Yixian Xu
Luminark: Training-free, Probabilistically-Certified Watermarking for General Vision Generative Models
Jan 03, 2026Abstract:In this paper, we introduce \emph{Luminark}, a training-free and probabilistically-certified watermarking method for general vision generative models. Our approach is built upon a novel watermark definition that leverages patch-level luminance statistics. Specifically, the service provider predefines a binary pattern together with corresponding patch-level thresholds. To detect a watermark in a given image, we evaluate whether the luminance of each patch surpasses its threshold and then verify whether the resulting binary pattern aligns with the target one. A simple statistical analysis demonstrates that the false positive rate of the proposed method can be effectively controlled, thereby ensuring certified detection. To enable seamless watermark injection across different paradigms, we leverage the widely adopted guidance technique as a plug-and-play mechanism and develop the \emph{watermark guidance}. This design enables Luminark to achieve generality across state-of-the-art generative models without compromising image quality. Empirically, we evaluate our approach on nine models spanning diffusion, autoregressive, and hybrid frameworks. Across all evaluations, Luminark consistently demonstrates high detection accuracy, strong robustness against common image transformations, and good performance on visual quality.
Diagnosing and Improving Diffusion Models by Estimating the Optimal Loss Value
Jun 16, 2025Abstract:Diffusion models have achieved remarkable success in generative modeling. Despite more stable training, the loss of diffusion models is not indicative of absolute data-fitting quality, since its optimal value is typically not zero but unknown, leading to confusion between large optimal loss and insufficient model capacity. In this work, we advocate the need to estimate the optimal loss value for diagnosing and improving diffusion models. We first derive the optimal loss in closed form under a unified formulation of diffusion models, and develop effective estimators for it, including a stochastic variant scalable to large datasets with proper control of variance and bias. With this tool, we unlock the inherent metric for diagnosing the training quality of mainstream diffusion model variants, and develop a more performant training schedule based on the optimal loss. Moreover, using models with 120M to 1.5B parameters, we find that the power law is better demonstrated after subtracting the optimal loss from the actual training loss, suggesting a more principled setting for investigating the scaling law for diffusion models.
Bridging Geometric States via Geometric Diffusion Bridge
Oct 31, 2024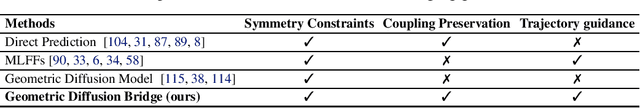

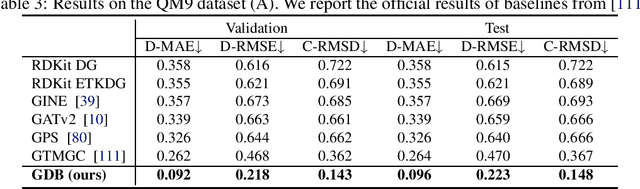
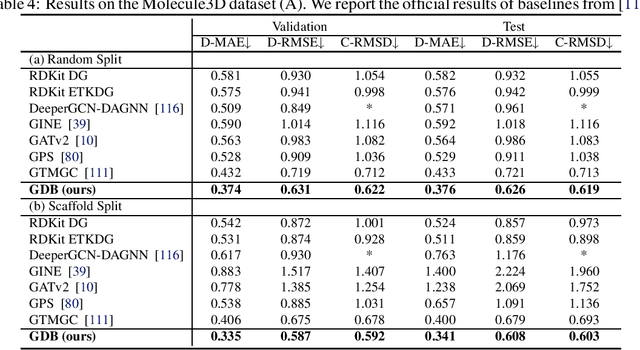
Abstract:The accurate prediction of geometric state evolution in complex systems is critical for advancing scientific domains such as quantum chemistry and material modeling. Traditional experimental and computational methods face challenges in terms of environmental constraints and computational demands, while current deep learning approaches still fall short in terms of precision and generality. In this work, we introduce the Geometric Diffusion Bridge (GDB), a novel generative modeling framework that accurately bridges initial and target geometric states. GDB leverages a probabilistic approach to evolve geometric state distributions, employing an equivariant diffusion bridge derived by a modified version of Doob's $h$-transform for connecting geometric states. This tailored diffusion process is anchored by initial and target geometric states as fixed endpoints and governed by equivariant transition kernels. Moreover, trajectory data can be seamlessly leveraged in our GDB framework by using a chain of equivariant diffusion bridges, providing a more detailed and accurate characterization of evolution dynamics. Theoretically, we conduct a thorough examination to confirm our framework's ability to preserve joint distributions of geometric states and capability to completely model the underlying dynamics inducing trajectory distributions with negligible error. Experimental evaluations across various real-world scenarios show that GDB surpasses existing state-of-the-art approaches, opening up a new pathway for accurately bridging geometric states and tackling crucial scientific challenges with improved accuracy and applicability.
One Transformer Can Understand Both 2D & 3D Molecular Data
Oct 04, 2022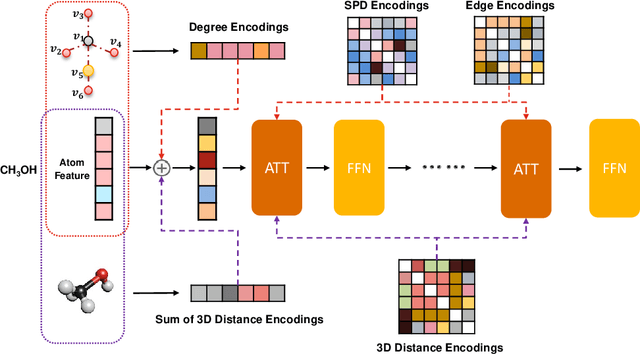
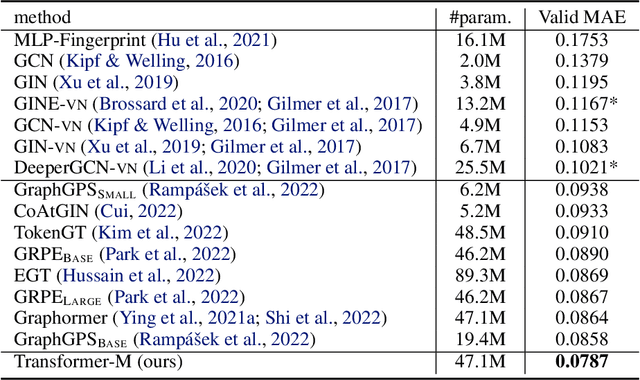
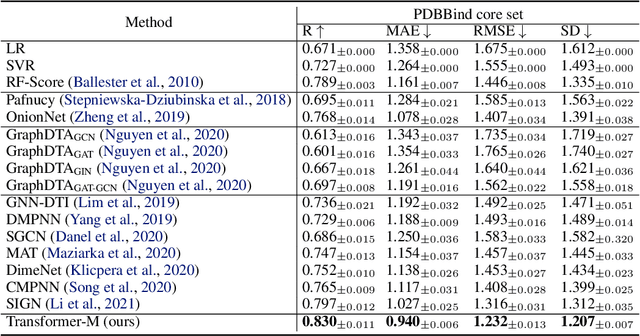
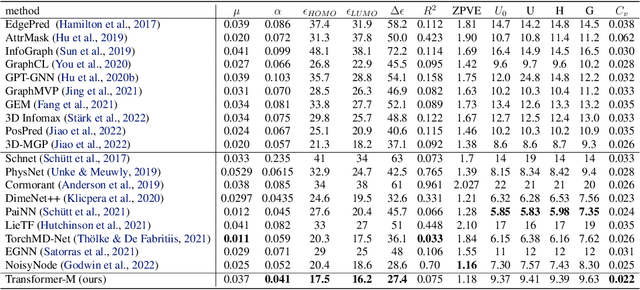
Abstract:Unlike vision and language data which usually has a unique format, molecules can naturally be characterized using different chemical formulations. One can view a molecule as a 2D graph or define it as a collection of atoms located in a 3D space. For molecular representation learning, most previous works designed neural networks only for a particular data format, making the learned models likely to fail for other data formats. We believe a general-purpose neural network model for chemistry should be able to handle molecular tasks across data modalities. To achieve this goal, in this work, we develop a novel Transformer-based Molecular model called Transformer-M, which can take molecular data of 2D or 3D formats as input and generate meaningful semantic representations. Using the standard Transformer as the backbone architecture, Transformer-M develops two separated channels to encode 2D and 3D structural information and incorporate them with the atom features in the network modules. When the input data is in a particular format, the corresponding channel will be activated, and the other will be disabled. By training on 2D and 3D molecular data with properly designed supervised signals, Transformer-M automatically learns to leverage knowledge from different data modalities and correctly capture the representations. We conducted extensive experiments for Transformer-M. All empirical results show that Transformer-M can simultaneously achieve strong performance on 2D and 3D tasks, suggesting its broad applicability. The code and models will be made publicly available at https://github.com/lsj2408/Transformer-M.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge