Youngsub Eom
AI-based automated Meibomian gland segmentation, classification and reflection correction in infrared Meibography
May 31, 2022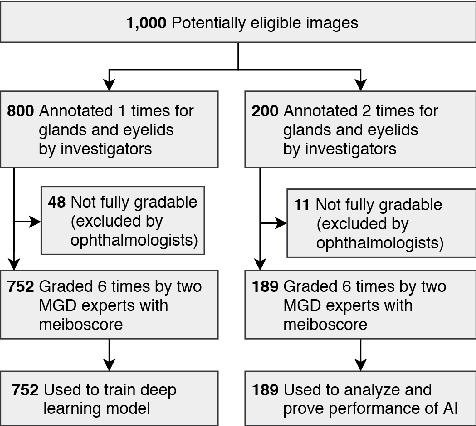
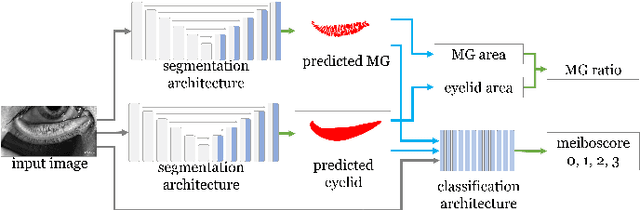
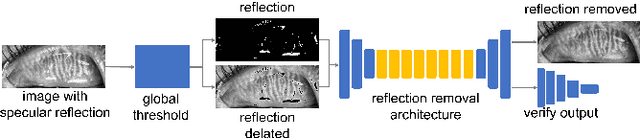
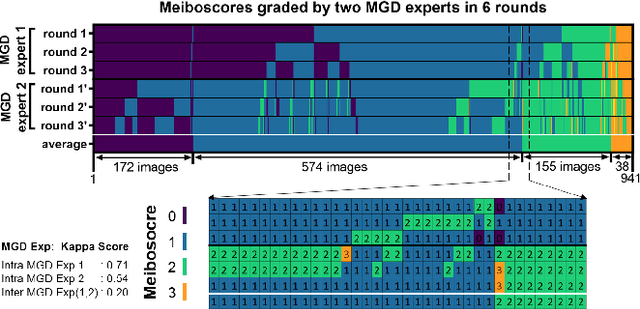
Abstract:Purpose: Develop a deep learning-based automated method to segment meibomian glands (MG) and eyelids, quantitatively analyze the MG area and MG ratio, estimate the meiboscore, and remove specular reflections from infrared images. Methods: A total of 1600 meibography images were captured in a clinical setting. 1000 images were precisely annotated with multiple revisions by investigators and graded 6 times by meibomian gland dysfunction (MGD) experts. Two deep learning (DL) models were trained separately to segment areas of the MG and eyelid. Those segmentation were used to estimate MG ratio and meiboscores using a classification-based DL model. A generative adversarial network was implemented to remove specular reflections from original images. Results: The mean ratio of MG calculated by investigator annotation and DL segmentation was consistent 26.23% vs 25.12% in the upper eyelids and 32.34% vs. 32.29% in the lower eyelids, respectively. Our DL model achieved 73.01% accuracy for meiboscore classification on validation set and 59.17% accuracy when tested on images from independent center, compared to 53.44% validation accuracy by MGD experts. The DL-based approach successfully removes reflection from the original MG images without affecting meiboscore grading. Conclusions: DL with infrared meibography provides a fully automated, fast quantitative evaluation of MG morphology (MG Segmentation, MG area, MG ratio, and meiboscore) which are sufficiently accurate for diagnosing dry eye disease. Also, the DL removes specular reflection from images to be used by ophthalmologists for distraction-free assessment.
TRk-CNN: Transferable Ranking-CNN for image classification of glaucoma, glaucoma suspect, and normal eyes
May 16, 2019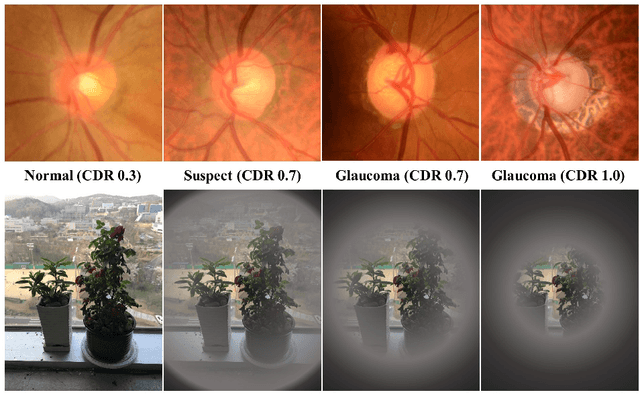
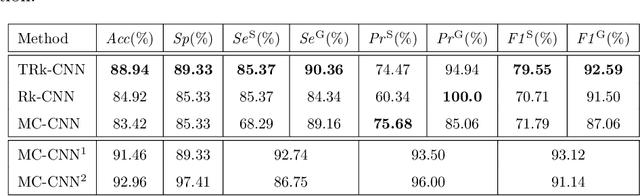
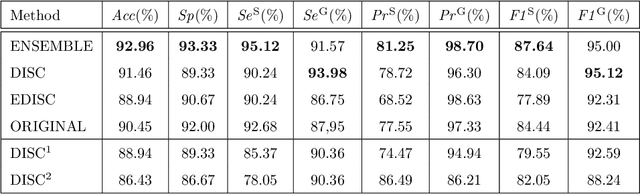
Abstract:In this paper, we proposed Transferable Ranking Convolutional Neural Network (TRk-CNN) that can be effectively applied when the classes of images to be classified show a high correlation with each other. The multi-class classification method based on the softmax function, which is generally used, is not effective in this case because the inter-class relationship is ignored. Although there is a Ranking-CNN that takes into account the ordinal classes, it cannot reflect the inter-class relationship to the final prediction. TRk-CNN, on the other hand, combines the weights of the primitive classification model to reflect the inter-class information to the final classification phase. We evaluated TRk-CNN in glaucoma image dataset that was labeled into three classes: normal, glaucoma suspect, and glaucoma eyes. Based on the literature we surveyed, this study is the first to classify three status of glaucoma fundus image dataset into three different classes. We compared the evaluation results of TRk-CNN with Ranking-CNN (Rk-CNN) and multi-class CNN (MC-CNN) using the DenseNet as the backbone CNN model. As a result, TRk-CNN achieved an average accuracy of 92.96%, specificity of 93.33%, sensitivity for glaucoma suspect of 95.12% and sensitivity for glaucoma of 93.98%. Based on average accuracy, TRk-CNN is 8.04% and 9.54% higher than Rk-CNN and MC-CNN and surprisingly 26.83% higher for sensitivity for suspicious than multi-class CNN. Our TRk-CNN is expected to be effectively applied to the medical image classification problem where the disease state is continuous and increases in the positive class direction.
Tournament Based Ranking CNN for the Cataract grading
Jul 07, 2018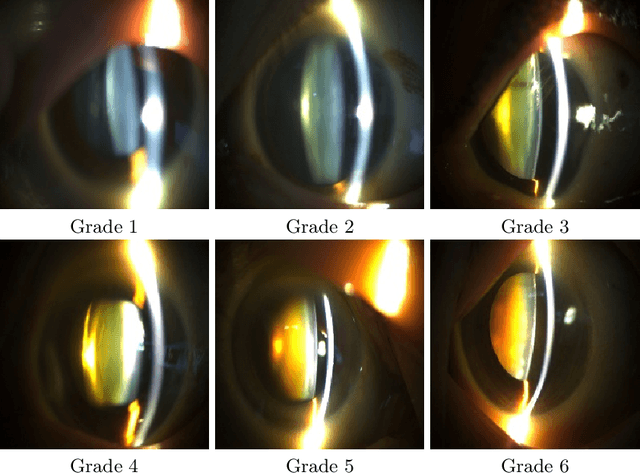
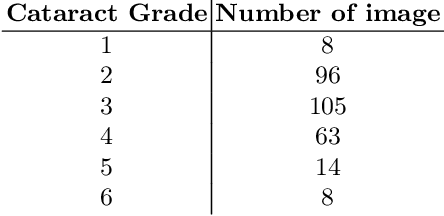
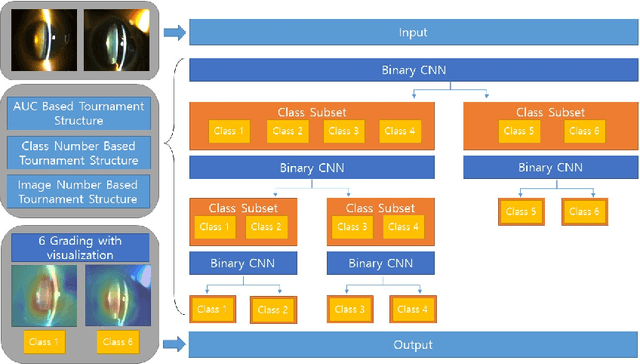
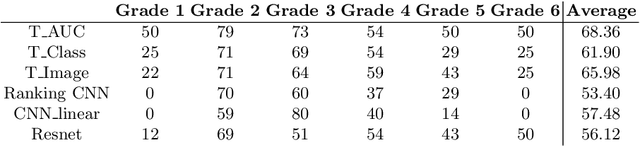
Abstract:Solving the classification problem, unbalanced number of dataset among the classes often causes performance degradation. Especially when some classes dominate the other classes with its large number of datasets, trained model shows low performance in identifying the dominated classes. This is common case when it comes to medical dataset. Because the case with a serious degree is not quite usual, there are imbalance in number of dataset between severe case and normal cases of diseases. Also, there is difficulty in precisely identifying grade of medical data because of vagueness between them. To solve these problems, we propose new architecture of convolutional neural network named Tournament based Ranking CNN which shows remarkable performance gain in identifying dominated classes while trading off very small accuracy loss in dominating classes. Our Approach complemented problems that occur when method of Ranking CNN that aggregates outputs of multiple binary neural network models is applied to medical data. By having tournament structure in aggregating method and using very deep pretrained binary models, our proposed model recorded 68.36% of exact match accuracy, while Ranking CNN recorded 53.40%, pretrained Resnet recorded 56.12% and CNN with linear regression recorded 57.48%. As a result, our proposed method is applied efficiently to cataract grading which have ordinal labels with imbalanced number of data among classes, also can be applied further to medical problems which have similar features to cataract and similar dataset configuration.
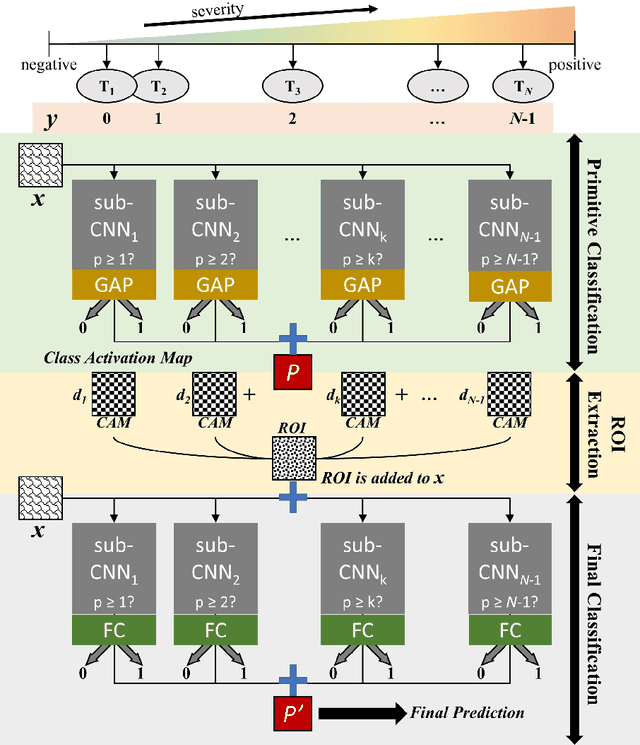
2sRanking-CNN: A 2-stage ranking-CNN for diagnosis of glaucoma from fundus images using CAM-extracted ROI as an intermediate input
Jul 04, 2018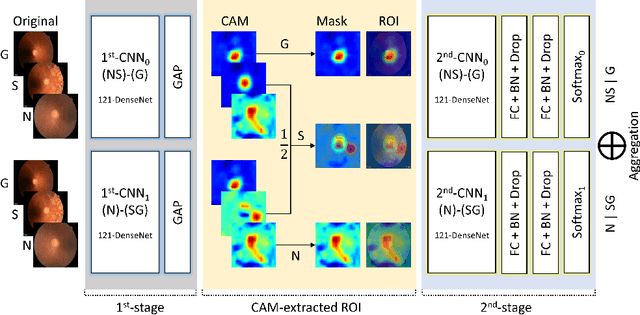
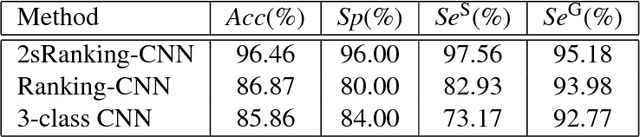
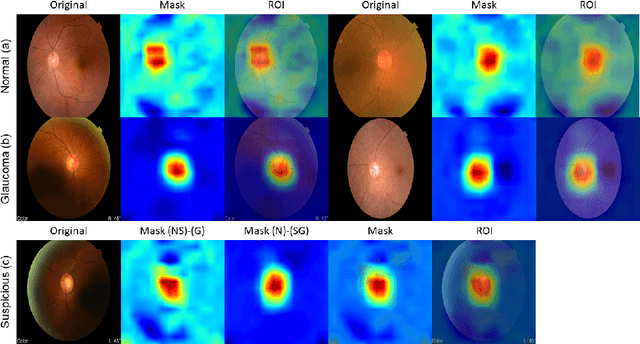
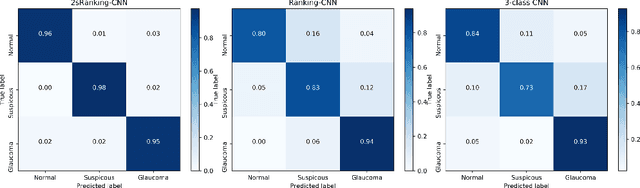
Abstract:Glaucoma is a disease in which the optic nerve is chronically damaged by the elevation of the intra-ocular pressure, resulting in visual field defect. Therefore, it is important to monitor and treat suspected patients before they are confirmed with glaucoma. In this paper, we propose a 2-stage ranking-CNN that classifies fundus images as normal, suspicious, and glaucoma. Furthermore, we propose a method of using the class activation map as a mask filter and combining it with the original fundus image as an intermediate input. Our results have improved the average accuracy by about 10% over the existing 3-class CNN and ranking-CNN, and especially improved the sensitivity of suspicious class by more than 20% over 3-class CNN. In addition, the extracted ROI was also found to overlap with the diagnostic criteria of the physician. The method we propose is expected to be efficiently applied to any medical data where there is a suspicious condition between normal and disease.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge