Youssef Mourchid
DynSTG-Mamba: Dynamic Spatio-Temporal Graph Mamba with Cross-Graph Knowledge Distillation for Gait Disorders Recognition
Mar 17, 2025Abstract:Gait disorder recognition plays a crucial role in the early diagnosis and monitoring of movement disorders. Existing approaches, including spatio-temporal graph convolutional networks (ST-GCNs), often face high memory demands and struggle to capture complex spatio-temporal dependencies, limiting their efficiency in clinical applications. To address these challenges, we introduce DynSTG-Mamba (Dynamic Spatio-Temporal Graph Mamba), a novel framework that combines DF-STGNN and STG-Mamba to enhance motion sequence modeling. The DF-STGNN incorporates a dynamic spatio-temporal filter that adaptively adjusts spatial connections between skeletal joints and temporal interactions across different movement phases. This approach ensures better feature propagation through dynamic graph structures by considering the hierarchical nature and dynamics of skeletal gait data. Meanwhile, STG-Mamba, an extension of Mamba adapted for skeletal motion data, ensures a continuous propagation of states, facilitating the capture of long-term dependencies while reducing computational complexity. To reduce the number of model parameters and computational costs while maintaining consistency, we propose Cross-Graph Relational Knowledge Distillation, a novel knowledge transfer mechanism that aligns relational information between teacher (large architecture) and student models (small architecture) while using shared memory. This ensures that the interactions and movement patterns of the joints are accurately preserved in the motion sequences. We validate our DynSTG-Mamba on KOA-NM, PD-WALK, and ATAXIA datasets, where it outperforms state-of-the-art approaches by achieving in terms of Accuracy, F1-score, and Recall. Our results highlight the efficiency and robustness of our approach, offering a lightweight yet highly accurate solution for automated gait analysis and movement disorder assessment.
An Improved 3D Skeletons UP-Fall Dataset: Enhancing Data Quality for Efficient Impact Fall Detection
Feb 26, 2025Abstract:Detecting impact where an individual makes contact with the ground within a fall event is crucial in fall detection systems, particularly for elderly care where prompt intervention can prevent serious injuries. The UP-Fall dataset, a key resource in fall detection research, has proven valuable but suffers from limitations in data accuracy and comprehensiveness. These limitations cause confusion in distinguishing between non-impact events, such as sliding, and real falls with impact, where the person actually hits the ground. This confusion compromises the effectiveness of current fall detection systems. This study presents enhancements to the UP-Fall dataset aiming at improving it for impact fall detection by incorporating 3D skeleton data. Our preprocessing techniques ensure high data accuracy and comprehensiveness, enabling a more reliable impact fall detection. Extensive experiments were conducted using various machine learning and deep learning algorithms to benchmark the improved 3D skeletons dataset. The results demonstrate substantial improvements in the performance of fall detection models trained on the enhanced dataset. This contribution aims to enhance the safety and well-being of the elderly population at risk. To support further research and development of building more reliable impact fall detection systems, we have made the improved 3D skeletons UP-Fall dataset publicly available at this link https://zenodo.org/records/12773013.
Improving Pain Classification using Spatio-Temporal Deep Learning Approaches with Facial Expressions
Jan 15, 2025Abstract:Pain management and severity detection are crucial for effective treatment, yet traditional self-reporting methods are subjective and may be unsuitable for non-verbal individuals (people with limited speaking skills). To address this limitation, we explore automated pain detection using facial expressions. Our study leverages deep learning techniques to improve pain assessment by analyzing facial images from the Pain Emotion Faces Database (PEMF). We propose two novel approaches1: (1) a hybrid ConvNeXt model combined with Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) blocks to analyze video frames and predict pain presence, and (2) a Spatio-Temporal Graph Convolution Network (STGCN) integrated with LSTM to process landmarks from facial images for pain detection. Our work represents the first use of the PEMF dataset for binary pain classification and demonstrates the effectiveness of these models through extensive experimentation. The results highlight the potential of combining spatial and temporal features for enhanced pain detection, offering a promising advancement in objective pain assessment methodologies.
A Framework for Building Point Cloud Cleaning, Plane Detection and Semantic Segmentation
Feb 01, 2024



Abstract:This paper presents a framework to address the challenges involved in building point cloud cleaning, plane detection, and semantic segmentation, with the ultimate goal of enhancing building modeling. We focus in the cleaning stage on removing outliers from the acquired point cloud data by employing an adaptive threshold technique based on z-score measure. Following the cleaning process, we perform plane detection using the robust RANSAC paradigm. The goal is to carry out multiple plane segmentations, and to classify segments into distinct categories, such as floors, ceilings, and walls. The resulting segments can generate accurate and detailed point clouds representing the building's architectural elements. Moreover, we address the problem of semantic segmentation, which plays a vital role in the identification and classification of different components within the building, such as walls, windows, doors, roofs, and objects. Inspired by the PointNet architecture, we propose a deep learning architecture for efficient semantic segmentation in buildings. The results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed framework in handling building modeling tasks, paving the way for improved accuracy and efficiency in the field of building modelization.
D-STGCNT: A Dense Spatio-Temporal Graph Conv-GRU Network based on transformer for assessment of patient physical rehabilitation
Dec 21, 2023Abstract:This paper tackles the challenge of automatically assessing physical rehabilitation exercises for patients who perform the exercises without clinician supervision. The objective is to provide a quality score to ensure correct performance and achieve desired results. To achieve this goal, a new graph-based model, the Dense Spatio-Temporal Graph Conv-GRU Network with Transformer, is introduced. This model combines a modified version of STGCN and transformer architectures for efficient handling of spatio-temporal data. The key idea is to consider skeleton data respecting its non-linear structure as a graph and detecting joints playing the main role in each rehabilitation exercise. Dense connections and GRU mechanisms are used to rapidly process large 3D skeleton inputs and effectively model temporal dynamics. The transformer encoder's attention mechanism focuses on relevant parts of the input sequence, making it useful for evaluating rehabilitation exercises. The evaluation of our proposed approach on the KIMORE and UI-PRMD datasets highlighted its potential, surpassing state-of-the-art methods in terms of accuracy and computational time. This resulted in faster and more accurate learning and assessment of rehabilitation exercises. Additionally, our model provides valuable feedback through qualitative illustrations, effectively highlighting the significance of joints in specific exercises.
Machine Learning and Feature Ranking for Impact Fall Detection Event Using Multisensor Data
Dec 21, 2023Abstract:Falls among individuals, especially the elderly population, can lead to serious injuries and complications. Detecting impact moments within a fall event is crucial for providing timely assistance and minimizing the negative consequences. In this work, we aim to address this challenge by applying thorough preprocessing techniques to the multisensor dataset, the goal is to eliminate noise and improve data quality. Furthermore, we employ a feature selection process to identify the most relevant features derived from the multisensor UP-FALL dataset, which in turn will enhance the performance and efficiency of machine learning models. We then evaluate the efficiency of various machine learning models in detecting the impact moment using the resulting data information from multiple sensors. Through extensive experimentation, we assess the accuracy of our approach using various evaluation metrics. Our results achieve high accuracy rates in impact detection, showcasing the power of leveraging multisensor data for fall detection tasks. This highlights the potential of our approach to enhance fall detection systems and improve the overall safety and well-being of individuals at risk of falls.
SPDGAN: A Generative Adversarial Network based on SPD Manifold Learning for Automatic Image Colorization
Dec 21, 2023Abstract:This paper addresses the automatic colorization problem, which converts a gray-scale image to a colorized one. Recent deep-learning approaches can colorize automatically grayscale images. However, when it comes to different scenes which contain distinct color styles, it is difficult to accurately capture the color characteristics. In this work, we propose a fully automatic colorization approach based on Symmetric Positive Definite (SPD) Manifold Learning with a generative adversarial network (SPDGAN) that improves the quality of the colorization results. Our SPDGAN model establishes an adversarial game between two discriminators and a generator. The latter is based on ResNet architecture with few alterations. Its goal is to generate fake colorized images without losing color information across layers through residual connections. Then, we employ two discriminators from different domains. The first one is devoted to the image pixel domain, while the second one is to the Riemann manifold domain which helps to avoid color misalignment. Extensive experiments are conducted on the Places365 and COCO-stuff databases to test the effect of each component of our SPDGAN. In addition, quantitative and qualitative comparisons with state-of-the-art methods demonstrate the effectiveness of our model by achieving more realistic colorized images with less artifacts visually, and good results of PSNR, SSIM, and FID values.
MR-STGN: Multi-Residual Spatio Temporal Graph Network Using Attention Fusion for Patient Action Assessment
Dec 21, 2023Abstract:Accurate assessment of patient actions plays a crucial role in healthcare as it contributes significantly to disease progression monitoring and treatment effectiveness. However, traditional approaches to assess patient actions often rely on manual observation and scoring, which are subjective and time-consuming. In this paper, we propose an automated approach for patient action assessment using a Multi-Residual Spatio Temporal Graph Network (MR-STGN) that incorporates both angular and positional 3D skeletons. The MR-STGN is specifically designed to capture the spatio-temporal dynamics of patient actions. It achieves this by integrating information from multiple residual layers, with each layer extracting features at distinct levels of abstraction. Furthermore, we integrate an attention fusion mechanism into the network, which facilitates the adaptive weighting of various features. This empowers the model to concentrate on the most pertinent aspects of the patient's movements, offering precise instructions regarding specific body parts or movements that require attention. Ablation studies are conducted to analyze the impact of individual components within the proposed model. We evaluate our model on the UI-PRMD dataset demonstrating its performance in accurately predicting real-time patient action scores, surpassing state-of-the-art methods.
Movienet: A Movie Multilayer Network Model using Visual and Textual Semantic Cues
Oct 18, 2019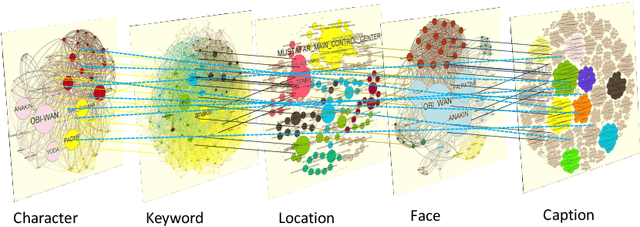
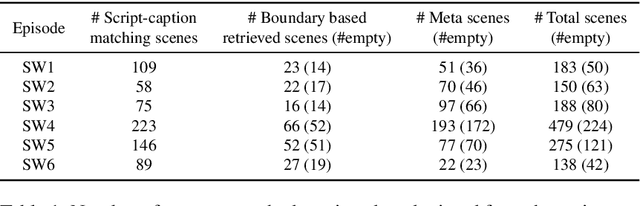
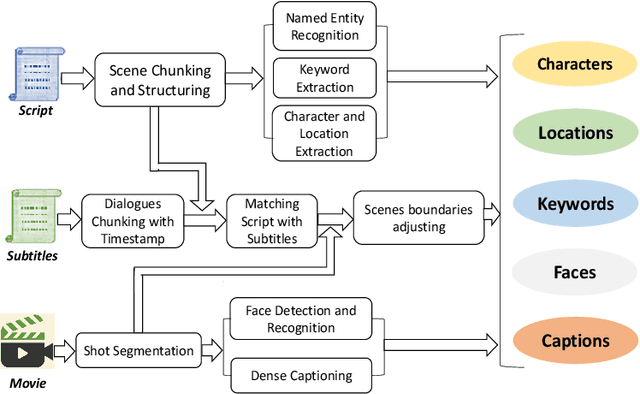
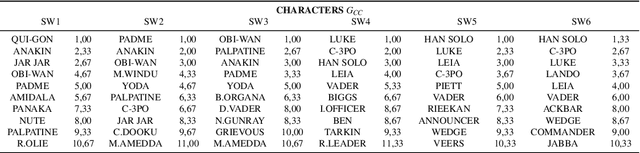
Abstract:Discovering content and stories in movies is one of the most important concepts in multimedia content research studies. Network models have proven to be an efficient choice for this purpose. When an audience watches a movie, they usually compare the characters and the relationships between them. For this reason, most of the models developed so far are based on social networks analysis. They focus essentially on the characters at play. By analyzing characters' interactions, we can obtain a broad picture of the narration's content. Other works have proposed to exploit semantic elements such as scenes, dialogues, etc. However, they are always captured from a single facet. Motivated by these limitations, we introduce in this work a multilayer network model to capture the narration of a movie based on its script, its subtitles, and the movie content. After introducing the model and the extraction process from the raw data, we perform a comparative analysis of the whole 6-movie cycle of the Star Wars saga. Results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed framework for video content representation and analysis.
A General Framework for Complex Network-Based Image Segmentation
Jul 04, 2019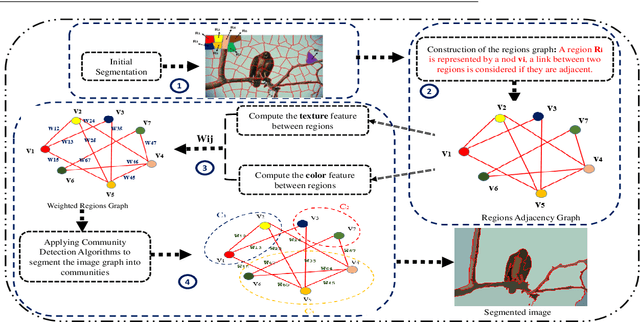
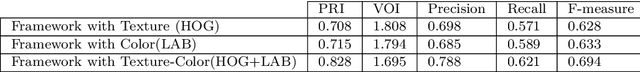
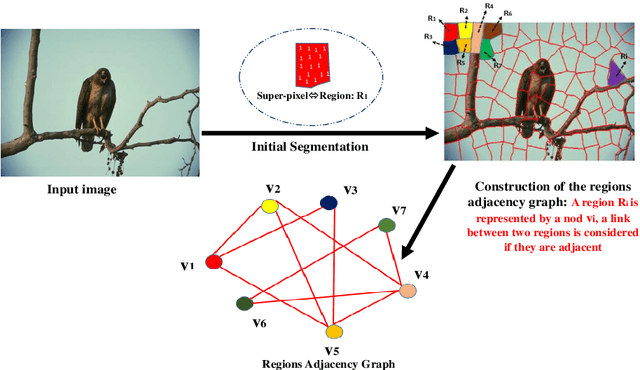
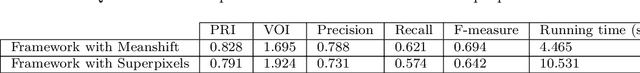
Abstract:With the recent advances in complex networks theory, graph-based techniques for image segmentation has attracted great attention recently. In order to segment the image into meaningful connected components, this paper proposes an image segmentation general framework using complex networks based community detection algorithms. If we consider regions as communities, using community detection algorithms directly can lead to an over-segmented image. To address this problem, we start by splitting the image into small regions using an initial segmentation. The obtained regions are used for building the complex network. To produce meaningful connected components and detect homogeneous communities, some combinations of color and texture based features are employed in order to quantify the regions similarities. To sum up, the network of regions is constructed adaptively to avoid many small regions in the image, and then, community detection algorithms are applied on the resulting adaptive similarity matrix to obtain the final segmented image. Experiments are conducted on Berkeley Segmentation Dataset and four of the most influential community detection algorithms are tested. Experimental results have shown that the proposed general framework increases the segmentation performances compared to some existing methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge