Yitong Yang
DiffStyle3D: Consistent 3D Gaussian Stylization via Attention Optimization
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:3D style transfer enables the creation of visually expressive 3D content, enriching the visual appearance of 3D scenes and objects. However, existing VGG- and CLIP-based methods struggle to model multi-view consistency within the model itself, while diffusion-based approaches can capture such consistency but rely on denoising directions, leading to unstable training. To address these limitations, we propose DiffStyle3D, a novel diffusion-based paradigm for 3DGS style transfer that directly optimizes in the latent space. Specifically, we introduce an Attention-Aware Loss that performs style transfer by aligning style features in the self-attention space, while preserving original content through content feature alignment. Inspired by the geometric invariance of 3D stylization, we propose a Geometry-Guided Multi-View Consistency method that integrates geometric information into self-attention to enable cross-view correspondence modeling. Based on geometric information, we additionally construct a geometry-aware mask to prevent redundant optimization in overlapping regions across views, which further improves multi-view consistency. Extensive experiments show that DiffStyle3D outperforms state-of-the-art methods, achieving higher stylization quality and visual realism.
YuFeng-XGuard: A Reasoning-Centric, Interpretable, and Flexible Guardrail Model for Large Language Models
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:As large language models (LLMs) are increasingly deployed in real-world applications, safety guardrails are required to go beyond coarse-grained filtering and support fine-grained, interpretable, and adaptable risk assessment. However, existing solutions often rely on rapid classification schemes or post-hoc rules, resulting in limited transparency, inflexible policies, or prohibitive inference costs. To this end, we present YuFeng-XGuard, a reasoning-centric guardrail model family designed to perform multi-dimensional risk perception for LLM interactions. Instead of producing opaque binary judgments, YuFeng-XGuard generates structured risk predictions, including explicit risk categories and configurable confidence scores, accompanied by natural language explanations that expose the underlying reasoning process. This formulation enables safety decisions that are both actionable and interpretable. To balance decision latency and explanatory depth, we adopt a tiered inference paradigm that performs an initial risk decision based on the first decoded token, while preserving ondemand explanatory reasoning when required. In addition, we introduce a dynamic policy mechanism that decouples risk perception from policy enforcement, allowing safety policies to be adjusted without model retraining. Extensive experiments on a diverse set of public safety benchmarks demonstrate that YuFeng-XGuard achieves stateof-the-art performance while maintaining strong efficiency-efficacy trade-offs. We release YuFeng-XGuard as an open model family, including both a full-capacity variant and a lightweight version, to support a wide range of deployment scenarios.
SplitFlux: Learning to Decouple Content and Style from a Single Image
Nov 19, 2025



Abstract:Disentangling image content and style is essential for customized image generation. Existing SDXL-based methods struggle to achieve high-quality results, while the recently proposed Flux model fails to achieve effective content-style separation due to its underexplored characteristics. To address these challenges, we conduct a systematic analysis of Flux and make two key observations: (1) Single Dream Blocks are essential for image generation; and (2) Early single stream blocks mainly control content, whereas later blocks govern style. Based on these insights, we propose SplitFlux, which disentangles content and style by fine-tuning the single dream blocks via LoRA, enabling the disentangled content to be re-embedded into new contexts. It includes two key components: (1) Rank-Constrained Adaptation. To preserve content identity and structure, we compress the rank and amplify the magnitude of updates within specific blocks, preventing content leakage into style blocks. (2) Visual-Gated LoRA. We split the content LoRA into two branches with different ranks, guided by image saliency. The high-rank branch preserves primary subject information, while the low-rank branch encodes residual details, mitigating content overfitting and enabling seamless re-embedding. Extensive experiments demonstrate that SplitFlux consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods, achieving superior content preservation and stylization quality across diverse scenarios.
FantasyStyle: Controllable Stylized Distillation for 3D Gaussian Splatting
Aug 11, 2025Abstract:The success of 3DGS in generative and editing applications has sparked growing interest in 3DGS-based style transfer. However, current methods still face two major challenges: (1) multi-view inconsistency often leads to style conflicts, resulting in appearance smoothing and distortion; and (2) heavy reliance on VGG features, which struggle to disentangle style and content from style images, often causing content leakage and excessive stylization. To tackle these issues, we introduce \textbf{FantasyStyle}, a 3DGS-based style transfer framework, and the first to rely entirely on diffusion model distillation. It comprises two key components: (1) \textbf{Multi-View Frequency Consistency}. We enhance cross-view consistency by applying a 3D filter to multi-view noisy latent, selectively reducing low-frequency components to mitigate stylized prior conflicts. (2) \textbf{Controllable Stylized Distillation}. To suppress content leakage from style images, we introduce negative guidance to exclude undesired content. In addition, we identify the limitations of Score Distillation Sampling and Delta Denoising Score in 3D style transfer and remove the reconstruction term accordingly. Building on these insights, we propose a controllable stylized distillation that leverages negative guidance to more effectively optimize the 3D Gaussians. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method consistently outperforms state-of-the-art approaches, achieving higher stylization quality and visual realism across various scenes and styles.
Prompt-Softbox-Prompt: A free-text Embedding Control for Image Editing
Aug 27, 2024Abstract:Text-driven diffusion models have achieved remarkable success in image editing, but a crucial component in these models-text embeddings-has not been fully explored. The entanglement and opacity of text embeddings present significant challenges to achieving precise image editing. In this paper, we provide a comprehensive and in-depth analysis of text embeddings in Stable Diffusion XL, offering three key insights. First, while the 'aug_embedding' captures the full semantic content of the text, its contribution to the final image generation is relatively minor. Second, 'BOS' and 'Padding_embedding' do not contain any semantic information. Lastly, the 'EOS' holds the semantic information of all words and contains the most style features. Each word embedding plays a unique role without interfering with one another. Based on these insights, we propose a novel approach for controllable image editing using a free-text embedding control method called PSP (Prompt-Softbox-Prompt). PSP enables precise image editing by inserting or adding text embeddings within the cross-attention layers and using Softbox to define and control the specific area for semantic injection. This technique allows for obejct additions and replacements while preserving other areas of the image. Additionally, PSP can achieve style transfer by simply replacing text embeddings. Extensive experimental results show that PSP achieves significant results in tasks such as object replacement, object addition, and style transfer.
DuEDL: Dual-Branch Evidential Deep Learning for Scribble-Supervised Medical Image Segmentation
May 23, 2024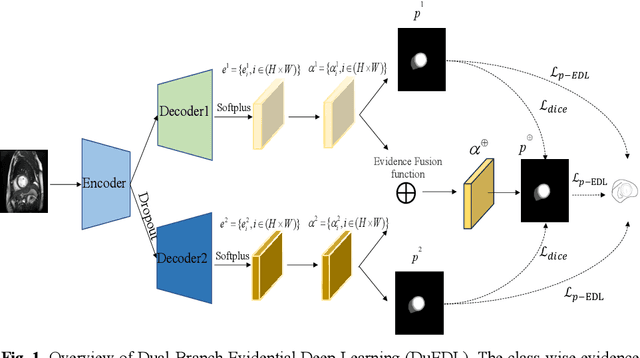
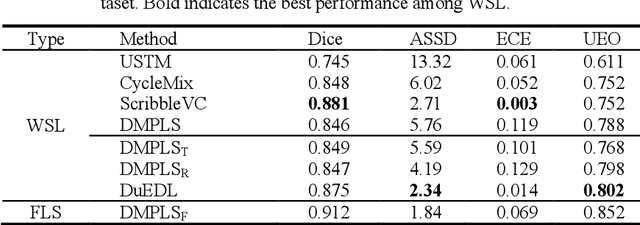
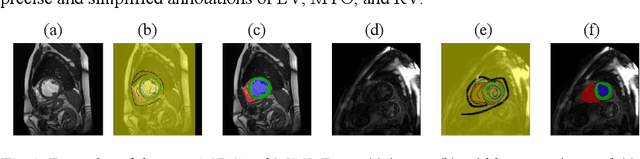
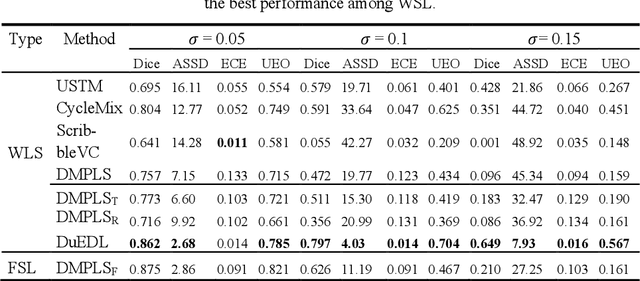
Abstract:Despite the recent progress in medical image segmentation with scribble-based annotations, the segmentation results of most models are still not ro-bust and generalizable enough in open environments. Evidential deep learn-ing (EDL) has recently been proposed as a promising solution to model predictive uncertainty and improve the reliability of medical image segmen-tation. However directly applying EDL to scribble-supervised medical im-age segmentation faces a tradeoff between accuracy and reliability. To ad-dress the challenge, we propose a novel framework called Dual-Branch Evi-dential Deep Learning (DuEDL). Firstly, the decoder of the segmentation network is changed to two different branches, and the evidence of the two branches is fused to generate high-quality pseudo-labels. Then the frame-work applies partial evidence loss and two-branch consistent loss for joint training of the model to adapt to the scribble supervision learning. The pro-posed method was tested on two cardiac datasets: ACDC and MSCMRseg. The results show that our method significantly enhances the reliability and generalization ability of the model without sacrificing accuracy, outper-forming state-of-the-art baselines. The code is available at https://github.com/Gardnery/DuEDL.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge