Kai-Shiang Chang
Where Will Players Move Next? Dynamic Graphs and Hierarchical Fusion for Movement Forecasting in Badminton
Nov 22, 2022



Abstract:Sports analytics has captured increasing attention since analysis of the various data enables insights for training strategies, player evaluation, etc. In this paper, we focus on predicting what types of returning strokes will be made, and where players will move to based on previous strokes. As this problem has not been addressed to date, movement forecasting can be tackled through sequence-based and graph-based models by formulating as a sequence prediction task. However, existing sequence-based models neglect the effects of interactions between players, and graph-based models still suffer from multifaceted perspectives on the next movement. Moreover, there is no existing work on representing strategic relations among players' shot types and movements. To address these challenges, we first introduce the procedure of the Player Movements (PM) graph to exploit the structural movements of players with strategic relations. Based on the PM graph, we propose a novel Dynamic Graphs and Hierarchical Fusion for Movement Forecasting model (DyMF) with interaction style extractors to capture the mutual interactions of players themselves and between both players within a rally, and dynamic players' tactics across time. In addition, hierarchical fusion modules are designed to incorporate the style influence of both players and rally interactions. Extensive experiments show that our model empirically outperforms both sequence- and graph-based methods and demonstrate the practical usage of movement forecasting.
ShuttleNet: Position-aware Fusion of Rally Progress and Player Styles for Stroke Forecasting in Badminton
Dec 02, 2021
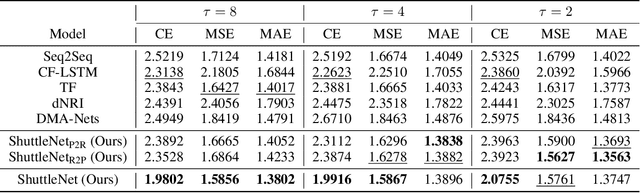
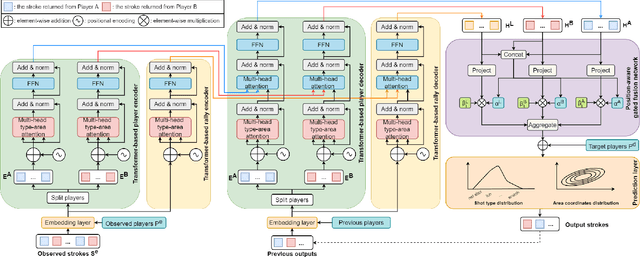
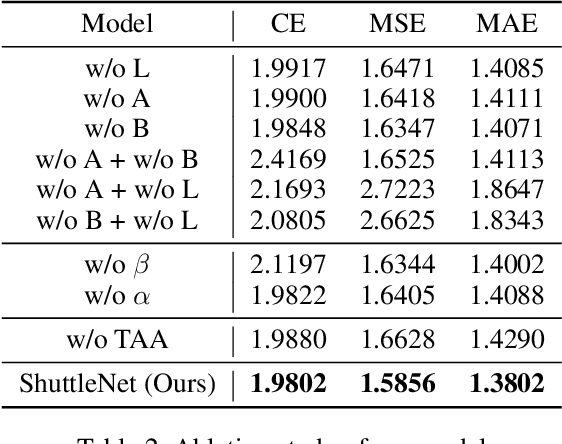
Abstract:The increasing demand for analyzing the insights in sports has stimulated a line of productive studies from a variety of perspectives, e.g., health state monitoring, outcome prediction. In this paper, we focus on objectively judging what and where to return strokes, which is still unexplored in turn-based sports. By formulating stroke forecasting as a sequence prediction task, existing works can tackle the problem but fail to model information based on the characteristics of badminton. To address these limitations, we propose a novel Position-aware Fusion of Rally Progress and Player Styles framework (ShuttleNet) that incorporates rally progress and information of the players by two modified encoder-decoder extractors. Moreover, we design a fusion network to integrate rally contexts and contexts of the players by conditioning on information dependency and different positions. Extensive experiments on the badminton dataset demonstrate that ShuttleNet significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art methods and also empirically validates the feasibility of each component in ShuttleNet. On top of that, we provide an analysis scenario for the stroke forecasting problem.
EmotionGIF-Yankee: A Sentiment Classifier with Robust Model Based Ensemble Methods
Jul 05, 2020
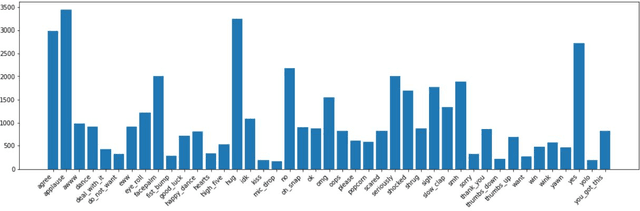
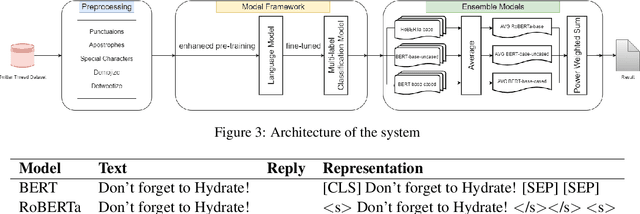
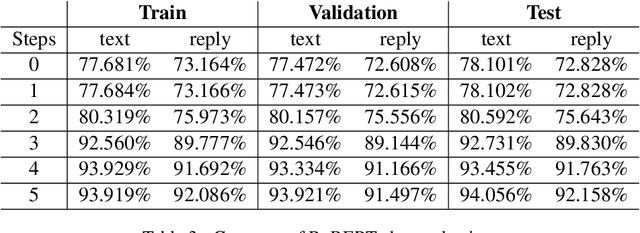
Abstract:This paper provides a method to classify sentiment with robust model based ensemble methods. We preprocess tweet data to enhance coverage of tokenizer. To reduce domain bias, we first train tweet dataset for pre-trained language model. Besides, each classifier has its strengths and weakness, we leverage different types of models with ensemble methods: average and power weighted sum. From the experiments, we show that our approach has achieved positive effect for sentiment classification. Our system reached third place among 26 teams from the evaluation in SocialNLP 2020 EmotionGIF competition.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge