Young-Chul Yoon
Online Multi-Object Tracking Framework with the GMPHD Filter and Occlusion Group Management
Jul 31, 2019



Abstract:In this paper, we propose an efficient online multi-object tracking framework based on the GMPHD filter and occlusion group management scheme where the GMPHD filter utilizes hierarchical data association to reduce the false negatives caused by miss detection. The hierarchical data association consists of two steps: detection-to-track and track-to-track associations, which can recover the lost tracks and their switched IDs. In addition, the proposed framework is equipped with an object grouping management scheme which handles occlusion problems with two main parts. The first part is "track merging" which can merge the false positive tracks caused by false positive detections from occlusions, where the false positive tracks are usually occluded with a measure. The measure is the occlusion ratio between visual objects, sum-of-intersection-over-area (SIOA) we defined instead of the IOU metric. The second part is "occlusion group energy minimization (OGEM)" which prevents the occluded true positive tracks from false "track merging". We define each group of the occluded objects as an energy function and find an optimal hypothesis which makes the energy minimal. We evaluate the proposed tracker in benchmark datasets such as MOT15 and MOT17 which are built for multi-person tracking. An ablation study in training dataset shows that not only "track merging" and "OGEM" complement each other but also the proposed tracking method has more robust performance and less sensitive to parameters than baseline methods. Also, SIOA works better than IOU for various sizes of false positives. Experimental results show that the proposed tracker efficiently handles occlusion situations and achieves competitive performance compared to the state-of-the-art methods. Especially, our method shows the best multi-object tracking accuracy among the online and real-time executable methods.
Online Multiple Pedestrian Tracking using Deep Temporal Appearance Matching Association
Jul 01, 2019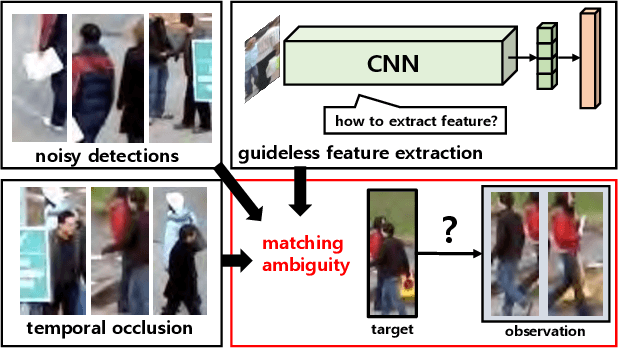
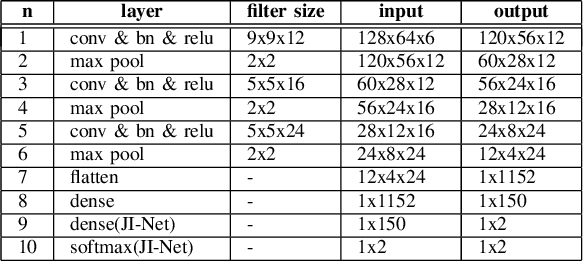
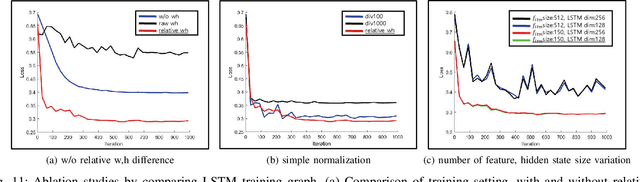
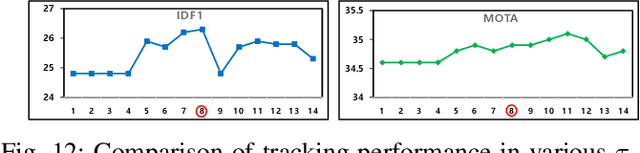
Abstract:In online multiple pedestrian tracking it is of great importance to construct reliable cost matrix for assigning observations to tracks. Each element of cost matrix is constructed by using similarity measure. Many previous works have proposed their own similarity calculation methods consisting of geometric model (e.g. bounding box coordinates) and appearance model. In particular, appearance model contains information with higher dimension compared to geometric model. Thanks to the recent success of deep learning based methods, handling of high dimensional appearance information becomes possible. Among many deep networks, a siamese network with triplet loss is popularly adopted as an appearance feature extractor. Since the siamese network can extract features of each input independently, it is possible to adaptively model tracks (e.g. linear update). However, it is not suitable for multi-object setting that requires comparison with other inputs. In this paper we propose a novel track appearance modeling based on joint inference network to address this issue. The proposed method enables comparison of two inputs to be used for adaptive appearance modeling. It contributes to disambiguating target-observation matching and consolidating the identity consistency. Intensive experimental results support effectiveness of our method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge