Modeling Basic Aspects of Cyber-Physical Systems, Part II
Paper and Code
Aug 05, 2014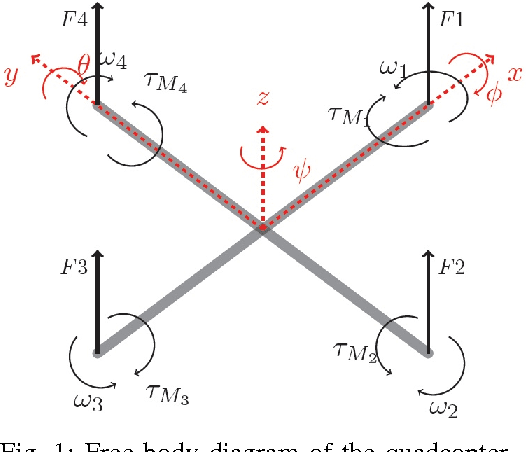
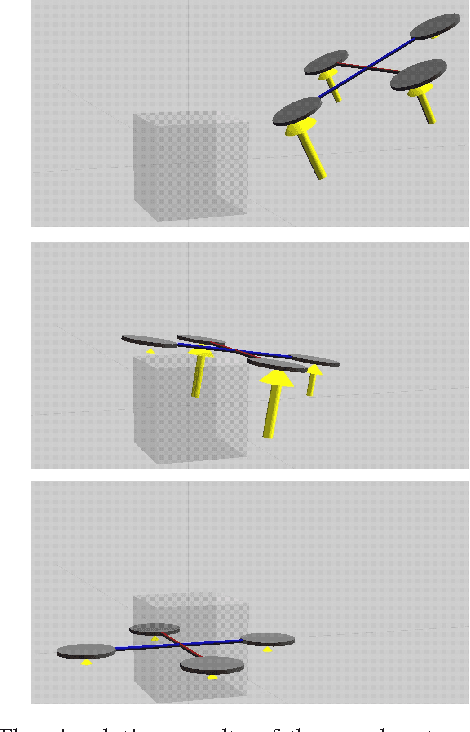
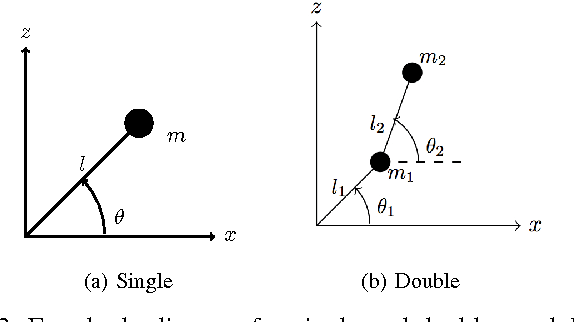
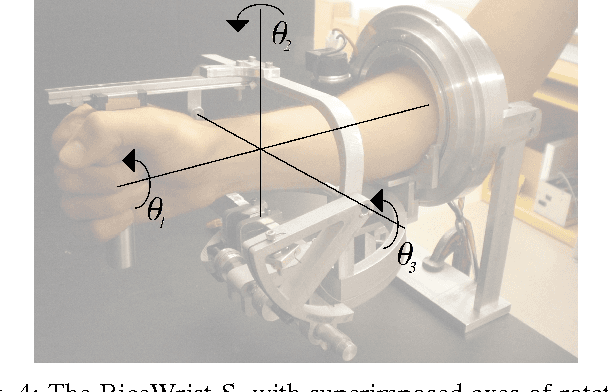
We continue to consider the question of what language features are needed to effectively model cyber-physical systems (CPS). In previous work, we proposed using a core language as a way to study this question, and showed how several basic aspects of CPS can be modeled clearly in a language with a small set of constructs. This paper reports on the result of our analysis of two, more complex, case studies from the domain of rigid body dynamics. The first one, a quadcopter, illustrates that previously proposed core language can support larger, more interesting systems than previously shown. The second one, a serial robot, provides a concrete example of why we should add language support for static partial derivatives, namely that it would significantly improve the way models of rigid body dynamics can be expressed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge