Yo-Seb Jeon
Context-Aware Iterative Token Detection and Masked Transmission for Wireless Token Communication
Jan 25, 2026Abstract:The success of large-scale language models has established tokens as compact and meaningful units for natural-language representation, which motivates token communication over wireless channels, where tokens are considered fundamental units for wireless transmission. We propose a context-aware token communication framework that uses a pretrained masked language model (MLM) as a shared contextual probability model between the transmitter (Tx) and receiver (Rx). At Rx, we develop an iterative token detection method that jointly exploits MLM-guided contextual priors and channel observations based on a Bayesian perspective. At Tx, we additionally introduce a context-aware masking strategy which skips highly predictable token transmission to reduce transmission rate. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed framework substantially improves reconstructed sentence quality and supports effective rate adaptation under various channel conditions.
Beam-Squint-Aided Hierarchical Sensing for Integrated Sensing and Communications with Uniform Planar Arrays
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel hierarchical sensing framework for wideband integrated sensing and communications with uniform planar arrays (UPAs). Leveraging the beam-squint effect inherent in wideband orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) systems, the proposed framework enables efficient two-dimensional angle estimation through a structured multi-stage sensing process. Specifically, the sensing procedure first searches over the elevation angle domain, followed by a dedicated search over the azimuth angle domain given the estimated elevation angles. In each stage, true-time-delay lines and phase shifters of the UPA are jointly configured to cover multiple grid points simultaneously across OFDM subcarriers. To enable accurate and efficient target localization, we formulate the angle estimation problem as a sparse signal recovery problem and develop a modified matching pursuit algorithm tailored to the hierarchical sensing architecture. Additionally, we design power allocation strategies that minimize total transmit power while meeting performance requirements for both sensing and communication. Numerical results demonstrate that the proposed framework achieves superior performance over conventional sensing methods with reduced sensing power.
Importance-Aware Semantic Communication in MIMO-OFDM Systems Using Vision Transformer
Aug 11, 2025Abstract:This paper presents a novel importance-aware quantization, subcarrier mapping, and power allocation (IA-QSMPA) framework for semantic communication in multiple-input multiple-output orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (MIMO-OFDM) systems, empowered by a pretrained Vision Transformer (ViT). The proposed framework exploits attention-based importance extracted from a pretrained ViT to jointly optimize quantization levels, subcarrier mapping, and power allocation. Specifically, IA-QSMPA maps semantically important features to high-quality subchannels and allocates resources in accordance with their contribution to task performance and communication latency. To efficiently solve the resulting nonconvex optimization problem, a block coordinate descent algorithm is employed. The framework is further extended to operate under finite blocklength transmission, where communication errors may occur. In this setting, a segment-wise linear approximation of the channel dispersion penalty is introduced to enable efficient joint optimization under practical constraints. Simulation results on a multi-view image classification task using the MVP-N dataset demonstrate that IA-QSMPA significantly outperforms conventional methods in both ideal and finite blocklength transmission scenarios, achieving superior task performance and communication efficiency.
Deep Learning-Based CSI Feedback for Wi-Fi Systems With Temporal Correlation
May 29, 2025Abstract:To achieve higher throughput in next-generation Wi-Fi systems, a station (STA) needs to efficiently compress channel state information (CSI) and feed it back to an access point (AP). In this paper, we propose a novel deep learning (DL)-based CSI feedback framework tailored for next-generation Wi-Fi systems. Our framework incorporates a pair of encoder and decoder neural networks to compress and reconstruct the angle parameters of the CSI. To enable an efficient finite-bit representation of the encoder output, we introduce a trainable vector quantization module, which is integrated after the encoder network and jointly trained with both the encoder and decoder networks in an end-to-end manner. Additionally, we further enhance our framework by leveraging the temporal correlation of the angle parameters. Specifically, we propose an angle-difference feedback strategy which transmits the difference between the current and previous angle parameters when the difference is sufficiently small. This strategy accounts for the periodicity of the angle parameters through proper preprocessing and mitigates error propagation effects using novel feedback methods. We also introduce a DL-based CSI refinement module for the AP, which improves the reconstruction accuracy of the angle parameters by simultaneously utilizing both the previous and current feedback information. Simulation results demonstrate that our framework outperforms the standard method employed in current Wi-Fi systems. Our results also demonstrate significant performance gains achieved by the angle-difference feedback strategy and the CSI refinement module.
ESC-MVQ: End-to-End Semantic Communication With Multi-Codebook Vector Quantization
Apr 16, 2025Abstract:This paper proposes a novel end-to-end digital semantic communication framework based on multi-codebook vector quantization (VQ), referred to as ESC-MVQ. Unlike prior approaches that rely on end-to-end training with a specific power or modulation scheme, often under a particular channel condition, ESC-MVQ models a channel transfer function as parallel binary symmetric channels (BSCs) with trainable bit-flip probabilities. Building on this model, ESC-MVQ jointly trains multiple VQ codebooks and their associated bit-flip probabilities with a single encoder-decoder pair. To maximize inference performance when deploying ESC-MVQ in digital communication systems, we devise an optimal communication strategy that jointly optimizes codebook assignment, adaptive modulation, and power allocation. To this end, we develop an iterative algorithm that selects the most suitable VQ codebook for semantic features and flexibly allocates power and modulation schemes across the transmitted symbols. Simulation results demonstrate that ESC-MVQ, using a single encoder-decoder pair, outperforms existing digital semantic communication methods in both performance and memory efficiency, offering a scalable and adaptive solution for realizing digital semantic communication in diverse channel conditions.
Robust Deep Joint Source Channel Coding for Task-Oriented Semantic Communications
Mar 17, 2025Abstract:Semantic communications based on deep joint source-channel coding (JSCC) aim to improve communication efficiency by transmitting only task-relevant information. However, ensuring robustness to the stochasticity of communication channels remains a key challenge in learning-based JSCC. In this paper, we propose a novel regularization technique for learning-based JSCC to enhance robustness against channel noise. The proposed method utilizes the Kullback-Leibler (KL) divergence as a regularizer term in the training loss, measuring the discrepancy between two posterior distributions: one under noisy channel conditions (noisy posterior) and one for a noise-free system (noise-free posterior). Reducing this KL divergence mitigates the impact of channel noise on task performance by keeping the noisy posterior close to the noise-free posterior. We further show that the expectation of the KL divergence given the encoded representation can be analytically approximated using the Fisher information matrix and the covariance matrix of the channel noise. Notably, the proposed regularization is architecture-agnostic, making it broadly applicable to general semantic communication systems over noisy channels. Our experimental results validate that the proposed regularization consistently improves task performance across diverse semantic communication systems and channel conditions.
Digital Deep Joint Source-Channel Coding with Blind Training for Adaptive Modulation and Power Control
Jan 04, 2025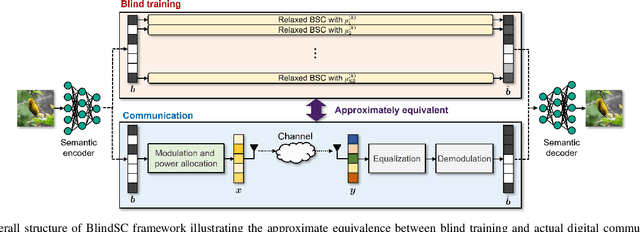
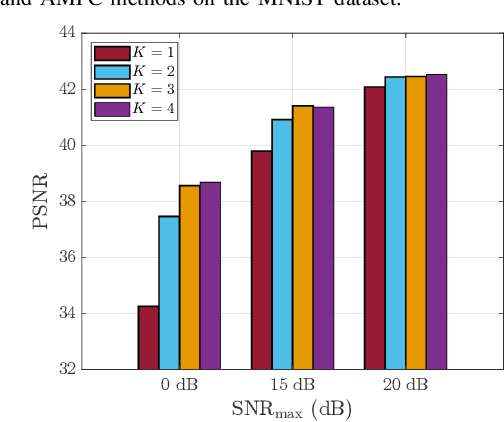
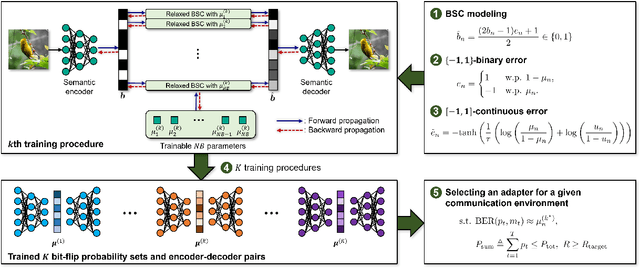
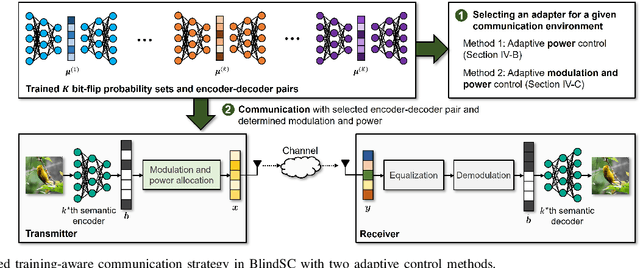
Abstract:This paper proposes a novel digital deep joint source-channel coding (DeepJSCC) framework that achieves robust performance across diverse communication environments without requiring extensive retraining and prior knowledge of communication environments. Traditional digital DeepJSCC techniques often face challenges in adapting to various communication environments, as they require significant training overhead and large amounts of communication data to develop either multiple specialized models or a single generalized model, in pre-defined communication environments. To address this challenge, in our framework, an error-adaptive blind training strategy is devised, which eliminates the need for prior knowledge of communication environments. This is achieved by modeling the relationship between the encoder's output and the decoder's input using binary symmetric channels, and optimizing bit-flip probabilities by treating them as trainable parameters. In our framework, a training-aware communication strategy is also presented, which dynamically selects the optimal encoder-decoder pair and transmission parameters based on current channel conditions. In particular, in this strategy, an adaptive power and modulation control method is developed to minimize the total transmission power, while maintaining high task performance. Simulation results demonstrate that our framework outperforms existing DeepJSCC methods, achieving higher peak signal-to-noise ratio, lower power consumption, and requiring significantly fewer encoder-decoder pairs for adaptation.
Vision Transformer-based Semantic Communications With Importance-Aware Quantization
Dec 08, 2024Abstract:Semantic communications provide significant performance gains over traditional communications by transmitting task-relevant semantic features through wireless channels. However, most existing studies rely on end-to-end (E2E) training of neural-type encoders and decoders to ensure effective transmission of these semantic features. To enable semantic communications without relying on E2E training, this paper presents a vision transformer (ViT)-based semantic communication system with importance-aware quantization (IAQ) for wireless image transmission. The core idea of the presented system is to leverage the attention scores of a pretrained ViT model to quantify the importance levels of image patches. Based on this idea, our IAQ framework assigns different quantization bits to image patches based on their importance levels. This is achieved by formulating a weighted quantization error minimization problem, where the weight is set to be an increasing function of the attention score. Then, an optimal incremental allocation method and a low-complexity water-filling method are devised to solve the formulated problem. Our framework is further extended for realistic digital communication systems by modifying the bit allocation problem and the corresponding allocation methods based on an equivalent binary symmetric channel (BSC) model. Simulations on single-view and multi-view image classification tasks show that our IAQ framework outperforms conventional image compression methods in both error-free and realistic communication scenarios.
Vector Quantization for Deep-Learning-Based CSI Feedback in Massive MIMO Systems
Mar 13, 2024Abstract:This paper presents a finite-rate deep-learning (DL)-based channel state information (CSI) feedback method for massive multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) systems. The presented method provides a finite-bit representation of the latent vector based on a vector-quantized variational autoencoder (VQ-VAE) framework while reducing its computational complexity based on shape-gain vector quantization. In this method, the magnitude of the latent vector is quantized using a non-uniform scalar codebook with a proper transformation function, while the direction of the latent vector is quantized using a trainable Grassmannian codebook. A multi-rate codebook design strategy is also developed by introducing a codeword selection rule for a nested codebook along with the design of a loss function. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed method reduces the computational complexity associated with VQ-VAE while improving CSI reconstruction performance under a given feedback overhead.
Deep Learning-Assisted Parallel Interference Cancellation for Grant-Free NOMA in Machine-Type Communication
Mar 12, 2024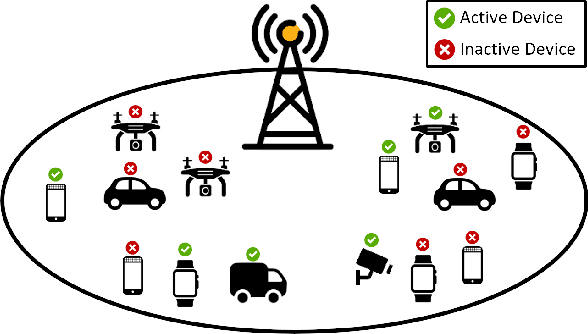
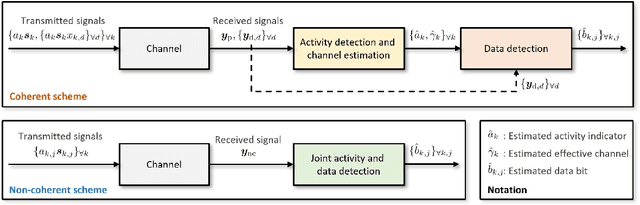
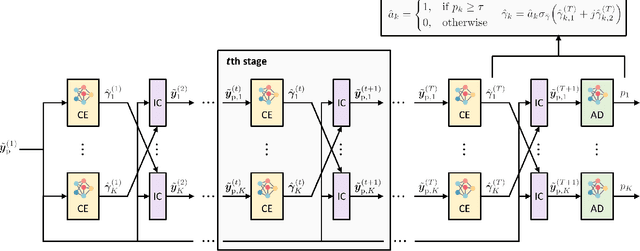
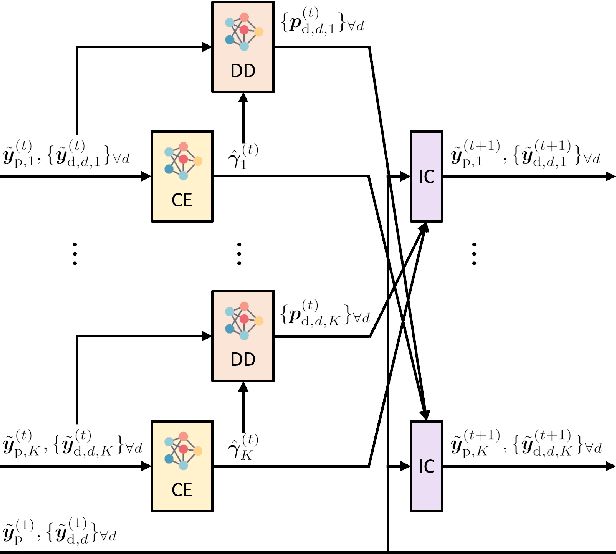
Abstract:In this paper, we present a novel approach for joint activity detection (AD), channel estimation (CE), and data detection (DD) in uplink grant-free non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) systems. Our approach employs an iterative and parallel interference removal strategy inspired by parallel interference cancellation (PIC), enhanced with deep learning to jointly tackle the AD, CE, and DD problems. Based on this approach, we develop three PIC frameworks, each of which is designed for either coherent or non-coherence schemes. The first framework performs joint AD and CE using received pilot signals in the coherent scheme. Building upon this framework, the second framework utilizes both the received pilot and data signals for CE, further enhancing the performances of AD, CE, and DD in the coherent scheme. The third framework is designed to accommodate the non-coherent scheme involving a small number of data bits, which simultaneously performs AD and DD. Through joint loss functions and interference cancellation modules, our approach supports end-to-end training, contributing to enhanced performances of AD, CE, and DD for both coherent and non-coherent schemes. Simulation results demonstrate the superiority of our approach over traditional techniques, exhibiting enhanced performances of AD, CE, and DD while maintaining lower computational complexity.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge