Yimin Xu
DSU-Net:An Improved U-Net Model Based on DINOv2 and SAM2 with Multi-scale Cross-model Feature Enhancement
Mar 31, 2025



Abstract:Despite the significant advancements in general image segmentation achieved by large-scale pre-trained foundation models (such as Meta's Segment Any-thing Model (SAM) series and DINOv2), their performance in specialized fields remains limited by two critical issues: the excessive training costs due to large model parameters, and the insufficient ability to represent specific domain characteristics. This paper proposes a multi-scale feature collabora-tion framework guided by DINOv2 for SAM2, with core innovations in three aspects: (1) Establishing a feature collaboration mechanism between DINOv2 and SAM2 backbones, where high-dimensional semantic features extracted by the self-supervised model guide multi-scale feature fusion; (2) Designing lightweight adapter modules and cross-modal, cross-layer feature fusion units to inject cross-domain knowledge while freezing the base model parameters; (3) Constructing a U-shaped network structure based on U-net, which utilizes attention mechanisms to achieve adaptive aggregation decoding of multi-granularity features. This framework surpasses existing state-of-the-art meth-ods in downstream tasks such as camouflage target detection and salient ob-ject detection, without requiring costly training processes. It provides a tech-nical pathway for efficient deployment of visual image segmentation, demon-strating significant application value in a wide range of downstream tasks and specialized fields within image segmentation.Project page: https://github.com/CheneyXuYiMin/SAM2DINO-Seg
DGSUnet: An Improved Unet Model with DINO-Guided SAM2 for Multi-Scale Feature Collaboration
Mar 27, 2025



Abstract:Despite the significant advancements in general image segmentation achieved by large-scale pre-trained foundation models (such as Meta's Segment Any-thing Model (SAM) series and DINOv2), their performance in specialized fields remains limited by two critical issues: the excessive training costs due to large model parameters, and the insufficient ability to represent specific domain characteristics. This paper proposes a multi-scale feature collabora-tion framework guided by DINOv2 for SAM2, with core innovations in three aspects: (1) Establishing a feature collaboration mechanism between DINOv2 and SAM2 backbones, where high-dimensional semantic features extracted by the self-supervised model guide multi-scale feature fusion; (2) Designing lightweight adapter modules and cross-modal, cross-layer feature fusion units to inject cross-domain knowledge while freezing the base model parameters; (3) Constructing a U-shaped network structure based on U-net, which utilizes attention mechanisms to achieve adaptive aggregation decoding of multi-granularity features. This framework surpasses existing state-of-the-art meth-ods in downstream tasks such as camouflage target detection and salient ob-ject detection, without requiring costly training processes. It provides a tech-nical pathway for efficient deployment of visual image segmentation, demon-strating significant application value in a wide range of downstream tasks and specialized fields within image segmentation.Project page: https://github.com/CheneyXuYiMin/SAM2DINO-Seg
Unified-Width Adaptive Dynamic Network for All-In-One Image Restoration
Jan 24, 2024Abstract:In contrast to traditional image restoration methods, all-in-one image restoration techniques are gaining increased attention for their ability to restore images affected by diverse and unknown corruption types and levels. However, contemporary all-in-one image restoration methods omit task-wise difficulties and employ the same networks to reconstruct images afflicted by diverse degradations. This practice leads to an underestimation of the task correlations and suboptimal allocation of computational resources. To elucidate task-wise complexities, we introduce a novel concept positing that intricate image degradation can be represented in terms of elementary degradation. Building upon this foundation, we propose an innovative approach, termed the Unified-Width Adaptive Dynamic Network (U-WADN), consisting of two pivotal components: a Width Adaptive Backbone (WAB) and a Width Selector (WS). The WAB incorporates several nested sub-networks with varying widths, which facilitates the selection of the most apt computations tailored to each task, thereby striking a balance between accuracy and computational efficiency during runtime. For different inputs, the WS automatically selects the most appropriate sub-network width, taking into account both task-specific and sample-specific complexities. Extensive experiments across a variety of image restoration tasks demonstrate that the proposed U-WADN achieves better performance while simultaneously reducing up to 32.3\% of FLOPs and providing approximately 15.7\% real-time acceleration. The code has been made available at \url{https://github.com/xuyimin0926/U-WADN}.
Shadow-Aware Dynamic Convolution for Shadow Removal
May 10, 2022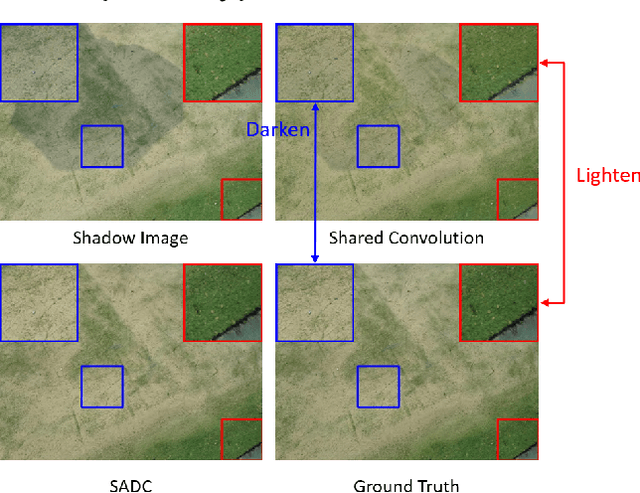

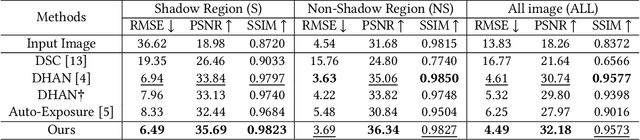

Abstract:With a wide range of shadows in many collected images, shadow removal has aroused increasing attention since uncontaminated images are of vital importance for many downstream multimedia tasks. Current methods consider the same convolution operations for both shadow and non-shadow regions while ignoring the large gap between the color mappings for the shadow region and the non-shadow region, leading to poor quality of reconstructed images and a heavy computation burden. To solve this problem, this paper introduces a novel plug-and-play Shadow-Aware Dynamic Convolution (SADC) module to decouple the interdependence between the shadow region and the non-shadow region. Inspired by the fact that the color mapping of the non-shadow region is easier to learn, our SADC processes the non-shadow region with a lightweight convolution module in a computationally cheap manner and recovers the shadow region with a more complicated convolution module to ensure the quality of image reconstruction. Given that the non-shadow region often contains more background color information, we further develop a novel intra-convolution distillation loss to strengthen the information flow from the non-shadow region to the shadow region. Extensive experiments on the ISTD and SRD datasets show our method achieves better performance in shadow removal over many state-of-the-arts. Our code is available at https://github.com/xuyimin0926/SADC.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge