Yina Guo
End-to-end translation of human neural activity to speech with a dual-dual generative adversarial network
Oct 13, 2021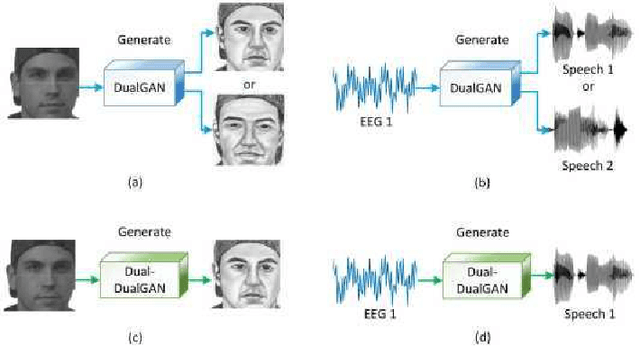
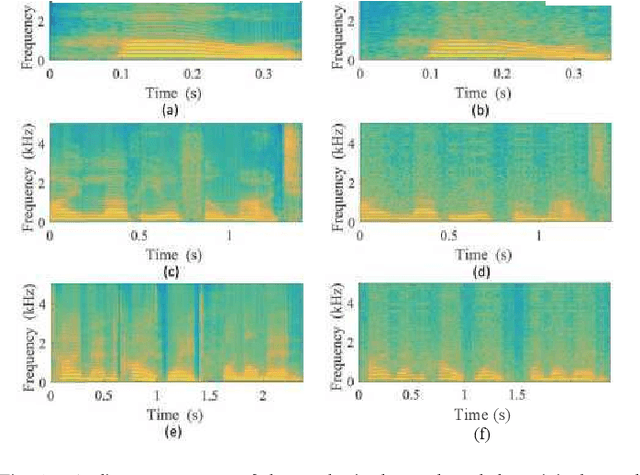
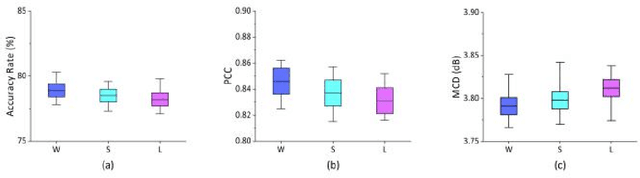
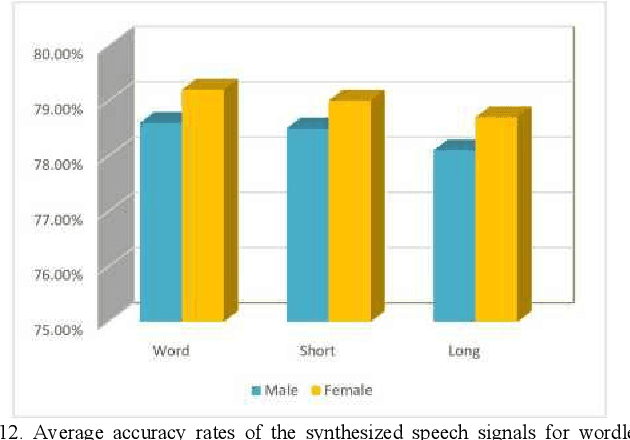
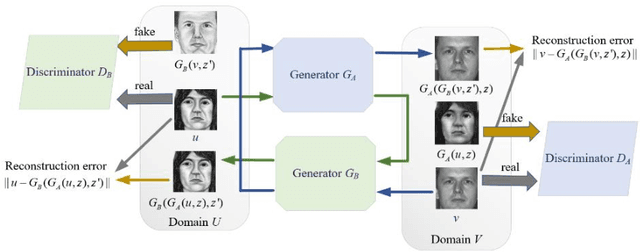
Abstract:In a recent study of auditory evoked potential (AEP) based brain-computer interface (BCI), it was shown that, with an encoder-decoder framework, it is possible to translate human neural activity to speech (T-CAS). However, current encoder-decoder-based methods achieve T-CAS often with a two-step method where the information is passed between the encoder and decoder with a shared dimension reduction vector, which may result in a loss of information. A potential approach to this problem is to design an end-to-end method by using a dual generative adversarial network (DualGAN) without dimension reduction of passing information, but it cannot realize one-to-one signal-to-signal translation (see Fig.1 (a) and (b)). In this paper, we propose an end-to-end model to translate human neural activity to speech directly, create a new electroencephalogram (EEG) datasets for participants with good attention by design a device to detect participants' attention, and introduce a dual-dual generative adversarial network (Dual-DualGAN) (see Fig. 1 (c) and (d)) to address an end-to-end translation of human neural activity to speech (ET-CAS) problem by group labelling EEG signals and speech signals, inserting a transition domain to realize cross-domain mapping. In the transition domain, the transition signals are cascaded by the corresponding EEG and speech signals in a certain proportion, which can build bridges for EEG and speech signals without corresponding features, and realize one-to-one cross-domain EEG-to-speech translation. The proposed method can translate word-length and sentence-length sequences of neural activity to speech. Experimental evaluation has been conducted to show that the proposed method significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods on both words and sentences of auditory stimulus.
One to Multiple Mapping Dual Learning: Learning Multiple Sources from One Mixed Signal
Oct 13, 2021
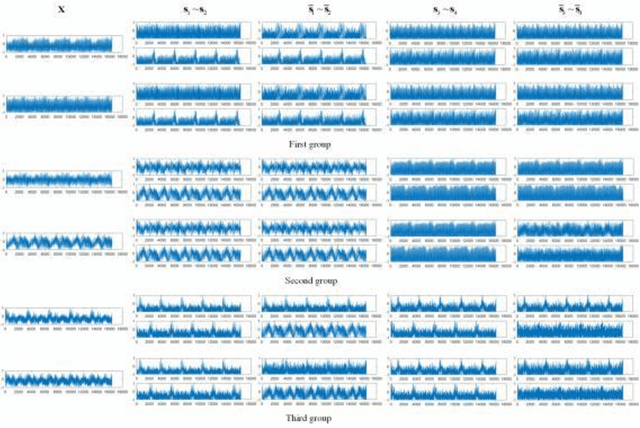
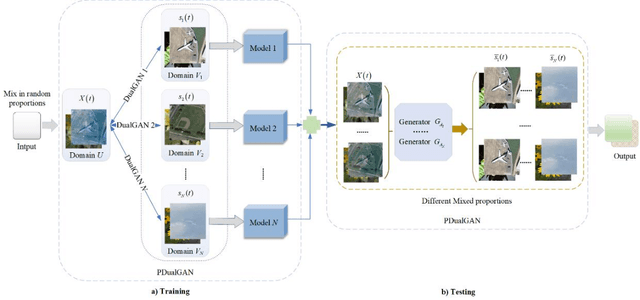
Abstract:Single channel blind source separation (SCBSS) refers to separate multiple sources from a mixed signal collected by a single sensor. The existing methods for SCBSS mainly focus on separating two sources and have weak generalization performance. To address these problems, an algorithm is proposed in this paper to separate multiple sources from a mixture by designing a parallel dual generative adversarial Network (PDualGAN) that can build the relationship between a mixture and the corresponding multiple sources to realize one-to-multiple cross-domain mapping. This algorithm can be applied to any mixed model such as linear instantaneous mixed model and convolutional mixed model. Besides, one-to-multiple datasets are created which including the mixtures and corresponding sources for this study. The experiment was carried out on four different datasets and tested with signals mixed in different proportions. Experimental results show that the proposed algorithm can achieve high performance in peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) and correlation, which outperforms state-of-the-art algorithms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge