accessible learning experiences. This study showcases how LLMs can bridge the gap between core content and supplementary learning, providing students with additional recommended resources while also assisting teachers in designing educational materials.
Template-Based Financial Report Generation in Agentic and Decomposed Information Retrieval
Apr 19, 2025


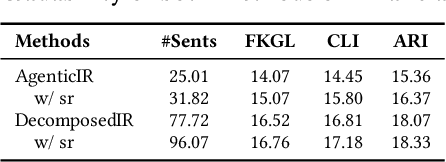
Abstract:Tailoring structured financial reports from companies' earnings releases is crucial for understanding financial performance and has been widely adopted in real-world analytics. However, existing summarization methods often generate broad, high-level summaries, which may lack the precision and detail required for financial reports that typically focus on specific, structured sections. While Large Language Models (LLMs) hold promise, generating reports adhering to predefined multi-section templates remains challenging. This paper investigates two LLM-based approaches popular in industry for generating templated financial reports: an agentic information retrieval (IR) framework and a decomposed IR approach, namely AgenticIR and DecomposedIR. The AgenticIR utilizes collaborative agents prompted with the full template. In contrast, the DecomposedIR approach applies a prompt chaining workflow to break down the template and reframe each section as a query answered by the LLM using the earnings release. To quantitatively assess the generated reports, we evaluated both methods in two scenarios: one using a financial dataset without direct human references, and another with a weather-domain dataset featuring expert-written reports. Experimental results show that while AgenticIR may excel in orchestrating tasks and generating concise reports through agent collaboration, DecomposedIR statistically significantly outperforms AgenticIR approach in providing broader and more detailed coverage in both scenarios, offering reflection on the utilization of the agentic framework in real-world applications.
RSVP: Customer Intent Detection via Agent Response Contrastive and Generative Pre-Training
Oct 15, 2023Abstract:The dialogue systems in customer services have been developed with neural models to provide users with precise answers and round-the-clock support in task-oriented conversations by detecting customer intents based on their utterances. Existing intent detection approaches have highly relied on adaptively pre-training language models with large-scale datasets, yet the predominant cost of data collection may hinder their superiority. In addition, they neglect the information within the conversational responses of the agents, which have a lower collection cost, but are significant to customer intent as agents must tailor their replies based on the customers' intent. In this paper, we propose RSVP, a self-supervised framework dedicated to task-oriented dialogues, which utilizes agent responses for pre-training in a two-stage manner. Specifically, we introduce two pre-training tasks to incorporate the relations of utterance-response pairs: 1) Response Retrieval by selecting a correct response from a batch of candidates, and 2) Response Generation by mimicking agents to generate the response to a given utterance. Our benchmark results for two real-world customer service datasets show that RSVP significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art baselines by 4.95% for accuracy, 3.4% for MRR@3, and 2.75% for MRR@5 on average. Extensive case studies are investigated to show the validity of incorporating agent responses into the pre-training stage.
NYCU-TWO at Memotion 3: Good Foundation, Good Teacher, then you have Good Meme Analysis
Feb 14, 2023Abstract:This paper presents a robust solution to the Memotion 3.0 Shared Task. The goal of this task is to classify the emotion and the corresponding intensity expressed by memes, which are usually in the form of images with short captions on social media. Understanding the multi-modal features of the given memes will be the key to solving the task. In this work, we use CLIP to extract aligned image-text features and propose a novel meme sentiment analysis framework, consisting of a Cooperative Teaching Model (CTM) for Task A and a Cascaded Emotion Classifier (CEC) for Tasks B&C. CTM is based on the idea of knowledge distillation, and can better predict the sentiment of a given meme in Task A; CEC can leverage the emotion intensity suggestion from the prediction of Task C to classify the emotion more precisely in Task B. Experiments show that we achieved the 2nd place ranking for both Task A and Task B and the 4th place ranking for Task C, with weighted F1-scores of 0.342, 0.784, and 0.535 respectively. The results show the robustness and effectiveness of our framework. Our code is released at github.
EmotionGIF-Yankee: A Sentiment Classifier with Robust Model Based Ensemble Methods
Jul 05, 2020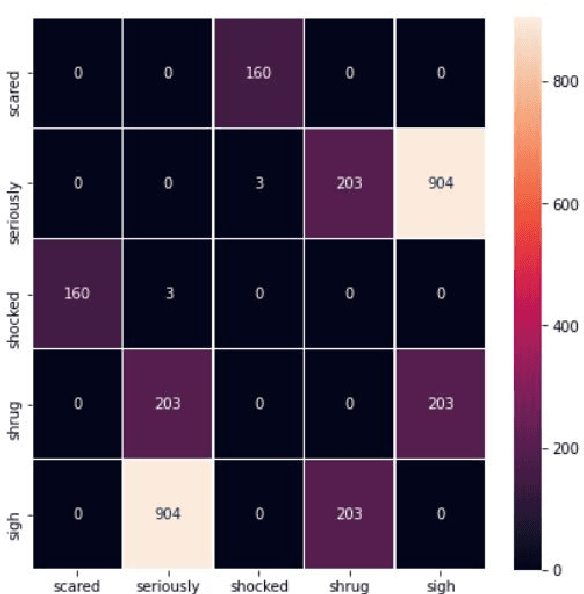
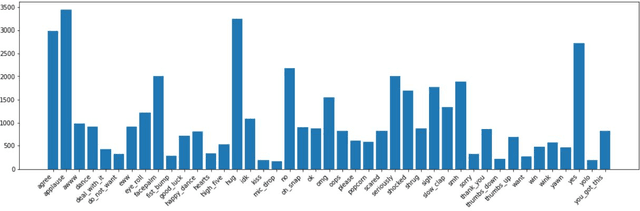
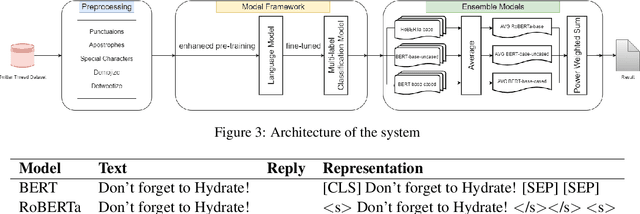
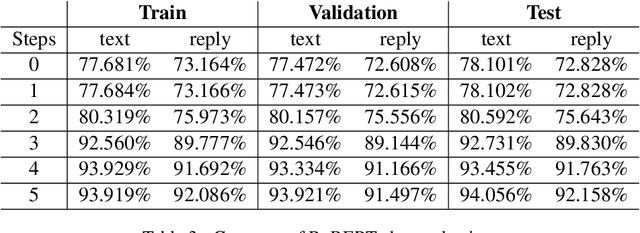
Abstract:This paper provides a method to classify sentiment with robust model based ensemble methods. We preprocess tweet data to enhance coverage of tokenizer. To reduce domain bias, we first train tweet dataset for pre-trained language model. Besides, each classifier has its strengths and weakness, we leverage different types of models with ensemble methods: average and power weighted sum. From the experiments, we show that our approach has achieved positive effect for sentiment classification. Our system reached third place among 26 teams from the evaluation in SocialNLP 2020 EmotionGIF competition.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge