Yingjie Zhai
ViSpec: Accelerating Vision-Language Models with Vision-Aware Speculative Decoding
Sep 17, 2025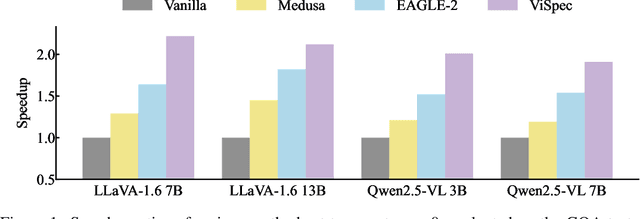
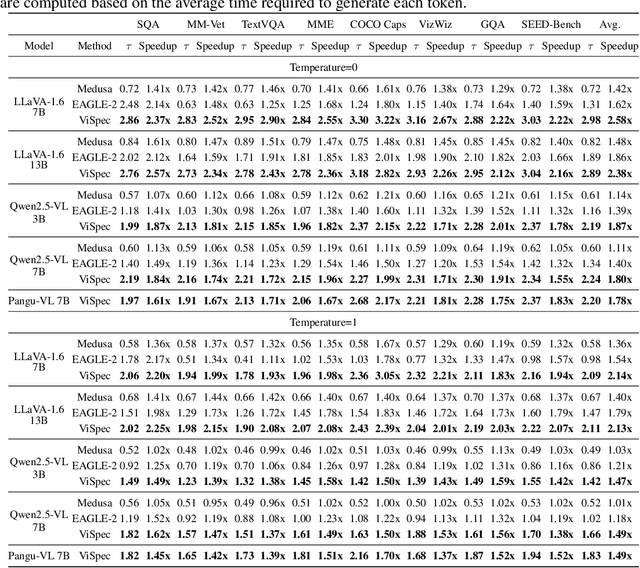
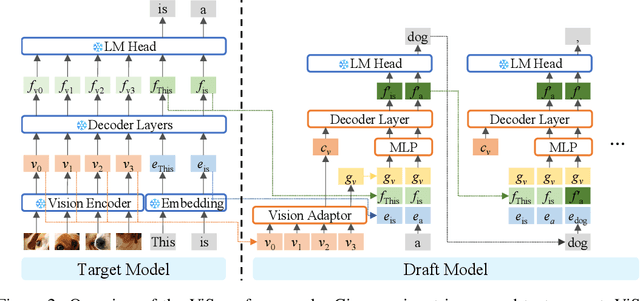
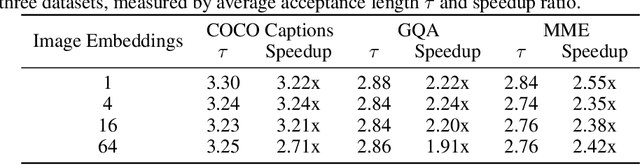
Abstract:Speculative decoding is a widely adopted technique for accelerating inference in large language models (LLMs), yet its application to vision-language models (VLMs) remains underexplored, with existing methods achieving only modest speedups (<1.5x). This gap is increasingly significant as multimodal capabilities become central to large-scale models. We hypothesize that large VLMs can effectively filter redundant image information layer by layer without compromising textual comprehension, whereas smaller draft models struggle to do so. To address this, we introduce Vision-Aware Speculative Decoding (ViSpec), a novel framework tailored for VLMs. ViSpec employs a lightweight vision adaptor module to compress image tokens into a compact representation, which is seamlessly integrated into the draft model's attention mechanism while preserving original image positional information. Additionally, we extract a global feature vector for each input image and augment all subsequent text tokens with this feature to enhance multimodal coherence. To overcome the scarcity of multimodal datasets with long assistant responses, we curate a specialized training dataset by repurposing existing datasets and generating extended outputs using the target VLM with modified prompts. Our training strategy mitigates the risk of the draft model exploiting direct access to the target model's hidden states, which could otherwise lead to shortcut learning when training solely on target model outputs. Extensive experiments validate ViSpec, achieving, to our knowledge, the first substantial speedup in VLM speculative decoding.
No Time to Waste: Squeeze Time into Channel for Mobile Video Understanding
May 14, 2024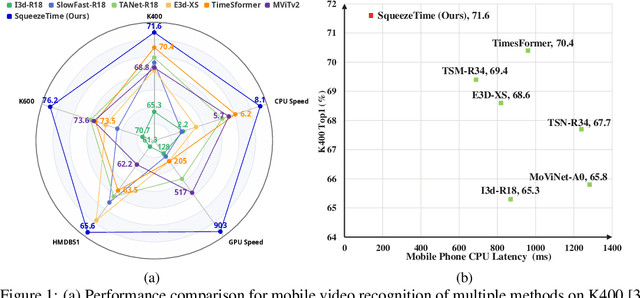
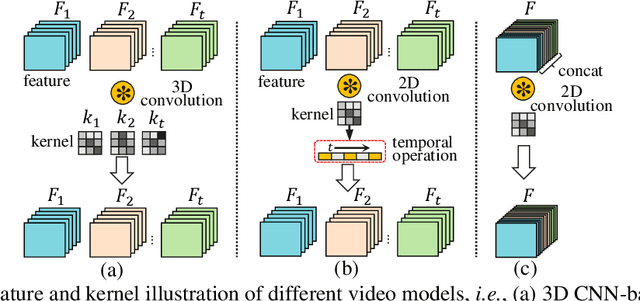
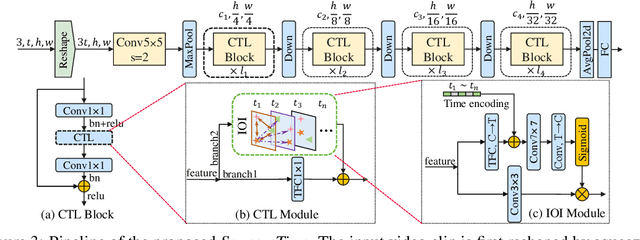
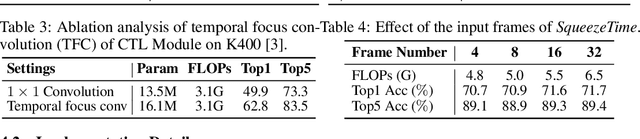
Abstract:Current architectures for video understanding mainly build upon 3D convolutional blocks or 2D convolutions with additional operations for temporal modeling. However, these methods all regard the temporal axis as a separate dimension of the video sequence, which requires large computation and memory budgets and thus limits their usage on mobile devices. In this paper, we propose to squeeze the time axis of a video sequence into the channel dimension and present a lightweight video recognition network, term as \textit{SqueezeTime}, for mobile video understanding. To enhance the temporal modeling capability of the proposed network, we design a Channel-Time Learning (CTL) Block to capture temporal dynamics of the sequence. This module has two complementary branches, in which one branch is for temporal importance learning and another branch with temporal position restoring capability is to enhance inter-temporal object modeling ability. The proposed SqueezeTime is much lightweight and fast with high accuracies for mobile video understanding. Extensive experiments on various video recognition and action detection benchmarks, i.e., Kinetics400, Kinetics600, HMDB51, AVA2.1 and THUMOS14, demonstrate the superiority of our model. For example, our SqueezeTime achieves $+1.2\%$ accuracy and $+80\%$ GPU throughput gain on Kinetics400 than prior methods. Codes are publicly available at https://github.com/xinghaochen/SqueezeTime and https://github.com/mindspore-lab/models/tree/master/research/huawei-noah/SqueezeTime.
Context-Guided Spatial Feature Reconstruction for Efficient Semantic Segmentation
May 10, 2024



Abstract:Semantic segmentation is an important task for many applications but it is still quite challenging to achieve advanced performance with limited computational costs. In this paper, we present CGRSeg, an efficient yet competitive segmentation framework based on context-guided spatial feature reconstruction. A Rectangular Self-Calibration Module is carefully designed for spatial feature reconstruction and pyramid context extraction. It captures the global context in both horizontal and vertical directions and gets the axial global context to explicitly model rectangular key areas. A shape self-calibration function is designed to make the key areas more close to the foreground object. Besides, a lightweight Dynamic Prototype Guided head is proposed to improve the classification of foreground objects by explicit class embedding. Our CGRSeg is extensively evaluated on ADE20K, COCO-Stuff, and Pascal Context benchmarks, and achieves state-of-the-art semantic performance. Specifically, it achieves $43.6\%$ mIoU on ADE20K with only $4.0$ GFLOPs, which is $0.9\%$ and $2.5\%$ mIoU better than SeaFormer and SegNeXt but with about $38.0\%$ fewer GFLOPs. Code is available at https://github.com/nizhenliang/CGRSeg.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge