Yingfu Zeng
ES-Gaussian: Gaussian Splatting Mapping via Error Space-Based Gaussian Completion
Oct 09, 2024Abstract:Accurate and affordable indoor 3D reconstruction is critical for effective robot navigation and interaction. Traditional LiDAR-based mapping provides high precision but is costly, heavy, and power-intensive, with limited ability for novel view rendering. Vision-based mapping, while cost-effective and capable of capturing visual data, often struggles with high-quality 3D reconstruction due to sparse point clouds. We propose ES-Gaussian, an end-to-end system using a low-altitude camera and single-line LiDAR for high-quality 3D indoor reconstruction. Our system features Visual Error Construction (VEC) to enhance sparse point clouds by identifying and correcting areas with insufficient geometric detail from 2D error maps. Additionally, we introduce a novel 3DGS initialization method guided by single-line LiDAR, overcoming the limitations of traditional multi-view setups and enabling effective reconstruction in resource-constrained environments. Extensive experimental results on our new Dreame-SR dataset and a publicly available dataset demonstrate that ES-Gaussian outperforms existing methods, particularly in challenging scenarios. The project page is available at https://chenlu-china.github.io/ES-Gaussian/.
Modeling Basic Aspects of Cyber-Physical Systems, Part II
Aug 05, 2014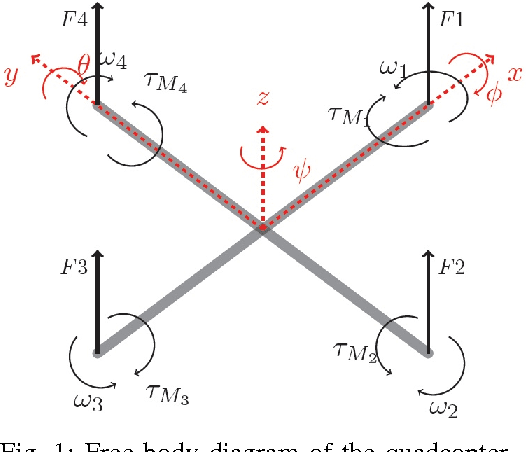
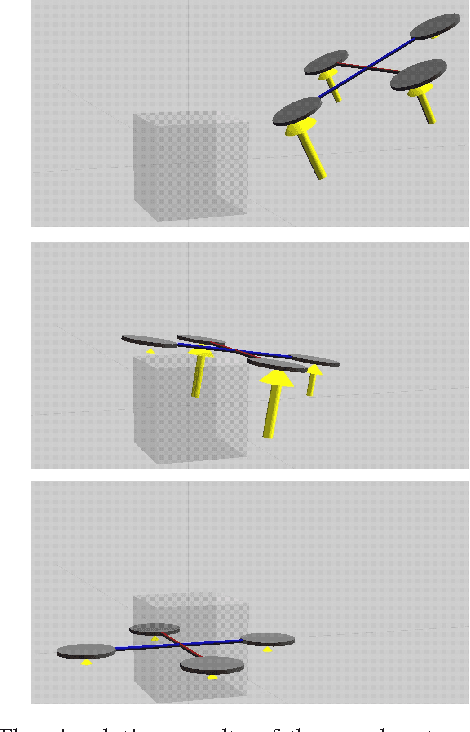
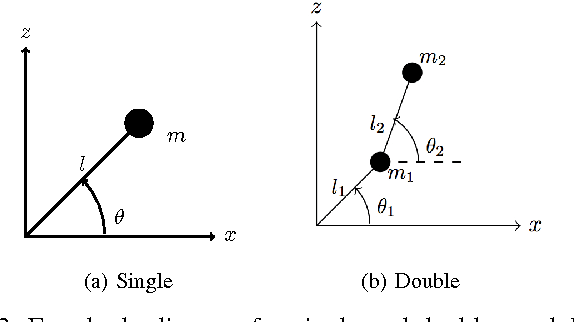
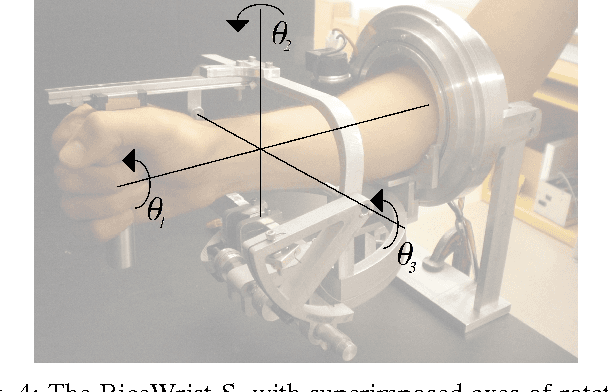
Abstract:We continue to consider the question of what language features are needed to effectively model cyber-physical systems (CPS). In previous work, we proposed using a core language as a way to study this question, and showed how several basic aspects of CPS can be modeled clearly in a language with a small set of constructs. This paper reports on the result of our analysis of two, more complex, case studies from the domain of rigid body dynamics. The first one, a quadcopter, illustrates that previously proposed core language can support larger, more interesting systems than previously shown. The second one, a serial robot, provides a concrete example of why we should add language support for static partial derivatives, namely that it would significantly improve the way models of rigid body dynamics can be expressed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge