Yongbin You
MSR-86K: An Evolving, Multilingual Corpus with 86,300 Hours of Transcribed Audio for Speech Recognition Research
Jun 26, 2024
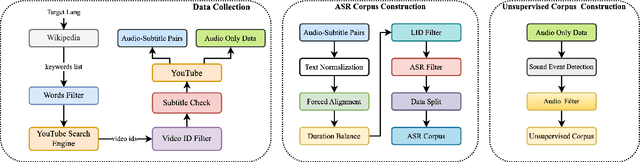


Abstract:Recently, multilingual artificial intelligence assistants, exemplified by ChatGPT, have gained immense popularity. As a crucial gateway to human-computer interaction, multilingual automatic speech recognition (ASR) has also garnered significant attention, as evidenced by systems like Whisper. However, the proprietary nature of the training data has impeded researchers' efforts to study multilingual ASR. This paper introduces MSR-86K, an evolving, large-scale multilingual corpus for speech recognition research. The corpus is derived from publicly accessible videos on YouTube, comprising 15 languages and a total of 86,300 hours of transcribed ASR data. We also introduce how to use the MSR-86K corpus and other open-source corpora to train a robust multilingual ASR model that is competitive with Whisper. MSR-86K will be publicly released on HuggingFace, and we believe that such a large corpus will pave new avenues for research in multilingual ASR.
Enhancing Multilingual Speech Recognition through Language Prompt Tuning and Frame-Level Language Adapter
Sep 19, 2023

Abstract:Multilingual intelligent assistants, such as ChatGPT, have recently gained popularity. To further expand the applications of multilingual artificial intelligence assistants and facilitate international communication, it is essential to enhance the performance of multilingual speech recognition, which is a crucial component of speech interaction. In this paper, we propose two simple and parameter-efficient methods: language prompt tuning and frame-level language adapter, to respectively enhance language-configurable and language-agnostic multilingual speech recognition. Additionally, we explore the feasibility of integrating these two approaches using parameter-efficient fine-tuning methods. Our experiments demonstrate significant performance improvements across seven languages using our proposed methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge