Yongjin Jeon
Focus or Not: A Baseline for Anomaly Event Detection On the Open Public Places with Satellite Images
Mar 21, 2023Abstract:In recent years, monitoring the world wide area with satellite images has been emerged as an important issue. Site monitoring task can be divided into two independent tasks; 1) Change Detection and 2) Anomaly Event Detection. Unlike to change detection research is actively conducted based on the numerous datasets(\eg LEVIR-CD, WHU-CD, S2Looking, xView2 and etc...) to meet up the expectations of industries or governments, research on AI models for detecting anomaly events is passively and rarely conducted. In this paper, we introduce a novel satellite imagery dataset(AED-RS) for detecting anomaly events on the open public places. AED-RS Dataset contains satellite images of normal and abnormal situations of 8 open public places from all over the world. Each places are labeled with different criteria based on the difference of characteristics of each places. With this dataset, we introduce a baseline model for our dataset TB-FLOW, which can be trained in weakly-supervised manner and shows reasonable performance on the AED-RS Dataset compared with the other NF(Normalizing-Flow) based anomaly detection models. Our dataset and code will be publicly open in \url{https://github.com/SIAnalytics/RS_AnomalyDetection.git}.
Self-Pair: Synthesizing Changes from Single Source for Object Change Detection in Remote Sensing Imagery
Dec 20, 2022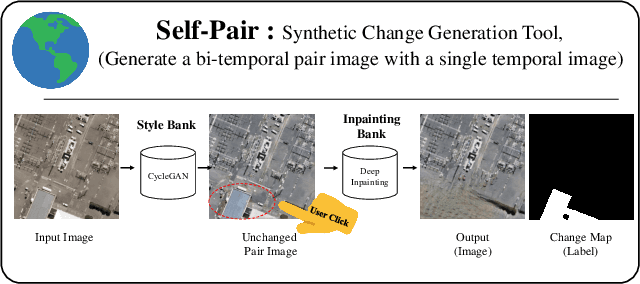
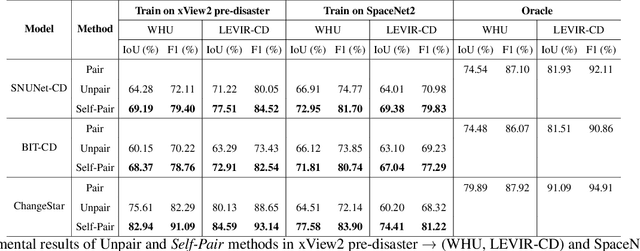
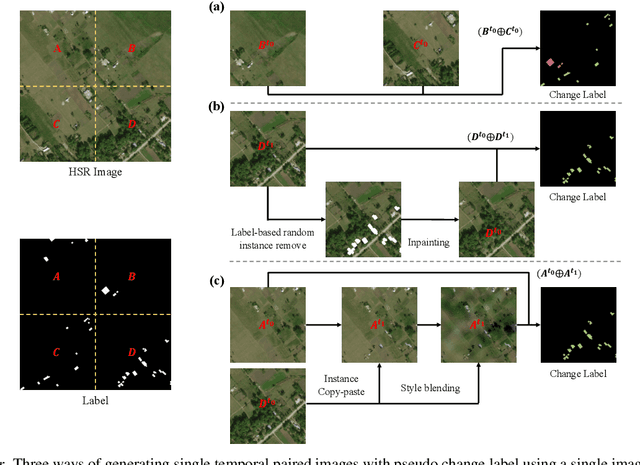
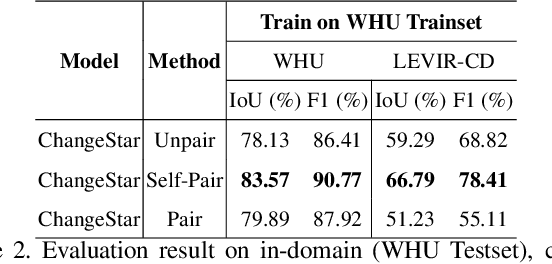
Abstract:For change detection in remote sensing, constructing a training dataset for deep learning models is difficult due to the requirements of bi-temporal supervision. To overcome this issue, single-temporal supervision which treats change labels as the difference of two semantic masks has been proposed. This novel method trains a change detector using two spatially unrelated images with corresponding semantic labels such as building. However, training on unpaired datasets could confuse the change detector in the case of pixels that are labeled unchanged but are visually significantly different. In order to maintain the visual similarity in unchanged area, in this paper, we emphasize that the change originates from the source image and show that manipulating the source image as an after-image is crucial to the performance of change detection. Extensive experiments demonstrate the importance of maintaining visual information between pre- and post-event images, and our method outperforms existing methods based on single-temporal supervision. code is available at https://github.com/seominseok0429/Self-Pair-for-Change-Detection.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge