Yasin N. Silva
Identifying Cyberbullying Roles in Social Media
Dec 21, 2024



Abstract:Social media has revolutionized communication, allowing people worldwide to connect and interact instantly. However, it has also led to increases in cyberbullying, which poses a significant threat to children and adolescents globally, affecting their mental health and well-being. It is critical to accurately detect the roles of individuals involved in cyberbullying incidents to effectively address the issue on a large scale. This study explores the use of machine learning models to detect the roles involved in cyberbullying interactions. After examining the AMiCA dataset and addressing class imbalance issues, we evaluate the performance of various models built with four underlying LLMs (i.e., BERT, RoBERTa, T5, and GPT-2) for role detection. Our analysis shows that oversampling techniques help improve model performance. The best model, a fine-tuned RoBERTa using oversampled data, achieved an overall F1 score of 83.5%, increasing to 89.3% after applying a prediction threshold. The top-2 F1 score without thresholding was 95.7%. Our method outperforms previously proposed models. After investigating the per-class model performance and confidence scores, we show that the models perform well in classes with more samples and less contextual confusion (e.g., Bystander Other), but struggle with classes with fewer samples (e.g., Bystander Assistant) and more contextual ambiguity (e.g., Harasser and Victim). This work highlights current strengths and limitations in the development of accurate models with limited data and complex scenarios.
Evaluating LLMs Capabilities Towards Understanding Social Dynamics
Nov 20, 2024

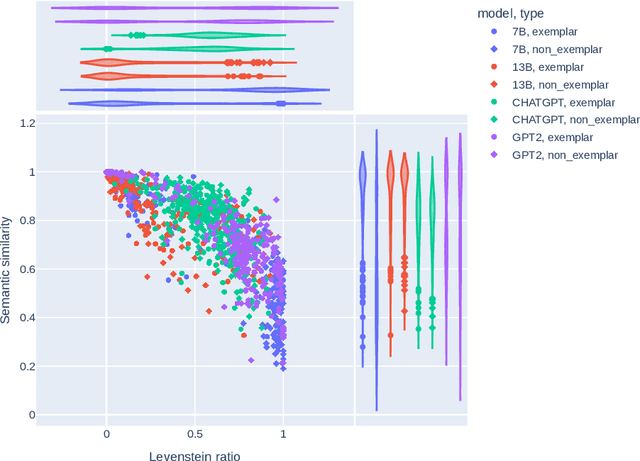
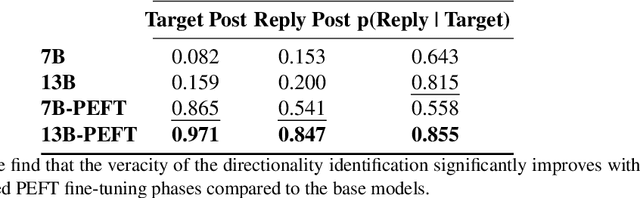
Abstract:Social media discourse involves people from different backgrounds, beliefs, and motives. Thus, often such discourse can devolve into toxic interactions. Generative Models, such as Llama and ChatGPT, have recently exploded in popularity due to their capabilities in zero-shot question-answering. Because these models are increasingly being used to ask questions of social significance, a crucial research question is whether they can understand social media dynamics. This work provides a critical analysis regarding generative LLM's ability to understand language and dynamics in social contexts, particularly considering cyberbullying and anti-cyberbullying (posts aimed at reducing cyberbullying) interactions. Specifically, we compare and contrast the capabilities of different large language models (LLMs) to understand three key aspects of social dynamics: language, directionality, and the occurrence of bullying/anti-bullying messages. We found that while fine-tuned LLMs exhibit promising results in some social media understanding tasks (understanding directionality), they presented mixed results in others (proper paraphrasing and bullying/anti-bullying detection). We also found that fine-tuning and prompt engineering mechanisms can have positive effects in some tasks. We believe that a understanding of LLM's capabilities is crucial to design future models that can be effectively used in social applications.
Toward Privacy and Utility Preserving Image Representation
Oct 17, 2020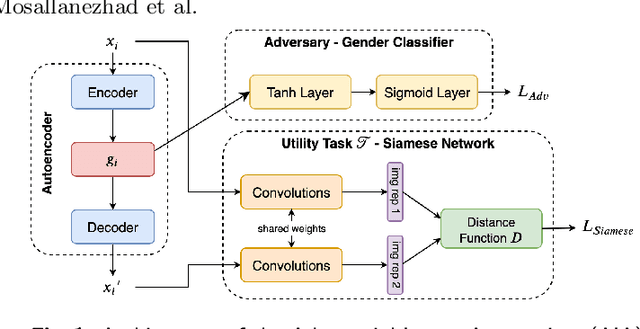
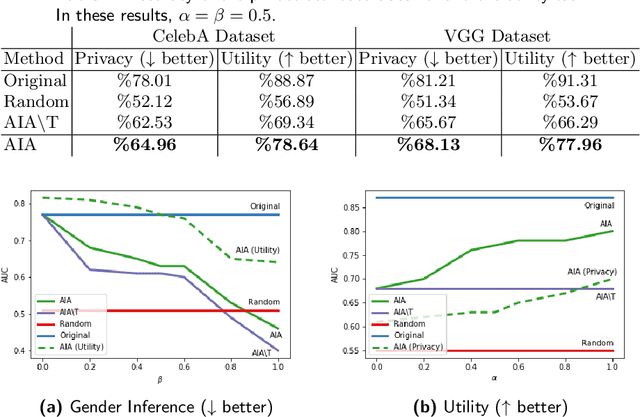

Abstract:Face images are rich data items that are useful and can easily be collected in many applications, such as in 1-to-1 face verification tasks in the domain of security and surveillance systems. Multiple methods have been proposed to protect an individual's privacy by perturbing the images to remove traces of identifiable information, such as gender or race. However, significantly less attention has been given to the problem of protecting images while maintaining optimal task utility. In this paper, we study the novel problem of creating privacy-preserving image representations with respect to a given utility task by proposing a principled framework called the Adversarial Image Anonymizer (AIA). AIA first creates an image representation using a generative model, then enhances the learned image representations using adversarial learning to preserve privacy and utility for a given task. Experiments were conducted on a publicly available data set to demonstrate the effectiveness of AIA as a privacy-preserving mechanism for face images.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge