Yixin Shen
Towards Automated Kernel Generation in the Era of LLMs
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:The performance of modern AI systems is fundamentally constrained by the quality of their underlying kernels, which translate high-level algorithmic semantics into low-level hardware operations. Achieving near-optimal kernels requires expert-level understanding of hardware architectures and programming models, making kernel engineering a critical but notoriously time-consuming and non-scalable process. Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) and LLM-based agents have opened new possibilities for automating kernel generation and optimization. LLMs are well-suited to compress expert-level kernel knowledge that is difficult to formalize, while agentic systems further enable scalable optimization by casting kernel development as an iterative, feedback-driven loop. Rapid progress has been made in this area. However, the field remains fragmented, lacking a systematic perspective for LLM-driven kernel generation. This survey addresses this gap by providing a structured overview of existing approaches, spanning LLM-based approaches and agentic optimization workflows, and systematically compiling the datasets and benchmarks that underpin learning and evaluation in this domain. Moreover, key open challenges and future research directions are further outlined, aiming to establish a comprehensive reference for the next generation of automated kernel optimization. To keep track of this field, we maintain an open-source GitHub repository at https://github.com/flagos-ai/awesome-LLM-driven-kernel-generation.
Open-Source Multimodal Moxin Models with Moxin-VLM and Moxin-VLA
Dec 22, 2025Abstract:Recently, Large Language Models (LLMs) have undergone a significant transformation, marked by a rapid rise in both their popularity and capabilities. Leading this evolution are proprietary LLMs like GPT-4 and GPT-o1, which have captured widespread attention in the AI community due to their remarkable performance and versatility. Simultaneously, open-source LLMs, such as LLaMA and Mistral, have made great contributions to the ever-increasing popularity of LLMs due to the ease to customize and deploy the models across diverse applications. Moxin 7B is introduced as a fully open-source LLM developed in accordance with the Model Openness Framework, which moves beyond the simple sharing of model weights to embrace complete transparency in training, datasets, and implementation detail, thus fostering a more inclusive and collaborative research environment that can sustain a healthy open-source ecosystem. To further equip Moxin with various capabilities in different tasks, we develop three variants based on Moxin, including Moxin-VLM, Moxin-VLA, and Moxin-Chinese, which target the vision-language, vision-language-action, and Chinese capabilities, respectively. Experiments show that our models achieve superior performance in various evaluations. We adopt open-source framework and open data for the training. We release our models, along with the available data and code to derive these models.
Optimal Sampling for Generalized Linear Model under Measurement Constraint with Surrogate Variables
Jan 01, 2025



Abstract:Measurement-constrained datasets, often encountered in semi-supervised learning, arise when data labeling is costly, time-intensive, or hindered by confidentiality or ethical concerns, resulting in a scarcity of labeled data. In certain cases, surrogate variables are accessible across the entire dataset and can serve as approximations to the true response variable; however, these surrogates often contain measurement errors and thus cannot be directly used for accurate prediction. We propose an optimal sampling strategy that effectively harnesses the available information from surrogate variables. This approach provides consistent estimators under the assumption of a generalized linear model, achieving theoretically lower asymptotic variance than existing optimal sampling algorithms that do not leverage surrogate data. By employing the A-optimality criterion from optimal experimental design, our strategy maximizes statistical efficiency. Numerical studies demonstrate that our approach surpasses existing optimal sampling methods, exhibiting reduced empirical mean squared error and enhanced robustness in algorithmic performance. These findings highlight the practical advantages of our strategy in scenarios where measurement constraints exist and surrogates are available.
Fully Open Source Moxin-7B Technical Report
Dec 08, 2024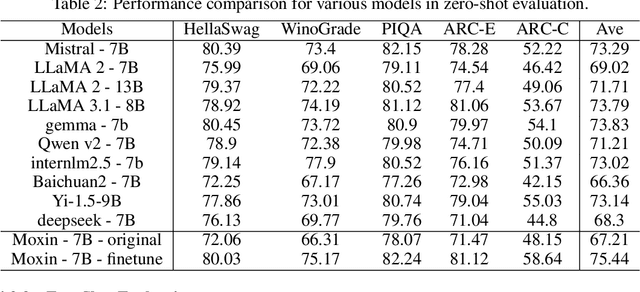
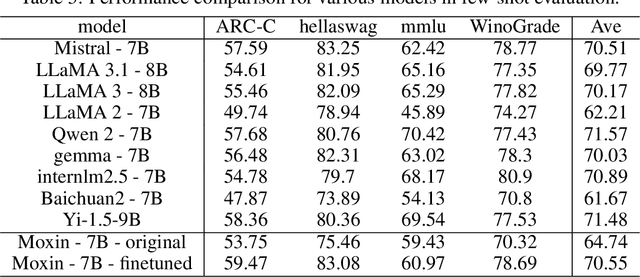


Abstract:Recently, Large Language Models (LLMs) have undergone a significant transformation, marked by a rapid rise in both their popularity and capabilities. Leading this evolution are proprietary LLMs like GPT-4 and GPT-o1, which have captured widespread attention in the AI community due to their remarkable performance and versatility. Simultaneously, open-source LLMs, such as LLaMA and Mistral, have made great contributions to the ever-increasing popularity of LLMs due to the ease to customize and deploy the models across diverse applications. Although open-source LLMs present unprecedented opportunities for innovation and research, the commercialization of LLMs has raised concerns about transparency, reproducibility, and safety. Many open-source LLMs fail to meet fundamental transparency requirements by withholding essential components like training code and data, and some use restrictive licenses whilst claiming to be "open-source," which may hinder further innovations on LLMs. To mitigate this issue, we introduce Moxin 7B, a fully open-source LLM developed in accordance with the Model Openness Framework (MOF), a ranked classification system that evaluates AI models based on model completeness and openness, adhering to principles of open science, open source, open data, and open access. Our model achieves the highest MOF classification level of "open science" through the comprehensive release of pre-training code and configurations, training and fine-tuning datasets, and intermediate and final checkpoints. Experiments show that our model achieves superior performance in zero-shot evaluation compared with popular 7B models and performs competitively in few-shot evaluation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge