Yihan Yang
Samba: Semantic Segmentation of Remotely Sensed Images with State Space Model
Apr 11, 2024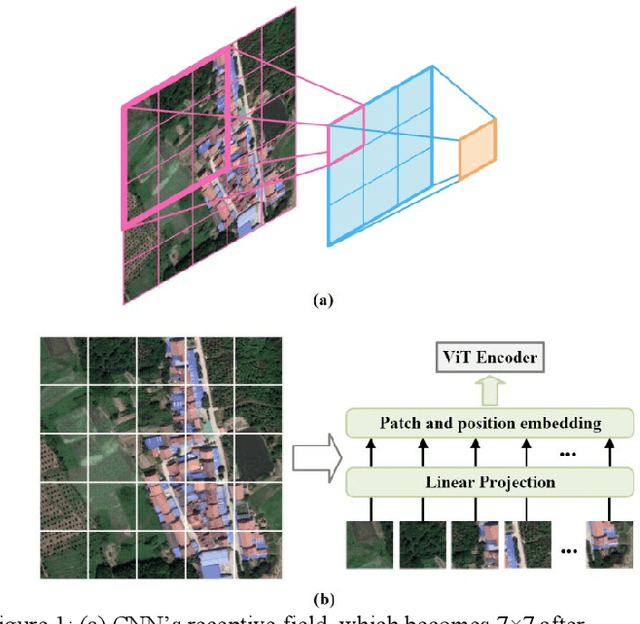
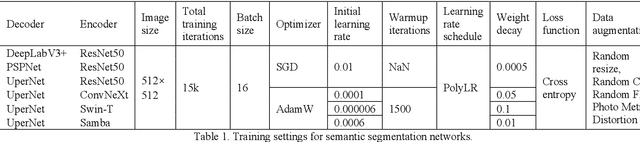
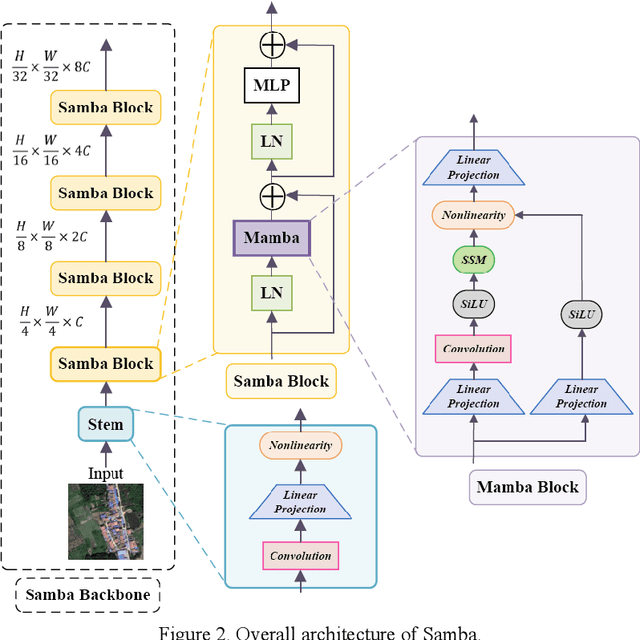
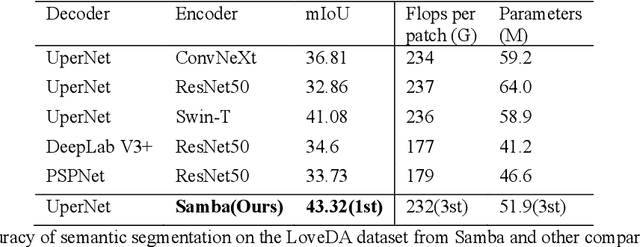
Abstract:High-resolution remotely sensed images pose a challenge for commonly used semantic segmentation methods such as Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) and Vision Transformer (ViT). CNN-based methods struggle with handling such high-resolution images due to their limited receptive field, while ViT faces challenges in handling long sequences. Inspired by Mamba, which adopts a State Space Model (SSM) to efficiently capture global semantic information, we propose a semantic segmentation framework for high-resolution remotely sensed images, named Samba. Samba utilizes an encoder-decoder architecture, with Samba blocks serving as the encoder for efficient multi-level semantic information extraction, and UperNet functioning as the decoder. We evaluate Samba on the LoveDA, ISPRS Vaihingen, and ISPRS Potsdam datasets, comparing its performance against top-performing CNN and ViT methods. The results reveal that Samba achieved unparalleled performance on commonly used remote sensing datasets for semantic segmentation. Our proposed Samba demonstrates for the first time the effectiveness of SSM in semantic segmentation of remotely sensed images, setting a new benchmark in performance for Mamba-based techniques in this specific application. The source code and baseline implementations are available at https://github.com/zhuqinfeng1999/Samba.
Multi-Head Online Learning for Delayed Feedback Modeling
May 24, 2022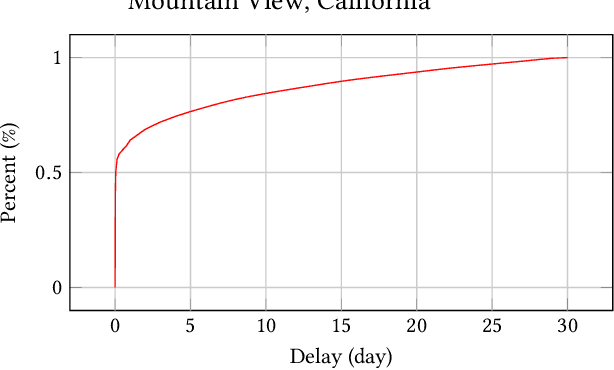

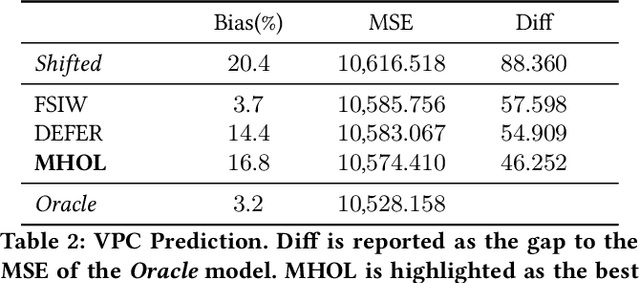
Abstract:In online advertising, it is highly important to predict the probability and the value of a conversion (e.g., a purchase). It not only impacts user experience by showing relevant ads, but also affects ROI of advertisers and revenue of marketplaces. Unlike clicks, which often occur within minutes after impressions, conversions are expected to happen over a long period of time (e.g., 30 days for online shopping). It creates a challenge, as the true labels are only available after the long delays. Either inaccurate labels (partial conversions) are used, or models are trained on stale data (e.g., from 30 days ago). The problem is more eminent in online learning, which focuses on the live performance on the latest data. In this paper, a novel solution is presented to address this challenge using multi-head modeling. Unlike traditional methods, it directly quantizes conversions into multiple windows, such as day 1, day 2, day 3-7, and day 8-30. A sub-model is trained specifically on conversions within each window. Label freshness is maximally preserved in early models (e.g., day 1 and day 2), while late conversions are accurately utilized in models with longer delays (e.g., day 8-30). It is shown to greatly exceed the performance of known methods in online learning experiments for both conversion rate (CVR) and value per click (VPC) predictions. Lastly, as a general method for delayed feedback modeling, it can be combined with any advanced ML techniques to further improve the performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge